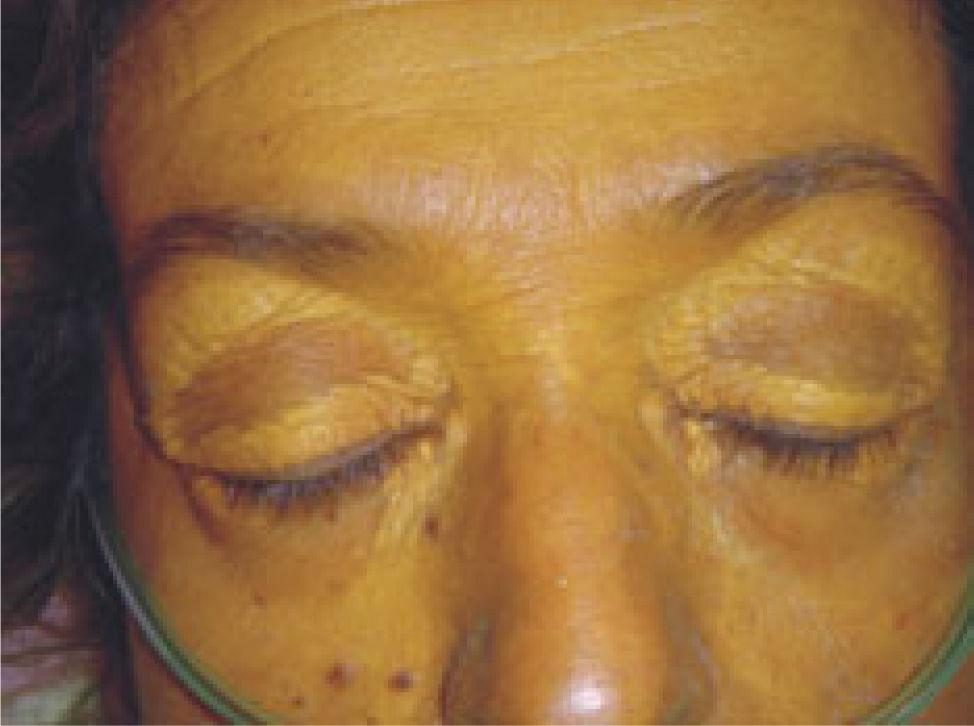
Primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC) is a chronic cholestatic liver disease that usually affects middle-aged women. The cause of PBC remains unknown, although genetic and immunologic factors appear to play a role. Many patients are asymptomatic at the time of diagnosis. The symptoms and signs of cholestasis develop as the disease progresses. At the physical examination the findings may vary and depend on the stage of the disease. Hypercholesterolemia is present in 50% of the patients and the xanthelasma and xanthomata correlate with it. Xanthelasmas are more common than xanthomata, but this findings are unnusual. Less than 5% of patients will eventually develop xanthomata (xanthomata striatum palmare), and are found on the palms of the hands and soles of the feet, over extensor surfaces of the elbows and knees, in tendons of the ankles and wrists, and on buttocks.
Consulte los artículos y contenidos publicados en este medio, además de los e-sumarios de las revistas científicas en el mismo momento de publicación
Esté informado en todo momento gracias a las alertas y novedades
Acceda a promociones exclusivas en suscripciones, lanzamientos y cursos acreditados