Evaluar los efectos del tratamiento con brinzolamida tópica en la agudeza visual y en la intensidad del nistagmo en pacientes con nistagmo congénito.
Material y métodosSe diseñó un estudio retrospectivo en el que se revisaron las historias clínicas de 11 pacientes con nistagmo congénito. A todos los pacientes se les realizó una exploración oftalmológica completa y una videooculografía mediante VOG-Perea, antes y a los 3 días de iniciar el tratamiento con brinzolamida tópica (Azopt) cada 8horas. Cinco investigadores expertos evaluaron la intensidad del nistagmo de forma enmascarada mediante un vídeo antes y después del tratamiento. Por último, se registró la mejoría subjetiva de los pacientes.
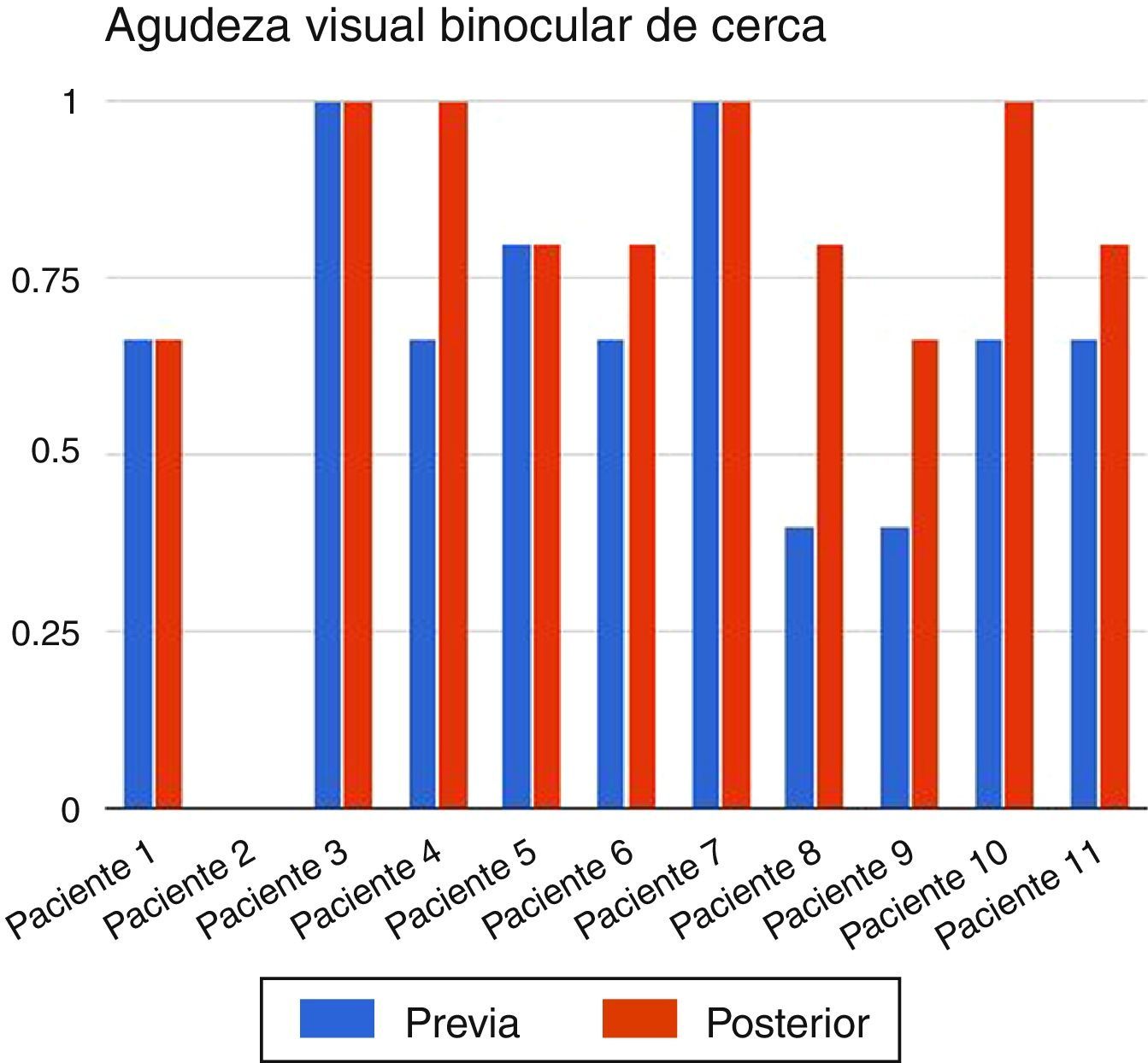
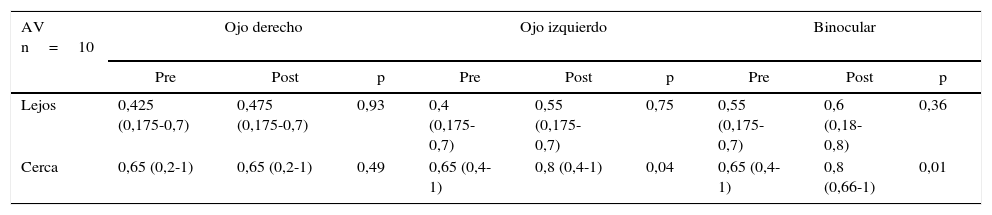
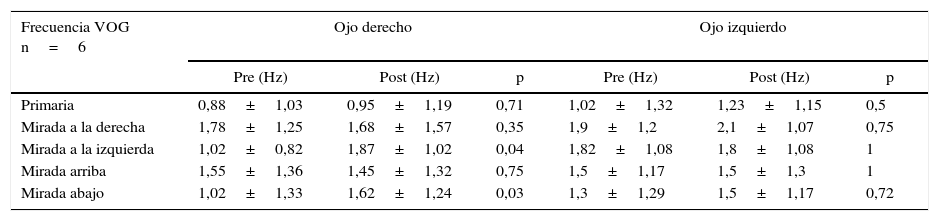
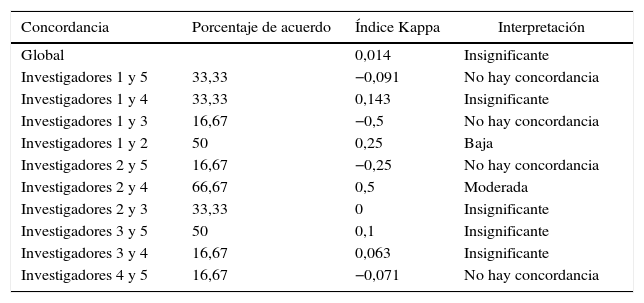
ResultadosSe encontraron diferencias estadísticamente significativas en la agudeza visual binocular de cerca previa y posterior al tratamiento. Se encontró un leve aumento de la frecuencia del nistagmo, que fue estadísticamente significativa en la mirada horizontal hacia la izquierda y con la mirada hacia abajo (p=0,04, p=0,03 significativo). El índice Kappa de concordancia entre los investigadores evaluando la intensidad del nistagmo fue de 0,014. Solo 2 de los pacientes notaron mejoría en la agudeza visual y un paciente notó mejoría en el aspecto estético.
ConclusionesA pesar de producirse una mejoría en el nistagmo, esta es leve, no apreciable cosméticamente por los pacientes en la mayoría de los casos, y no se relacionó con una mejoría significativa en la agudeza visual ni en la calidad de vida de los pacientes. Son necesarios nuevos estudios para evaluar los efectos de la brinzolamida tópica y establecer las posibles indicaciones terapéuticas en el nistagmo.
To evaluate the effect of treatment with topical brinzolamide on visual acuity and nystagmus intensity in patients with congenital nystagmus.
Material and methodsA retrospective study was designed in which the clinical records of 14 patients with congenital nystagmus were reviewed. All patients underwent a complete ophthalmological examination and a Perea video-oculography (VOG) before, and three days after, initiation of treatment with topical brinzolamide (Azopt). Five expert researchers evaluated the intensity of nystagmus by video before and after treatment. Finally, the subjective improvement of the patients was recorded.
ResultsStatistically significant differences were found in pre- and post-treatment binocular near visual acuity. A slight increase in the frequency of nystagmus was found, which was statistically significant with the horizontal gaze to the left and with the gaze downwards (P=.04, P=.03, respectively). The kappa index concordance between the researchers evaluating the intensity of nystagmus was 0.014. Only two of the patients noticed improvement in visual acuity, and one patient noticed improvement in the aesthetic aspect.
ConclusionsIn spite of an improvement in nystagmus, it was slight, not cosmetically appreciable by patients in most cases, and was not related to a significant improvement in visual acuity or in patient quality of life. Further studies are needed to evaluate the effects of topical brinzolamide, and to establish potential therapeutic indications in nystagmus.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora