The global emergence of carbapenemases led to the need of developing new methods for their rapid detection. The aim of this study was to evaluate the performance of the rapid tests for carbapenemase-producing and non-producing Enterobacteriaceae. Carbapenem non-susceptible Enterobacteriaceae from a surveillance study submitted to a multiplex real time PCR for carbapenemase detection were included in this study. The isolates were subjected to the rapid phenotypic tests Carba NP, Blue-Carba and Carbapenem Inactivation Method (CIM). A total of 83 carbapenemase-producing (43) and non-producing (40) isolates were included in the study. The sensitivity/specificity were 62.7%/97.5%, 95.3%/100%, and 74.4%/97.5% for Carba NP, Blue-Carba and CIM, respectively. Both Carba NP and Blue-Carba presented their final results after 75min of incubation; the final results for CIM were obtained only after 8h. Failure to detect OXA-370 carbapenemase was the main problem for Carba NP and CIM assays. As the Blue-Carba presented the highest sensitivity, it can be considered the best screening test. Conversely, CIM might be the easiest to perform, as it does not require special reagents. The early detection of carbapenemases aids to establish infection control measures and prevent carbapenemases to spread reducing the risk of healthcare associated infections and therapeutic failure.
Nowadays carbapenem resistance among Enterobacteriaceae is a major concern. These bacteria become resistant to this antibiotic class mainly due to three mechanisms, either isolated or combined: efflux pumps; permeability loss; and carbapenemase production.1 The latter represents a growing concern, since these enzymes hydrolyze not only carbapenems but also other β-lactams and their dissemination is usually plasmid-mediated.2
Carbapenemases can be classified as class A, B or D β-lactamases,3 based on their molecular structure. In Brazil, different carbapenemase classes have emerged over the years but the Klebsiella pneumoniae carbapenemase (KPC) is already considered endemic.2 We have also observed the spread of the New Delhi Metallo-β-lactamase (NDM) in recent years4,5 and the emergence of OXA-370 in some regions.5 Moreover, scattered reports of GES-5 and IMP-1 have been described over the country.6,7
The global emergence of carbapenemases brought to light the need of developing new methods for its rapid detection. The enzymatic activity of carbapenemases is explored as an alternative for their detection in some recent studies. This activity might be detected by biochemical assays such as Carba NP and Blue-Carba methods,8,9 in which the hydrolysis of the β-lactam ring is visualized by the colour change of a pH indicator, or using mass spectroscopy in which the absence of the carbapenem molecular ion is observed in the presence of a carbapenemase-producing bacteria.10,11 Van der Zwaluw et al. also proposed a methodology (the Carbapenem Inactivation Method – CIM) in which a carbapenem-susceptible E. coli strain is able to grow near a meropenem disk after its incubation with a carbapenemase-producing strain.12 Recently, the Clinical & Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) proposed the use of Carba NP and the CIM assays as screening methods for carbapenemase detection.13
The aim of this study was to evaluate the performance of the rapid tests Carba NP, Blue-Carba and CIM against carbapenemase-producing and -non-producing Enterobacteriaceae.
Material and methodsBacterial isolatesCarbapenem non-susceptible Enterobacteriaceae, from a previous surveillance study, were identified by biochemical characterization and, when necessary, confirmed using VITEK2 system (BioMérieux, France). Isolates resistant to, at least, imipenem and/or meropenem were selected for this study.
Genotypic detection of carbapenemasesCarbapenemase genes were detected by a multiplex real-time PCR with specific primers for the blaKPC, blaGES, blaIMP, blaNDM, blaVIM and blaOXA-48-like.14 PCR products of isolates positive for blaGES and blaOXA-48-like were purified using the ExoStar kit (GE Healthcare) and sequenced using a BigDye Terminator kit (version 3.1) and an ABI 3500 Genetic Analyzer (Applied Biosystems).
Phenotypic detection of carbapenemasesCarba NPThe carbapenemase detection by Carba NP was performed and interpreted as previously described by Nordmann et al.8 Briefly, overnight cultured colonies grown in Mueller Hinton agar were submitted to extraction with B-PERII (Bacterial Protein Extraction Reagent, Thermo Scientific Pierce, Rockford, USA) and incubated for 2h in a solution containing phenol-red and imipenem. The bacterial extract was also incubated in a phenol-red solution without antibiotic. The result was considered positive when the solution containing imipenem became orange or yellow. The result was not validated if the solution without antibiotic presented a colour change more expressive than the solution containing imipenem. A known KPC-2 producer was used as positive control, and E. coli ATCC 25922 was tested as negative control.
Blue-CarbaCarbapenemase detection by Blue-Carba was performed and interpreted as previously described by Pires et al.9 Briefly, overnight cultured colonies grown in Mueller Hinton agar were incubated for 2h in a solution containing bromothymol blue and imipenem. The bacterial colonies were also incubated in a bromothymol blue solution without antibiotic. The result was considered positive when the solution containing imipenem became green or yellow, and its color was different from the one observed in the negative control. The result was not validated if the solution without antibiotic presented the same or stronger colour change as the solution containing imipenem. A known KPC-2 producer was utilized as positive control, and a test tube containing only bacteria inoculum and Blue-Carba solution was used as negative control for each isolate tested.
Carbapenemase inhibition method (CIM)The CIM was performed as previously described by van der Zwaluw et al.12 Briefly, overnight cultured colonies were incubated for 2h with a meropenem disk in 400μL of water, with zinc sulfate supplementation for metallo-beta-lactamase-producing isolates. After the incubation, the disk was placed on a Mueller-Hinton agar plate previously inoculated with a susceptible E. coli (ATCC 25922) and incubated at 35°C up to the growth of the strain (around 6h). The result was considered positive when the E. coli presented an inhibition zone ≤16mm around the meropenem disk, according to the CLSI interpretation criteria.13 A known KPC-2 producer was utilized as positive control, and E. coli ATCC 25922 was tested as negative control.
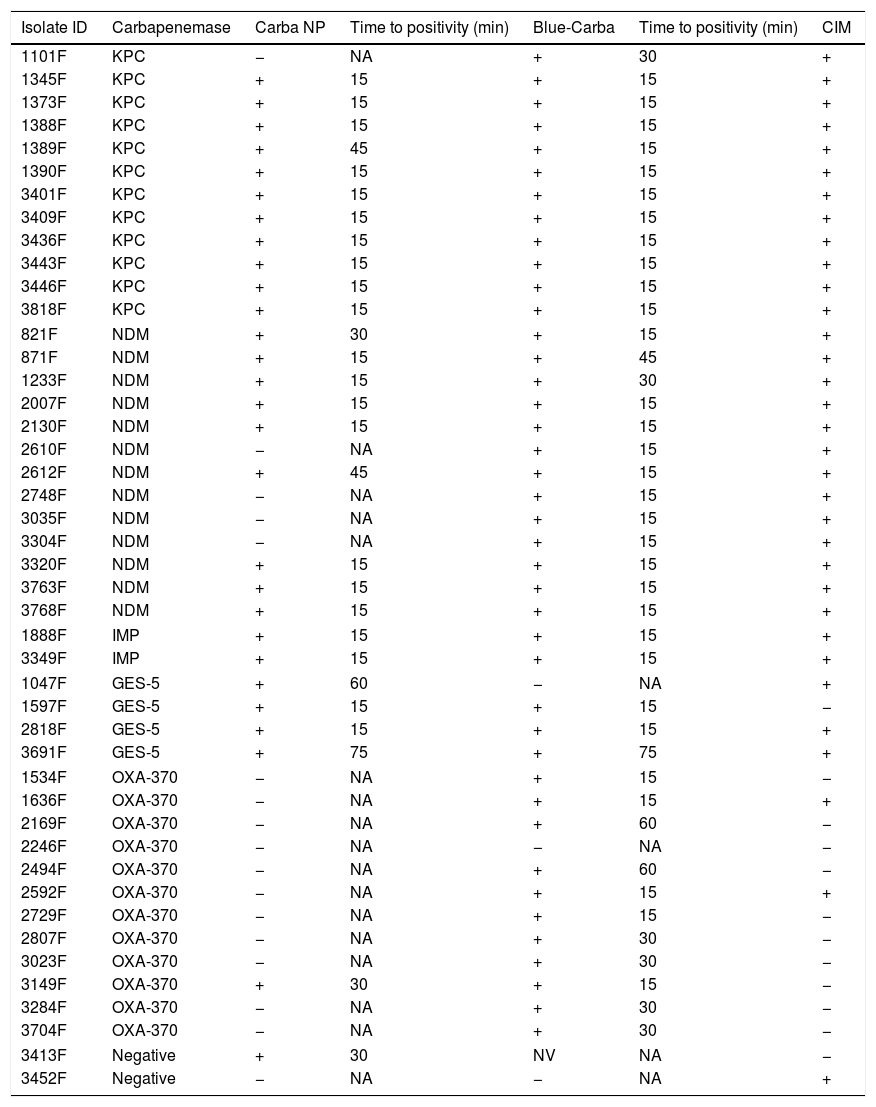
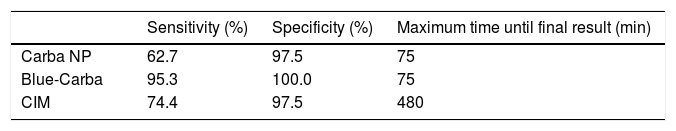
ResultsA total of 83 carbapenem-non-susceptible Enterobacteriaceae isolates were selected for this study: 12 KPC, 13 NDM, 12 OXA-370, four GES-5, and two IMP producers, as well as 40 carbapenemase non-producers. All isolates were submitted to the rapid tests Carba NP, Blue-Carba and CIM. The results for carbapenemase-producing isolates, as well as the two carbapenemase-non-producing isolates with at least one false positive result, are presented in Table 1. The 38 carbapenemase-non-producing isolates that were not included in the table presented negative results for all tests performed. The Carba NP test presented a sensitivity of 62.7% and a specificity of 97.5%. The vast majority of isolates with positive results presented a clear color change within 15min of incubation; only one isolate required the maximum time of 75min to become positive (Table 2). The sensitivity of Blue-Carba was 95.3% and its specificity was 100%. As observed in Carba NP, most isolates with positive results in the Blue-Carba presented the final result within 15min of incubation; only one isolate required the maximum time of 75min to become positive (Table 2). The Carbapenemase Inactivation Method presented a sensitivity of 74.4% and specificity of 97.5%. The CIM required a standard time of at least 480min between the beginning and the final results of the test (Table 2).
