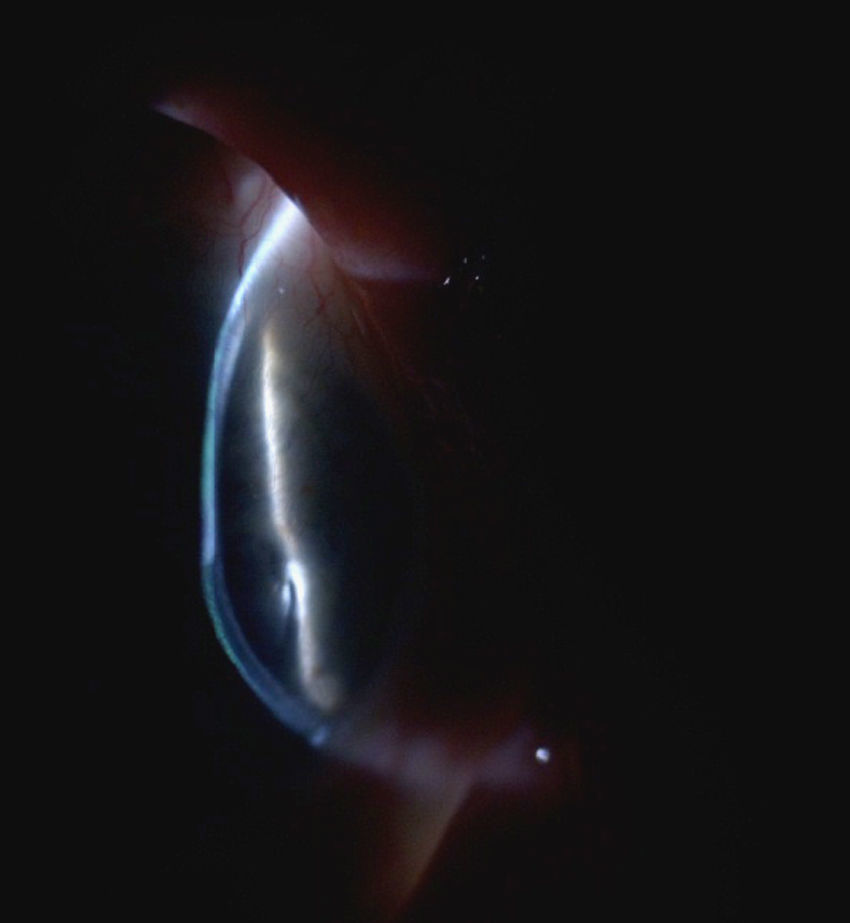
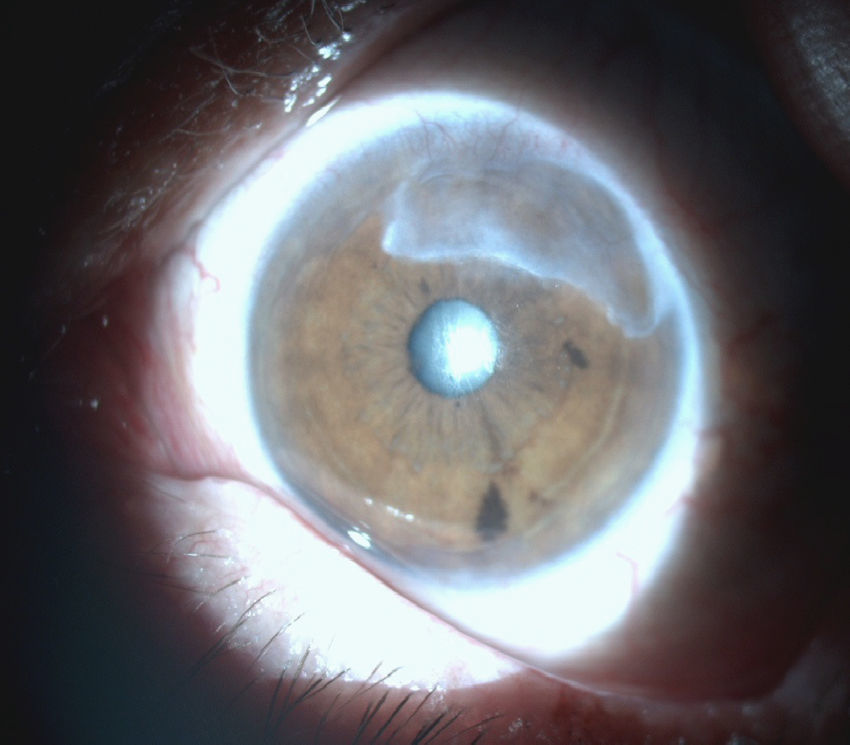
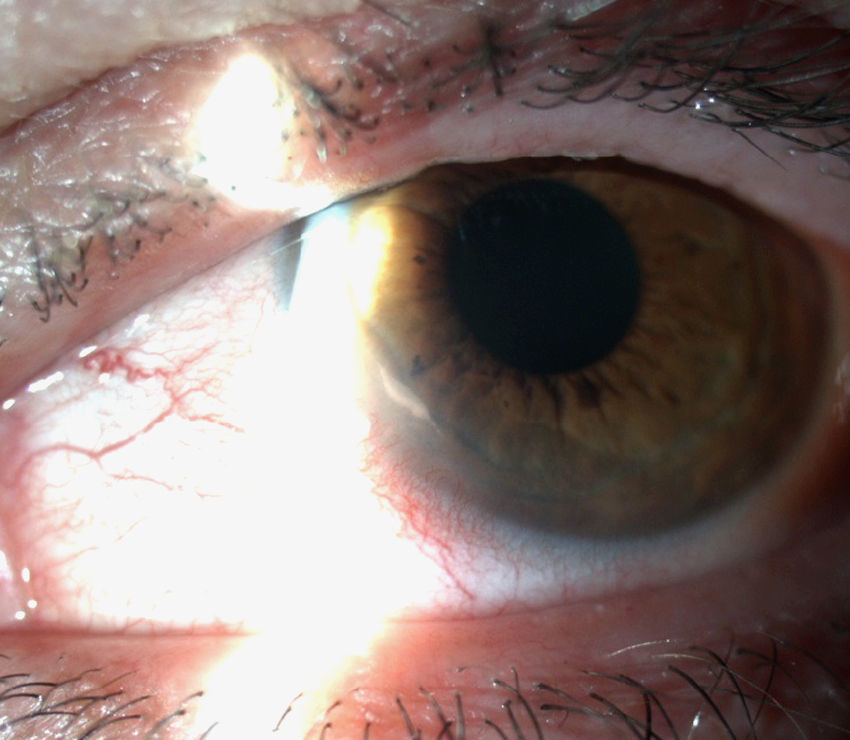
: Se presentan dos pacientes diagnosticadas de artritis reumatoide de larga evolución que desarrollaron una queratitis ulcerativa periférica (QUP) grave. Habían sido tratadas previamente con fármacos modificadores de la enfermedad (FAME) y terapia biológica (TB) sin alcanzar un control clínico-biológico óptimo de su enfermedad. Se trataron inicialmente con corticoides sistémicos a dosis altas sin éxito. Rituximab indujo la regresión de las lesiones corneales y el control de su artritis reumatoidea.
DiscusiónRituximab puede ser una alternativa para detener la progresión de la QUP asociada a artritis reumatoide refractaria a otros fármacos.
We report two cases of patients affected by longstanding rheumatoid arthritis who developed a severe form of peripheral ulcerative keratitis (PUK). Neither of them had an optimal biological and clinical control of their systemic illness despite being treated with several disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) and biologic therapy. High-dose systemic corticosteroids were given to treat the PUK without any success. Rituximab resulted in a favourable response with resolution of the corneal lesions and optimal control of their systemic illness.
DiscussionRituximab may be an additional tool to arrest progressive rheumatoid arthritis-associated PUK that is refractory to other drugs.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora