Estudiar la concordancia, así como comparar las medidas obtenidas por un topógrafo basado en tecnología de diodo-emisor de luz a color (Cassini®) y un topógrafo basado en tecnología Scheimpflug (Pentacam®) en la evaluación del poder dióptrico corneal y el astigmatismo anterior, posterior y total.
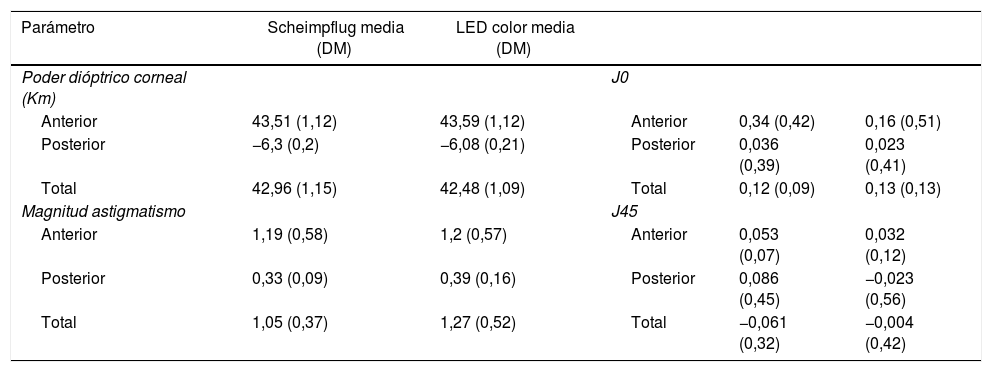
MétodoTreinta ojos sanos de 30 pacientes fueron valorados de manera consecutiva mediante ambos dispositivos. Las principales medidas evaluadas fueron el poder dióptrico corneal anterior, posterior y total, así como un análisis vectorial del astigmatismo. La concordancia fue estudiada mediante el coeficiente de correlación intraclase (CCI) y mediante representaciones de Bland-Altman. La comparación de medias se realizó mediante el test de la t-Student para datos apareados.
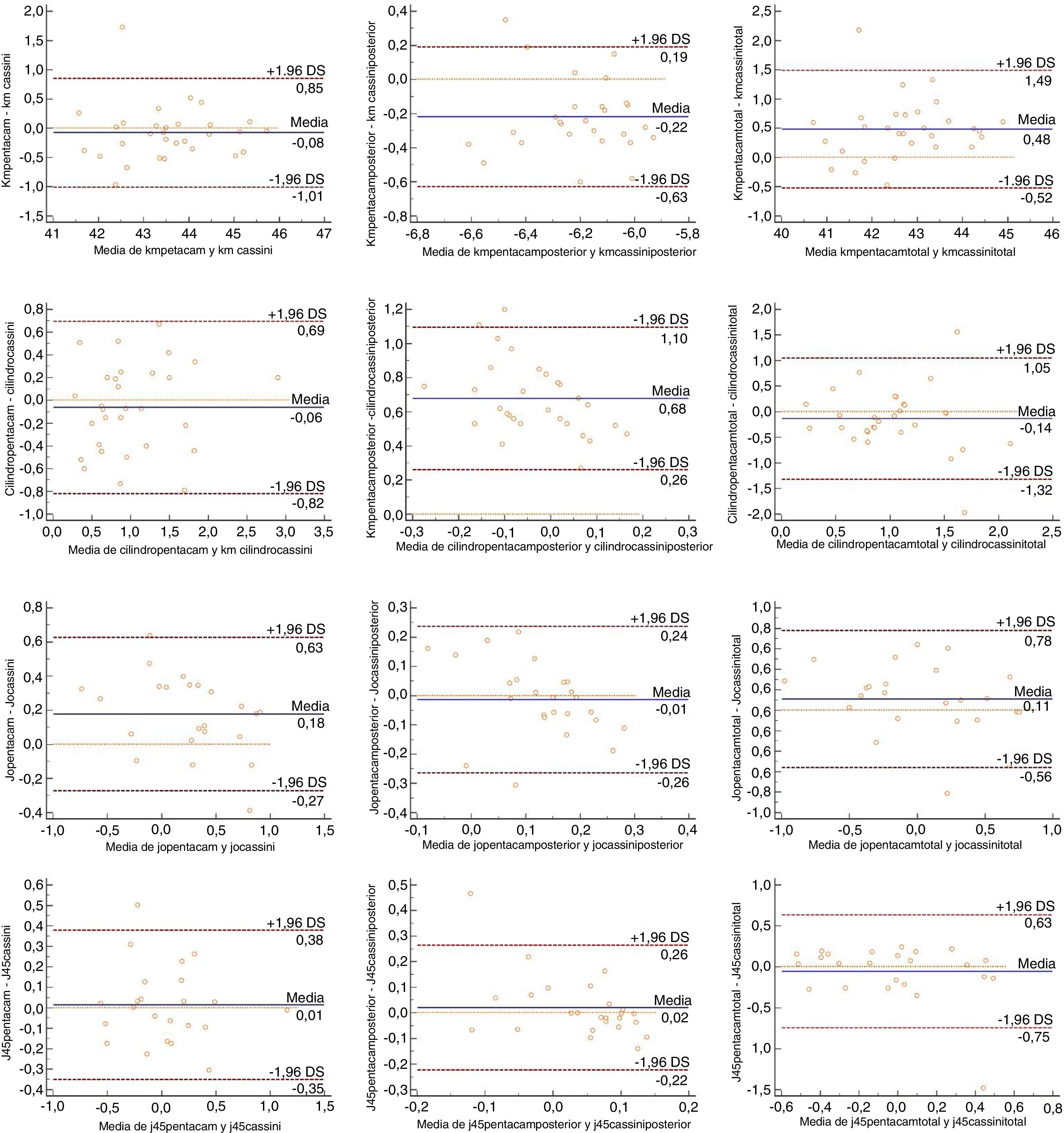
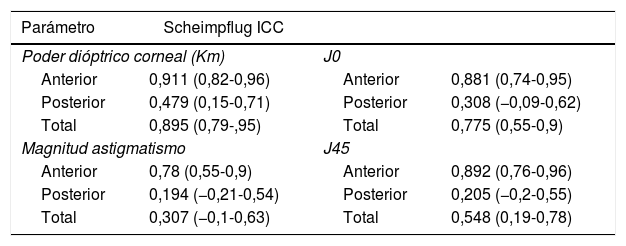
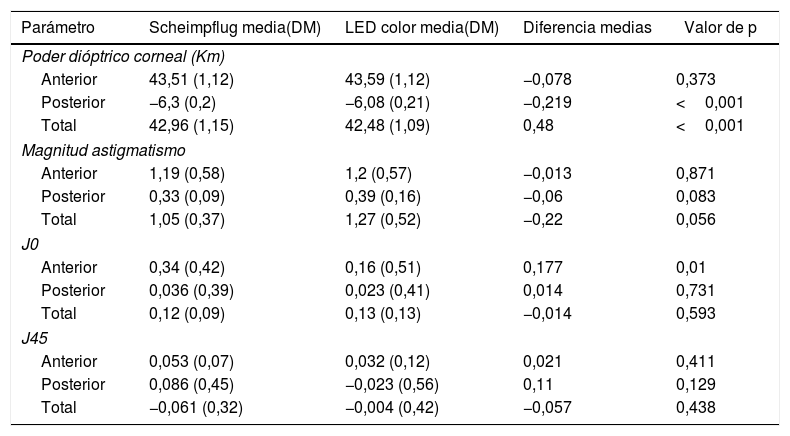
ResultadosLa concordancia entre los 2 dispositivos fue muy elevada (CCI>0,85) en la comparación del poder dióptrico de la córnea anterior y total, no así al estudiar la córnea posterior (CCI<0,5). En el análisis del astigmatismo, las medidas correspondientes a la cara anterior obtuvieron también una concordancia excelente (CCI>0,78), pero pobre al estudiar la cara posterior (CCI<0,31). No se encontraron diferencias estadísticamente significativas entre ambos topógrafos al estudiar la queratometría anterior (p>0,05), pero sí al estudiar la posterior y total (p<0,001) donde Pentacam® obtiene valores superiores. No se encontraron diferencias significativas entre ambos dispositivos en el estudio de la magnitud del astigmatismo.
ConclusiónLos valores obtenidos por ambos topógrafos presentan una excelente concordancia al estudiar la cara anterior de la córnea. En cambio, los valores que incluyen la cara posterior de la córnea presentan una concordancia pobre-moderada. Los datos obtenidos por ambos topógrafos, por lo tanto, no son intercambiables.
To determine the agreement and to compare the measurements obtained from a colour light-emitting diode based (CassiniTM) and Scheimpflug (PentacamTM) based topography in the evaluation of the anterior, posterior, and total corneal power and astigmatism.
MethodsA total of 30 eyes from 30 healthy patients were consecutively measured using PentacamTM and CassiniTM. The main evaluated parameters were the anterior, posterior, and total dioptric power, and a power vector analysis of the astigmatism. The agreement between both devices was analysed using the intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) and performing Bland-Altman plots. The comparison of means was performed using paired Student t-test.
ResultsThe agreement between both devices when comparing the anterior and total corneal dioptric power was very high (ICC>0.85), but not when studying the posterior cornea (ICC<0.5). In the astigmatism analysis, measurements from the anterior cornea also showed an excellent agreement (ICC>0.78), but was poor for the corneal posterior surface (ICC<0.31). When studying the corneal dioptric power, no statistically significant differences were found for the anterior surface (P>.05), but PentacamTM obtained higher values for posterior and total surfaces (P<.001). As regards the magnitude of the astigmatism, no significant differences were found between both devices.
ConclusionBoth devices were highly comparable when studying the anterior cornea, but the agreement was poor-moderate when measuring posterior cornea. Therefore, the data obtained by both topographers are not interchangeable.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora