Abstracts of the 2023 Annual Meeting of the ALEH
Más datosAutoimmune liver diseases (AILD) are entities of uncertain cause that affect all ages, genders, and ethnicities. Timely treatment drastically modifies the prognosis, but epidemiological heterogeneity represents a challenge. Adherence to international guidelines for its management is especially important for liver transplantation programs. This study aims to establish the epidemiological profile of a Central American cohort and analyze adherence to diagnostic and therapeutic guidelines in the specialized clinical practice of a Liver Transplant center.
Materials and MethodsObservational, retrospective study of a cohort diagnosed as AILD based on the digital records of a specialized hospital: autoimmune hepatitis (AIH), primary biliary cholangitis (PBC), primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) and variant syndromes.
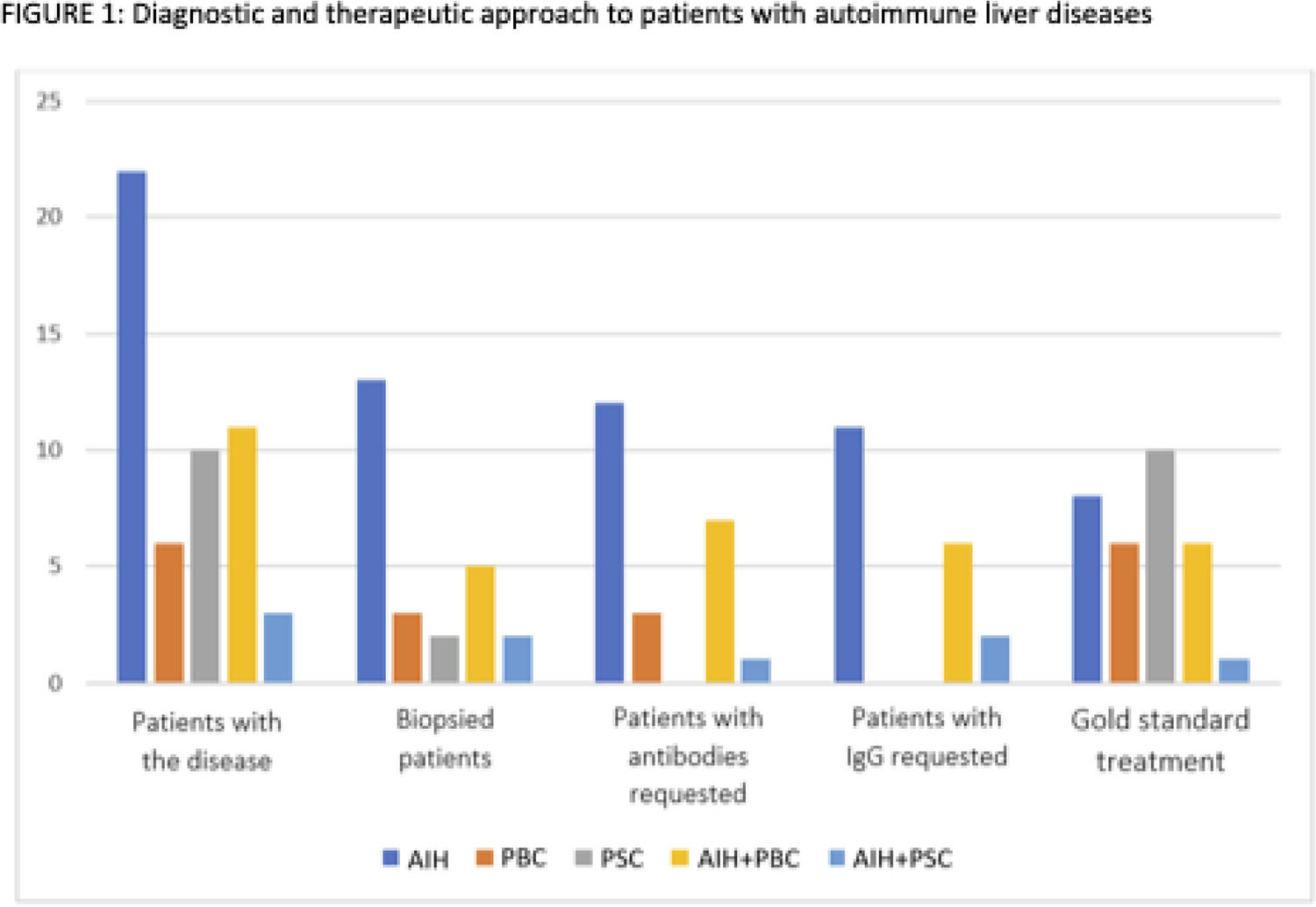
ResultsFrom 1998-2021, 52 patients were identified: 42% HAI, 19% CEP, 12% CBP, 21% HAI+CBP, 6% HAI+CEP. Mean age: 59 years (SD+/-12.2), 81% women. The main comorbidities were autoimmune diseases 52% (Hashimoto's thyroiditis 19%, Sjögren's 10% and rheumatoid arthritis 10%). Liver biopsy was performed in 25 patients (48%) (F3+F4: 16%). The serological study with antibodies and IgGs was requested in 60% of those classified as HAI, the simplified score for HAI was calculated in 55% (9% probable, 0% definitive) and one of 11 (9%) patients classified as HAI+CBP fulfilled the Paris criteria. Thirty-six percent of patients classified as HAI were treated according to current guidelines (37% complete response and 31% partial response) and all PBC and PSC were treated with ursodeoxycholic acid. Female sex and histological grade of fibrosis were significantly associated with better response to HAI treatment (p=0.003 and p=0.044, respectively).
ConclusionsA high percentage of patients approached as AILD in daily clinical practice does not conform to established guidelines and is based on individualized medical judgment. The application of protocolized guidelines for the management of AILD minimizes the possibility of etiologic overdiagnosis.