Smoking is an important risk factor for Graves orbitopathy (GO) and it is modifiable. The advice to stop smoking has been included in all the clinical practice guidelines of GO. However, the effectiveness of this practice remains unknown. The purpose of this study is to assess the change in the smoking habit in patients affected with GO after an oral counselling for smoking cessation.
Material and methodsA retrospective cohort of GO patients was studied. The patients received a significant oral counsel during the first consultation with the ophthalmologist. 33 GO patients were explored in the ophthalmology clinic during 2013 and 2014 and the study was done throughout a telephone questionnaire in 2015. The main outcome was the number of cigarettes smoked daily before and after consultation with the endocrinologist and the ophthalmologist. Other medical and socioeconomic factors were recorded.
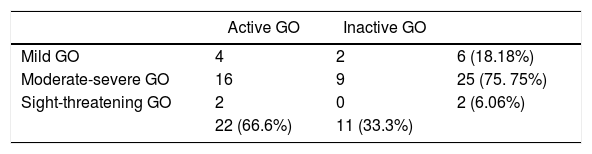
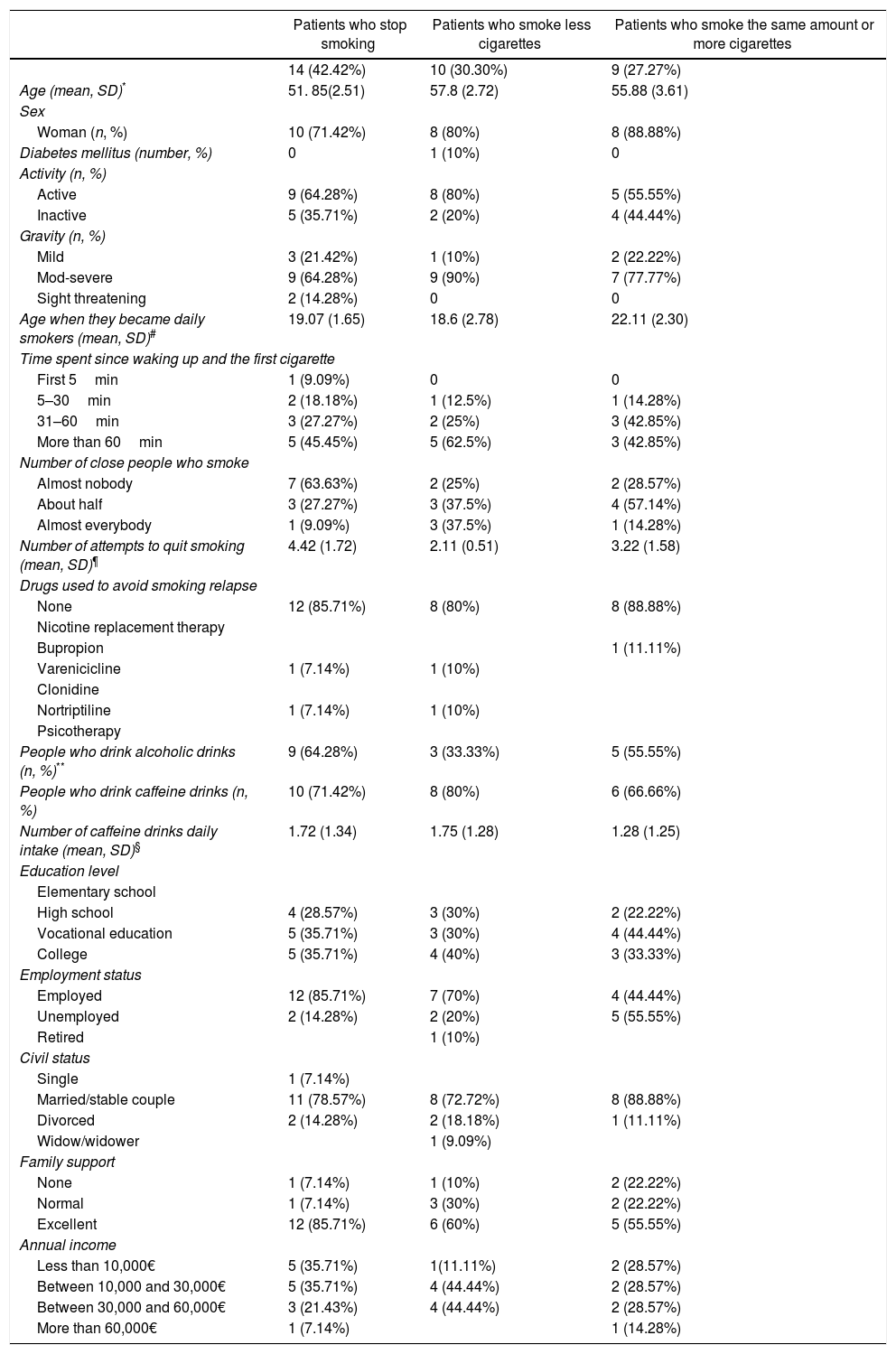
ResultsThe mean number of cigarettes that were smoked was 13.6 (SD 9.66) and 6.3 (SD 7.73) before and after the consultation done at the ophthalmology office (T-test paired, p=0.0006). 42.42% achieved smoking cessation and 30.3% decreased their smoking habit. Patients who stopped smoking suffered usually from active and severe GO, had more stable jobs and received greater support from their relatives and friends.
ConclusionA firm and strong oral counsel held for smoke cessation was effective in GO patients. This disease deeply affects patients’ quality of life, making them more prone to change their habits.
El tabaco es un factor de riesgo en la orbitopatía de Graves (GO) y es modificable. El consejo médico para dejar de fumar se ha incluido en todas las guías de práctica clínica de esta enfermedad, aunque su efectividad no ha sido evaluada. El objetivo de este estudio es conocer el cambio producido en el hábito tabáquico en pacientes con GO tras una recomendación verbal para dejar de fumar.
Material y métodosSe estudió una cohorte retrospectiva de pacientes con GO. Todos los pacientes recibieron consejo médico sobre la importancia de dejar de fumar en la primera consulta del oftalmólogo. Entre 2013 y 2014 se atendió a 33 pacientes en la consulta, que fueron preguntados sobre el cambio en su hábito tabáquico en 2015. La variable principal de estudio fue el número de cigarros fumados al día antes y después de las consultas en endocrinología y oftalmología. Aparte, se recogieron otros datos personales médicos y socioeconómicos.
ResultadosEl número medio de cigarros fumados fue de 13,6 (DE 9,66) y 6,3 (DE 7,73) antes y después de la primera consulta en oftalmología, respectivamente (test t pareado, p <0,05). El 42,42% de los pacientes dejó de fumar y el 30,3% disminuyó el consumo de cigarrillos. Los pacientes que consiguieron dejar de fumar presentaban con mayor frecuencia formas de enfermedad de Graves activas y graves, tenían trabajos estables y estaban apoyados por sus familiares y amigos.
ConclusiónUn consejo fuerte y firme recomendando dejar de fumar es efectivo en pacientes con GO. Esta enfermedad afecta seriamente la calidad de vida de los pacientes, lo que hace que sean más susceptibles de cambiar a la hora de modificar sus hábitos.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora