Background and aim: SARSCov-2 infection, currently responsible virus for the pandemic, can have a multi-organic impact, recent studies show that liver injury could be a manifestation of the disease, and liver disease could also be related to a worst prognosis. AIM: To compare the characteristics of patients with severe COVID-19 due to SARSCov-2 disease requiring intubation versus stable patients.
Methods. Type of study: Observational, a case-control, nested in a cohort study. Procedure: Complete medical records of patients admitted for COVID-19 at a third level center were reviewed. Clinical and biochemical data were collected and then characteristics between seriously ill patients who required intubation were compared versus stable patients without mechanical ventilation.
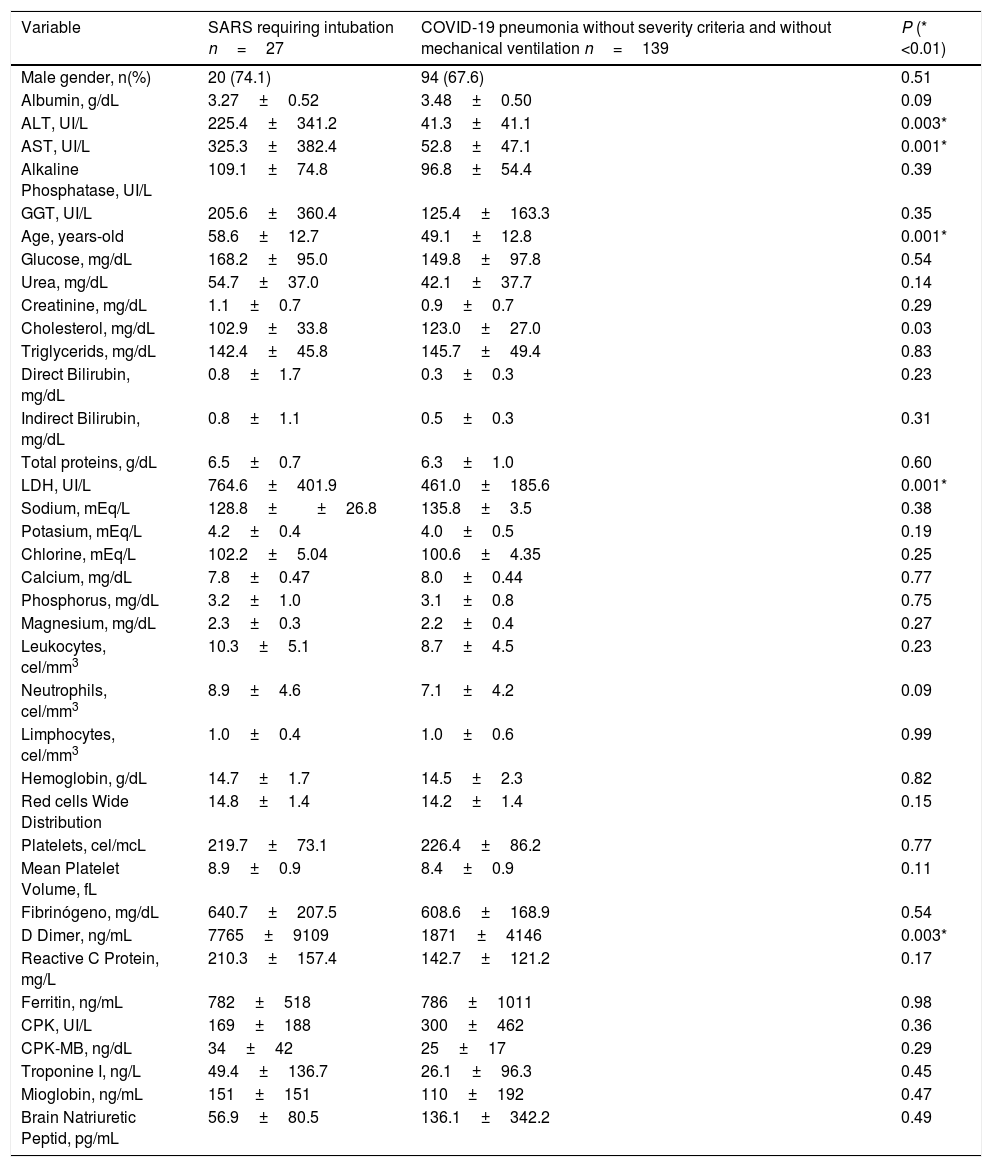
Results: We included 166 patients with COVID-19 due to SARSCov-2 infection, 114(68.7%) were men, mean age was 50.6±13.3 years old, 27(16.3%) were assessed as seriously ill patients requiring intubation for SARS. The comparative analysis between those who required intubation versus those who remained without requiring intubation showed significant elevation of ALT, AST, LDH and D-dimer, also older age, see Table.
which compares characteristics between patients who developed SARS and required intubation, versus those with COVID-19 pneumonia without severity criteria for intubation.
| Variable | SARS requiring intubation n=27 | COVID-19 pneumonia without severity criteria and without mechanical ventilation n=139 | P (*<0.01) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Male gender, n(%) | 20 (74.1) | 94 (67.6) | 0.51 |
| Albumin, g/dL | 3.27±0.52 | 3.48±0.50 | 0.09 |
| ALT, UI/L | 225.4±341.2 | 41.3±41.1 | 0.003* |
| AST, UI/L | 325.3±382.4 | 52.8±47.1 | 0.001* |
| Alkaline Phosphatase, UI/L | 109.1±74.8 | 96.8±54.4 | 0.39 |
| GGT, UI/L | 205.6±360.4 | 125.4±163.3 | 0.35 |
| Age, years-old | 58.6±12.7 | 49.1±12.8 | 0.001* |
| Glucose, mg/dL | 168.2±95.0 | 149.8±97.8 | 0.54 |
| Urea, mg/dL | 54.7±37.0 | 42.1±37.7 | 0.14 |
| Creatinine, mg/dL | 1.1±0.7 | 0.9±0.7 | 0.29 |
| Cholesterol, mg/dL | 102.9±33.8 | 123.0±27.0 | 0.03 |
| Triglycerids, mg/dL | 142.4±45.8 | 145.7±49.4 | 0.83 |
| Direct Bilirubin, mg/dL | 0.8±1.7 | 0.3±0.3 | 0.23 |
| Indirect Bilirubin, mg/dL | 0.8±1.1 | 0.5±0.3 | 0.31 |
| Total proteins, g/dL | 6.5±0.7 | 6.3±1.0 | 0.60 |
| LDH, UI/L | 764.6±401.9 | 461.0±185.6 | 0.001* |
| Sodium, mEq/L | 128.8±±26.8 | 135.8±3.5 | 0.38 |
| Potasium, mEq/L | 4.2±0.4 | 4.0±0.5 | 0.19 |
| Chlorine, mEq/L | 102.2±5.04 | 100.6±4.35 | 0.25 |
| Calcium, mg/dL | 7.8±0.47 | 8.0±0.44 | 0.77 |
| Phosphorus, mg/dL | 3.2±1.0 | 3.1±0.8 | 0.75 |
| Magnesium, mg/dL | 2.3±0.3 | 2.2±0.4 | 0.27 |
| Leukocytes, cel/mm3 | 10.3±5.1 | 8.7±4.5 | 0.23 |
| Neutrophils, cel/mm3 | 8.9±4.6 | 7.1±4.2 | 0.09 |
| Limphocytes, cel/mm3 | 1.0±0.4 | 1.0±0.6 | 0.99 |
| Hemoglobin, g/dL | 14.7±1.7 | 14.5±2.3 | 0.82 |
| Red cells Wide Distribution | 14.8±1.4 | 14.2±1.4 | 0.15 |
| Platelets, cel/mcL | 219.7±73.1 | 226.4±86.2 | 0.77 |
| Mean Platelet Volume, fL | 8.9±0.9 | 8.4±0.9 | 0.11 |
| Fibrinógeno, mg/dL | 640.7±207.5 | 608.6±168.9 | 0.54 |
| D Dimer, ng/mL | 7765±9109 | 1871±4146 | 0.003* |
| Reactive C Protein, mg/L | 210.3±157.4 | 142.7±121.2 | 0.17 |
| Ferritin, ng/mL | 782±518 | 786±1011 | 0.98 |
| CPK, UI/L | 169±188 | 300±462 | 0.36 |
| CPK-MB, ng/dL | 34±42 | 25±17 | 0.29 |
| Troponine I, ng/L | 49.4±136.7 | 26.1±96.3 | 0.45 |
| Mioglobin, ng/mL | 151±151 | 110±192 | 0.47 |
| Brain Natriuretic Peptid, pg/mL | 56.9±80.5 | 136.1±342.2 | 0.49 |
Conclusions: This is the first study in a Mexican cohort, which demonstrate that
seriously ill patients have significant raises of liver enzymes (AST, ALT) with prognostic implications in the SARSCov-2 disease course.
Conflicts of interest: The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.