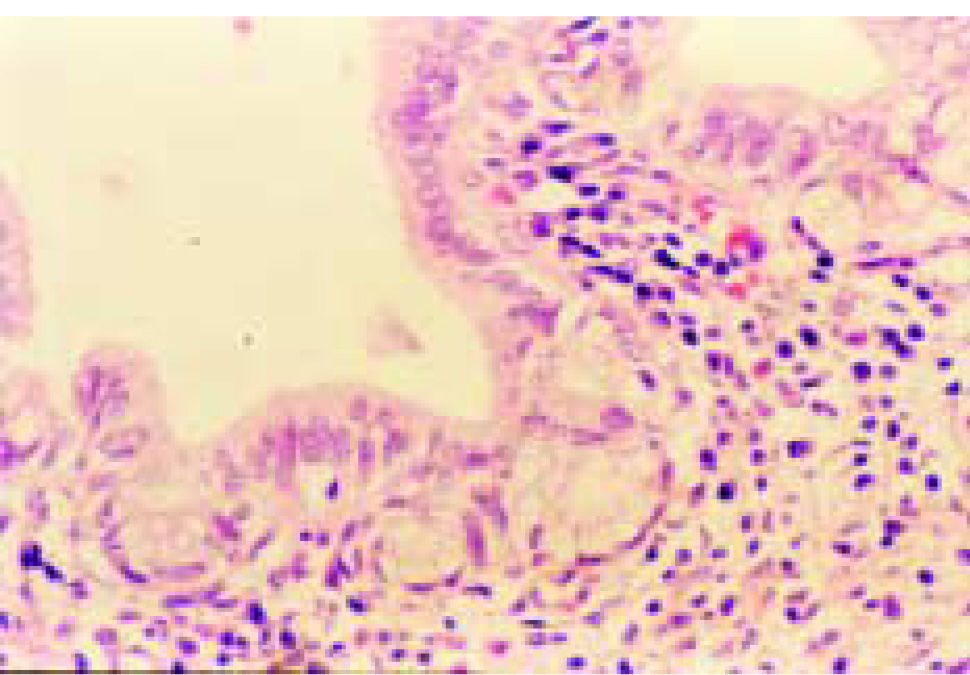
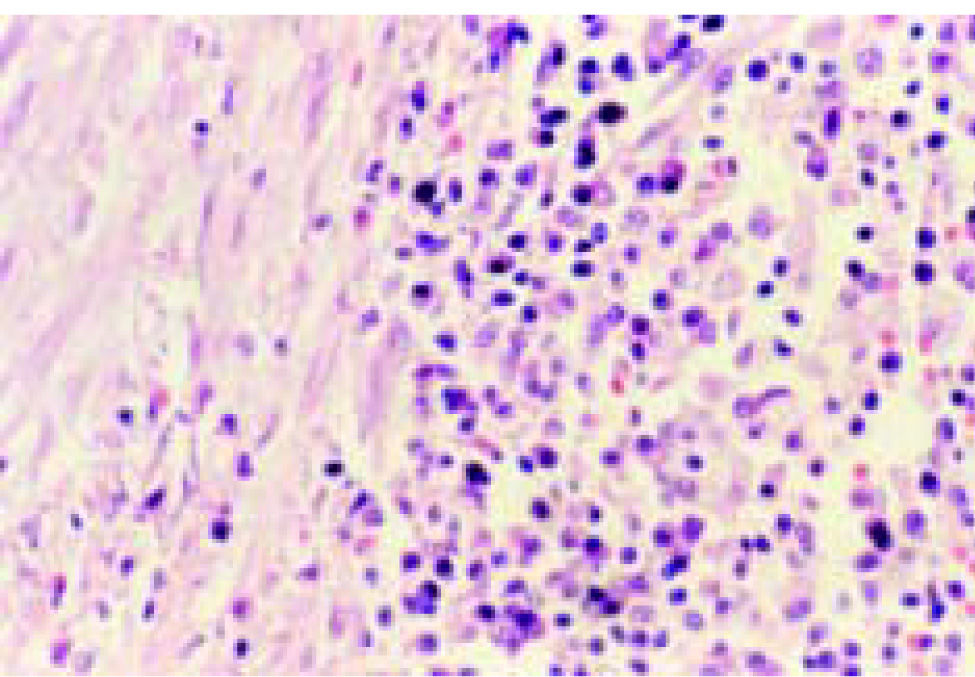
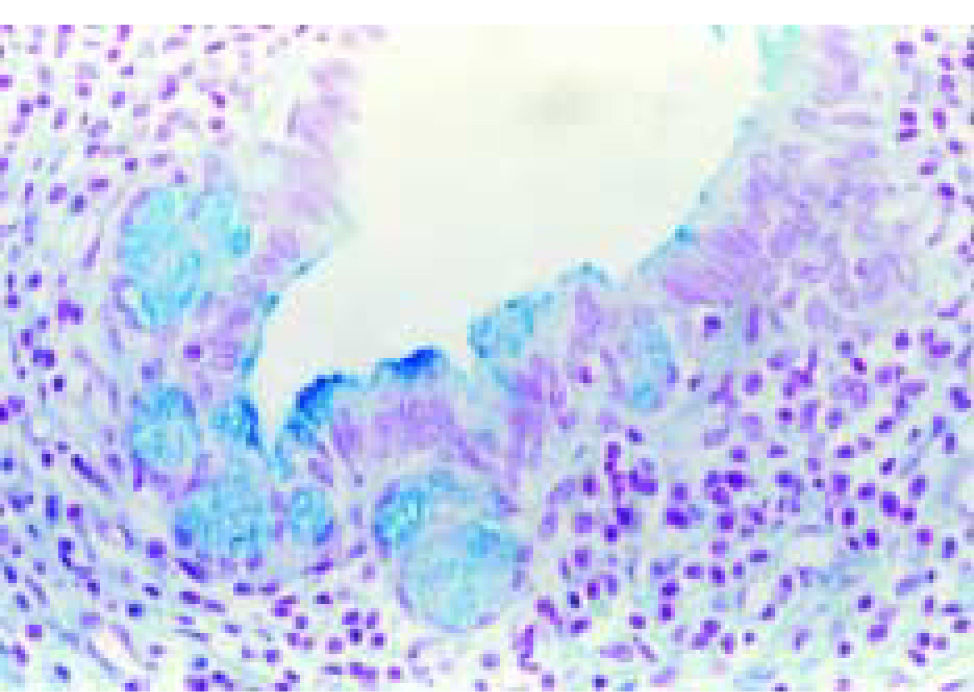
A 12-year old male was admitted to the hospital with fifteen days of fever and right upper abdominal pain during last two moths, and normal liver function tests. Computed tomographic showed a solitary hypoattenuating hepatic lesion into segment IV, which was resected. Figure 1A shows the resected specimen. A well-circumscribed, round, with yellow and white areas. Figure 1B shows chronic inflammatory infiltrates with foamy histiocytes, plasmacytes, and lymphocytes, and fibroblastic proliferation. Figures 1C and 1D show chronic cholangitis and intestinal metaplasia.
Inflammatory pseudotumor of the liver is a benign hepatic lesion characterized by a large population of polyclonal plasma cells with a variable amount of fibrosis, foamy histiocytes, and other chronic inflammatory cells, and therefore are commonly misdiagnosed as malignant tumors or liver abscesses.