INTRODUCTION
Acetylsalicylic acid (ASA) and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) represent one of the pharmacotherapeutic groups mainly used as analgesic and anti-inflammatory drugs not only in orthopaedic-rheumatologic, but also in otological, odontological and gynaecological pathologies1. However ASA and NSAIDs may cause side effects involving kidneys, liver and in particular the gastro-intestinal tract2,3. Pseudo-allergic reactions (asthma, urticaria) against ASA and NSAIDs involve 0.3 to 0.5 % of the overall population4. This kind of reactions considerably increases in patients with bronchial asthma and in particular in those with concomitant nasal polyposis, thus reaching a rate of 20 to 30 %5. Twenty-one to 30 % of patients with chronic urticaria also show pseudo-allergic phenomena against such group of drugs6. Even subjects who do not suffer from asthma or urticaria may however develop urticarial and/or angioedematous eruptions after taking ASA or NSAIDs7.
There is a high uniformity of opinions towards the concept that the anti-inflammatory activity of ASA and NSAIDs rises from the inhibition of COX-2, while undesirable side effects are the result of the COX-1's block8.
The purpose of the present study is to determine the clinical tolerance of Celecoxib (a 1.5 diaryl-pyrazole-base compound), a specific COX-2 inhibitor, in patients with a clinical history of pseudo-allergic skin reactions (diffuse erythema or urticaria/angioedema) due to ASA and NSAIDs in patients with multiple drug-induced urticaria-angioedema according to the classification of Stevenson et al9.
PATIENTS AND METHODS
Ninety-eight patients (63 women and 35 men) aging from 46 to 69 years (mean age 55.2) were enrolled in the study, all suffering from osteoarthrosis. Patient enrolment was carried out with the following criteria (table I):
1.Proven intolerance against oral administration of ASA/NSAIDs with phenomena of diffuse erythema or urticaria/angioedema, as resulting from anamnestic data and admission visit at the allergy outpatient's service;
2.Appearance of the above-mentioned skin eruptions during at least the 4-5 months before the beginning of the study, but not during the latest 3 weeks;
3.No administration of antihistaminic drugs over the 8 to 10 days before the oral challenge test.
Subjects suffering from asthma and/or ASA-induced asthma have not been included in the study.
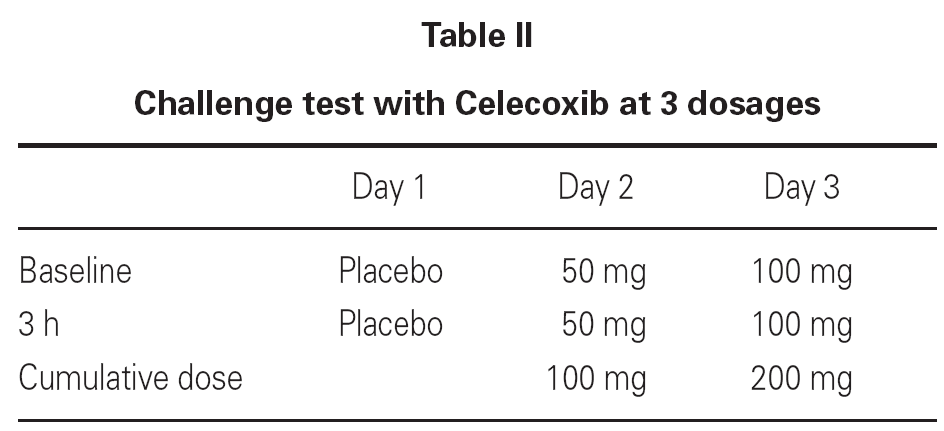
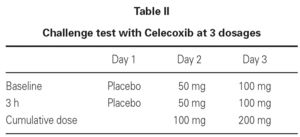
In agreement with the SIAIC (Italian Society of Allergy and Clinical Immunology) Memorandum11, we did not carried out any oral challenge test with ASA/NSAIDs, due to ethical reasons, in order to avoid possible severe adverse reactions12, and because the clinical history was sufficient to reach a diagnosis. Patients taking beta-blockers or ACE-inhibitors or with contraindications for epinephrine administration were not enrolled in the study. In order to exclude any adverse reaction due to the prolonged administration of the drug, we observed 44 patients with osteoarthrosis, who were treated with a 200-400 mg/day dose of the drug 5-6 times a week, over a period of 75 days. Each patient signed an informed consent. A single-blind oral challenge test was carried out (table II), and the patients were observed 6, 24, 48, 72 hours after the last drug intake to verify the eventual onset of late responses.
