The dental degree programme contains a lot of information about oral cancer to make students aware of the importance of its future role in the diagnosis and treatment of them. Malignancies affect a variety of anatomic subsites, including oral cavity, salivary glands, pharynx, larynx, and paranasal sinuses.1
The American Cancer Society estimated that in 2017 the number of new was 49,670 and 9700 deaths occurred as a result of oral cavity and pharyngeal cancer. Overall, 5-year survival was 64.7% based on data from 2007 to 2013. In the European Union there are an estimated 66,650 new cases each year.2 Risk factors include exposure to tobacco smoke, alcohol, and Human Papilloma Virus. Polycyclic hydrocarbons and nitrosamines are carcinogenic molecules in tobacco that increase the incidence of oral cancer. Alcohol and tobacco appear to have a synergistic effect, although alcohol alone is linked to increased cancer risk.
Typically, HPV16 and HPV18 are viruses that cause premalignant squamous intraepithelial neoplasms that can progress to cancer. They are the key drivers of tumorigenesis by inactivating tumour suppressors, pRb and p53.3,4 The diagnosis procedure includes inspection, palpation and observation of the extent and the texture of the lesion. The diagnosis is confirmed by radiographic findings, depending on type of lesion. If the dentist notices the problem, it is important to be prompt by all possible means.
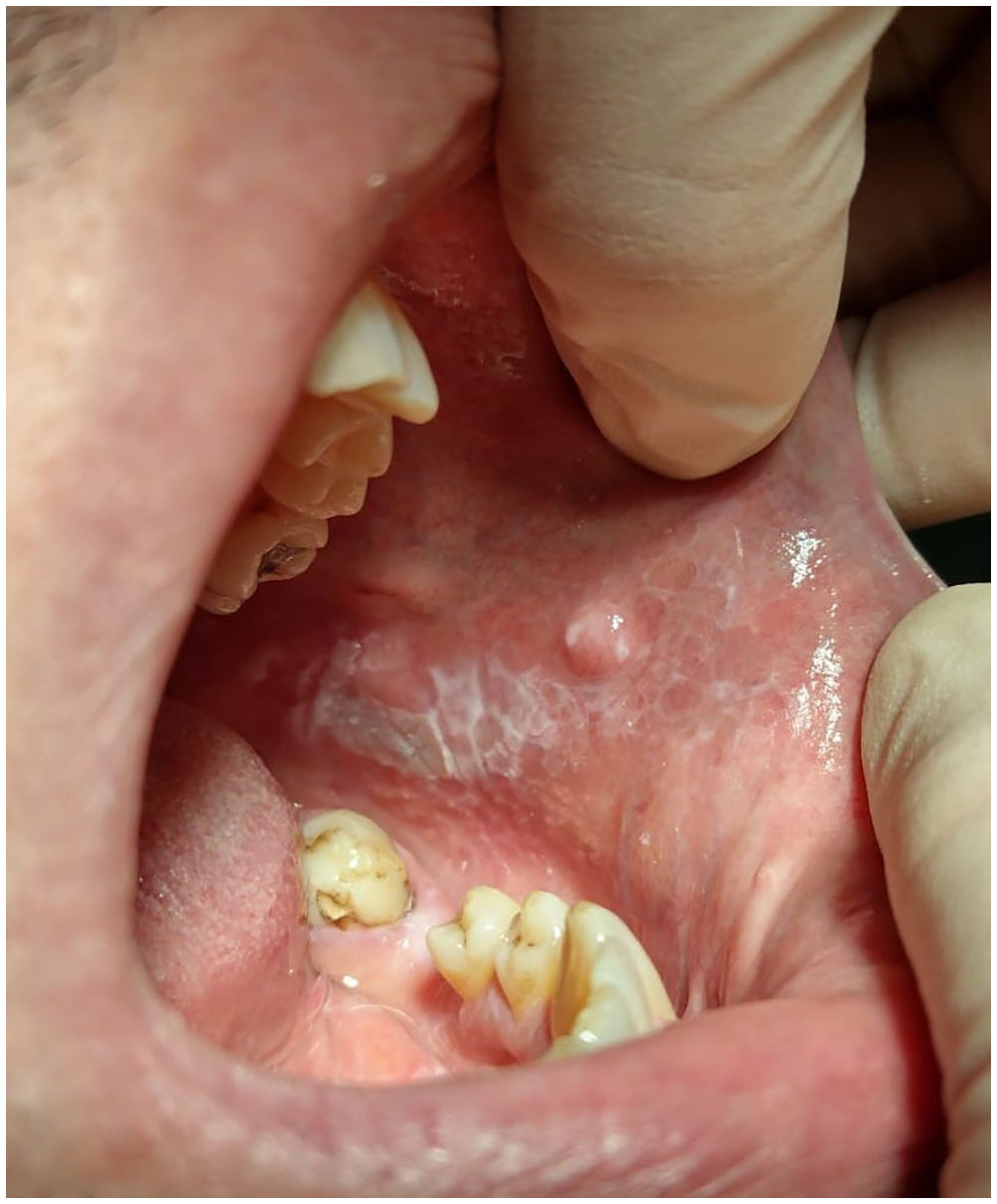
Case reportA 47-year-old male patient presents to his dentist with an extensive lesion of the oral cavity. The man is hospitalized in the Maxillofacial Surgery Department of the “S. Salvatore” of the ASL 1 Avezzano-Sulmona-L’Aquila. In the anamnesis, the patient does not report any systemic pathology or pharmacological therapy and admits a certain propensity to smoke. The number of cigarettes per day is more than ten. This lesion appears to be asymptomatic, and painless. It is not possible to trace any occasional or repeated traumatic event that could interfere with the health of the tissues of the oral cavity. There have been no significant changes in the last three months. The extraoral examination showed no lymph node alterations in the cervical area. Close intraoral examination reveals an asymmetrical lesion extending to both the left and right buccal portions, where its manifestation is most evident (Fig. 1).
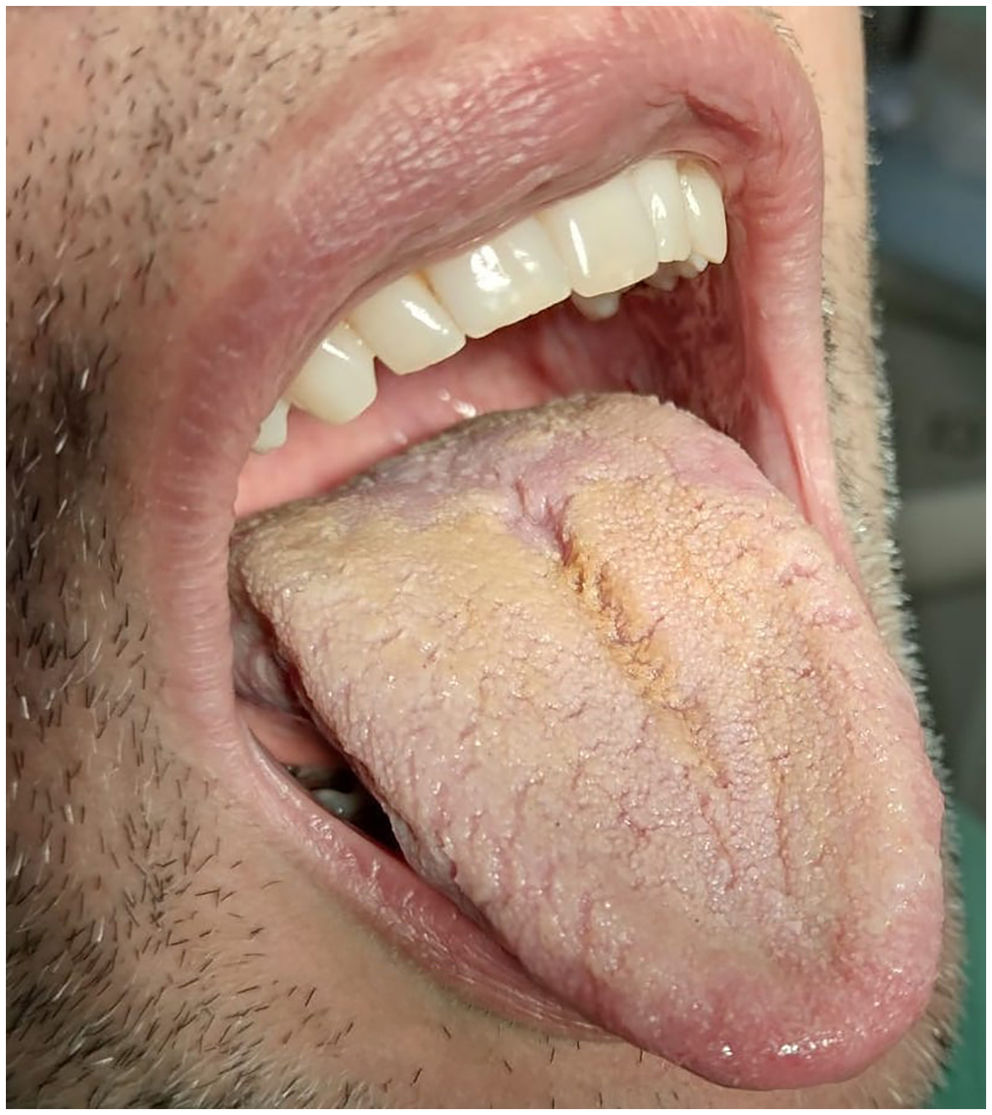
Here the whitish lesion is characterized by a plaque shape whose irregular margins fade towards the corner of the mouth. There are also predominantly light pink hard-elastic exophytic breakfast nodules on which small whitish patches persist. The longitudinal extension is about 5cm. In the left site the lesion has a much more nuanced, whitish, and non-ulcerative manifestation. The tongue has a typical “hairy tongue” appearance, associated with the high number of cigarettes (Fig. 2).
The first level radiographic examination requested for dental reasons did not show signs of further lesions or bone manifestations.
DiscussionThe biopsy examination made use of the multiple incision technique, focused on the analysis of the most representative manifestations of the lesion.
The histological analysis of the samples taken allowed the diagnosis of orthokeratosis leukokeratosis.
Due to the frequency with which these leukoplastic manifestations transform into malignant forms (36%), it is necessary to ask the patient to completely abstain from smoking.5 Greater attention is required for home oral hygiene manoeuvres which can improve the appearance of the tongue.
After 3 months, a scrupulous follow-up programme was planned, according to the “wait and see” surveillance approach. Surveillance will inevitably be both clinical and histological in order to allow timely diagnosis of squamous cell carcinoma and subsequent early treatment.6 It is important for scientific journals to publish the morphology of lesions so as to train physicians to recognize.
Written consentThe authors obtained written consent to publish the clinical report and the images.
Ethical approvalAuthors declare compliance with all relevant ethical regulations.
FundingNone declared.
Conflict of interestNone declared.