RESULTS
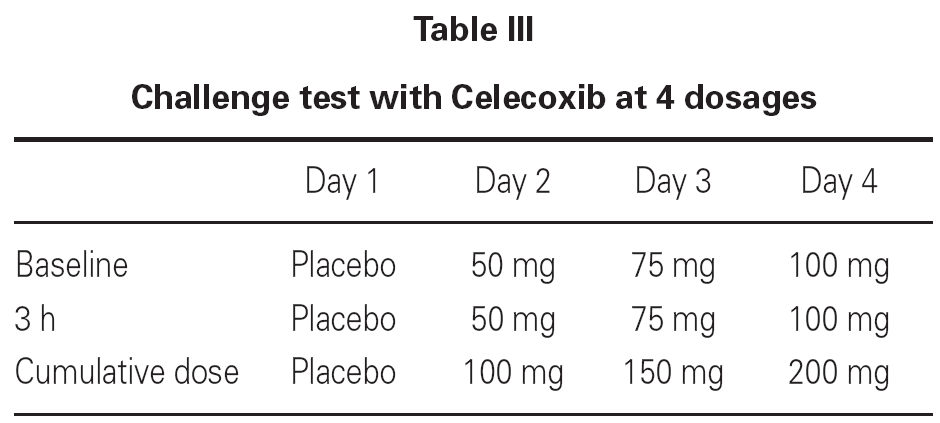
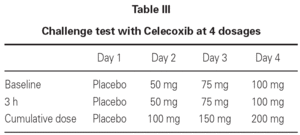
Due to the fact that 3 out of 32 patients showed urticarial eruptions on the chest and the back 2-3 hours after the first administration of the 100 mg dose, we decided to continue with a more progressive schedule in the remaining 54 patients (table III).
By adopting the second schedule, just one patient showed mild erythema 3 hours after the cumulative administration of 200 mg dose of Celecoxib.
Just in one patient urticarial pomphi on the back and the chest were reported on the day 36. No patient complained mild or severe gastroenteric disorders, but just mild pyrosis that was well-controlled with the administration of drugs containing magnesium and aluminium hydroxide, while osteoarthrosic signs and symptoms have showed good improvement.
DISCUSSION
An allergic mechanism of such affections was never established because the skin-tests carried out with ASA-lysine always reported negative results, the same as the several investigations performed to try to detect specific antibodies12.
The cyclooxygenase theory that Szczeklik proposed in 199013 was confirmed by the subsequent studies14-17. ASA and NSAID intolerance would be caused by the inhibition of cyclooxygenase with the block of the prostaglandin formation and deviation towards the pathway of the 5-lipooxygenase, with the production of cysteinil-leucotrienes LTC 4, LTD 4 and LTE 413,16,18.
NSAIDs and ASA inhibit both cyclooxygenase isoforms (COX-1 and COX-2), but with different intensity. At low doses, acetaminophen weakly inhibits both COX-1 and COX-216, and nimesulid induce a relative inhibition of COX-2 and a lower inhibition of COX-116, COX-1 is a constitutive enzyme existing in mast cells and tissues where it produces prostaglandins that are important for preserving homeostatic functions, e.g. the maintenance of renal and gastro-intestinal function's integrity19. COX-2 is instead an inducible enzyme whose synthesis is rapidly and temporarily induced as a result of tissue damages, inflammatory, allergic and immune stimuli8,20.
Various authors reported a good Celecoxib tolerance in patients complaining bronchial asthma attacks (not object of present study) due to the administration of ASA/NSAIDs21-24, or showing skin reactions25-28. However, there are reports about Celecoxib-induced anaphylactoid reactions29-34 or severe toxicodermia35. It is important to notice that in the study made by Marques et al35. Celecoxib was administered to the patient in association with acetaminophen and codeine.
A maculopapular reaction36 and a Sweet's syndrome, or acute febrile neutrophilic dermatosis37 were also observed after the administration of Celecoxib.
The Australian Adverse Drug Reactions Bulletin reported also urticarial reactions38. Mommens et al39 and Sanchez-Borges40 reported a glottis oedema in a publication that however ended with the following conclusion: "In general, most NSAID-sensitive patients tolerate COX-2 inhibitors without any reaction. If challenge tests are positive, strict avoidance of all NSAIDs is mandatory"41.
A cross reaction was observed between Celebrex and sulphamethoxazole42. The subsequent publications43,44 do not confirm this cross-reaction because antimicrobial sulphamides contain an aromatic aminogroup, and, in particular, in sulphamethoxazole the sulphonamide is bound to a methylated heterocyclic ring and a benzoyl ring. In Celebrex nor aromatic amine nor heterocyclic ring exist, but in this specific COX-2 inhibitor there is a non-aromatic amine43. According to Knowles et al43, the adverse side-effects are attributed to the heterocyclic ring or to the aromatic aminogroup that are not present in Celecoxib, as previously reported.
By the oral challenge test, one of us successfully employed nimesulid44, imidazole salicylate45 as an alternative to ASA and NSAIDs.
Despite the publication of Fradet et al46 that described a hypersensitivity syndrome against Celecoxib characterized by toxic skin reactions, fever and liver involvement (increased serum transaminase, CK, and γGT), we can agree with the studies carried out by Deeks et al47 and by Moskowitz et al48, which state the efficacy and the safety of Celecoxib in the treatment of osteoarthrosis. An original aspect of present study in respect to literature is the length of the observation period after the challenge tests (6, 24, 48 and 72 hours), and during the Celecoxib treatment to verify its tolerability (75 days, in 37 out of 86 patients in study).
Correspondence:
Dr. Paolo Falagiani
Lofarma S.p.A.
Viale Cassala, 40
20143 Milan - Italy
Tel. + 39 02 581981
Fax + 39 02 58198302
E-mail: lofscie@lofarma.it