Results of rapid tests Carba NP, Blue-Carba and CIM for carbapenemase-producing and non-producing Enterobacteriaceae.
| Isolate ID | Carbapenemase | Carba NP | Time to positivity (min) | Blue-Carba | Time to positivity (min) | CIM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1101F | KPC | − | NA | + | 30 | + |
| 1345F | KPC | + | 15 | + | 15 | + |
| 1373F | KPC | + | 15 | + | 15 | + |
| 1388F | KPC | + | 15 | + | 15 | + |
| 1389F | KPC | + | 45 | + | 15 | + |
| 1390F | KPC | + | 15 | + | 15 | + |
| 3401F | KPC | + | 15 | + | 15 | + |
| 3409F | KPC | + | 15 | + | 15 | + |
| 3436F | KPC | + | 15 | + | 15 | + |
| 3443F | KPC | + | 15 | + | 15 | + |
| 3446F | KPC | + | 15 | + | 15 | + |
| 3818F | KPC | + | 15 | + | 15 | + |
| 821F | NDM | + | 30 | + | 15 | + |
| 871F | NDM | + | 15 | + | 45 | + |
| 1233F | NDM | + | 15 | + | 30 | + |
| 2007F | NDM | + | 15 | + | 15 | + |
| 2130F | NDM | + | 15 | + | 15 | + |
| 2610F | NDM | − | NA | + | 15 | + |
| 2612F | NDM | + | 45 | + | 15 | + |
| 2748F | NDM | − | NA | + | 15 | + |
| 3035F | NDM | − | NA | + | 15 | + |
| 3304F | NDM | − | NA | + | 15 | + |
| 3320F | NDM | + | 15 | + | 15 | + |
| 3763F | NDM | + | 15 | + | 15 | + |
| 3768F | NDM | + | 15 | + | 15 | + |
| 1888F | IMP | + | 15 | + | 15 | + |
| 3349F | IMP | + | 15 | + | 15 | + |
| 1047F | GES-5 | + | 60 | − | NA | + |
| 1597F | GES-5 | + | 15 | + | 15 | − |
| 2818F | GES-5 | + | 15 | + | 15 | + |
| 3691F | GES-5 | + | 75 | + | 75 | + |
| 1534F | OXA-370 | − | NA | + | 15 | − |
| 1636F | OXA-370 | − | NA | + | 15 | + |
| 2169F | OXA-370 | − | NA | + | 60 | − |
| 2246F | OXA-370 | − | NA | − | NA | − |
| 2494F | OXA-370 | − | NA | + | 60 | − |
| 2592F | OXA-370 | − | NA | + | 15 | + |
| 2729F | OXA-370 | − | NA | + | 15 | − |
| 2807F | OXA-370 | − | NA | + | 30 | − |
| 3023F | OXA-370 | − | NA | + | 30 | − |
| 3149F | OXA-370 | + | 30 | + | 15 | − |
| 3284F | OXA-370 | − | NA | + | 30 | − |
| 3704F | OXA-370 | − | NA | + | 30 | − |
| 3413F | Negative | + | 30 | NV | NA | − |
| 3452F | Negative | − | NA | − | NA | + |
NA, not applicable; NV, not validated.
Lately a variety of novel methods for carbapenemase detection have been proposed.9,12,15–17 All methods explore the carbapenem-hydrolysing activity of the β-lactamases and are supposed to present high sensitivity and specificity within a short period of time, with results interpretable in a single day of work. In this study, we evaluated the rapid tests Carba NP, Blue-Carba and CIM.
Carba NP presented high specificity, but its sensitivity was the lowest among the other methodologies. The reduced sensitivity of Carba NP was mostly due to OXA-370 isolates. This finding was also reported in other studies that evaluated the performance of Carba NP with OXA-48-producing isolates.18,19 The Carba NP method proved to be a very fast methodology as most positive results were observed in 15min. In fact, although the bacterial extract and the carbapenem were incubated for 120min, no significant colour change was observed after 75min, which was considered the final time results for this test.
The Blue-Carba methodology presented the highest sensitivity and specificity among the three methodologies. Only one OXA-370 positive isolate and one GES positive isolate were not detected by Blue-Carba. Pasteran et al. observed very similar results of sensitivity and specificity for this assay when they tested isolates from very diverse locations in Latin America.21 As found in the Carba NP test, most isolates presented positive results in 15min and the final result for Blue-Carba was observed after 75min of incubation.
Regarding CIM, we have modified the original protocol of van der Zwaluw et al.12 and added zinc sulphate in the suspension of bacteria with the meropenem disk to achieve a higher sensitivity of the method regarding the detection of metallo-beta-lactamase. As observed with Carba NP, a lower sensitivity was obtained among the OXA-370 producers. The major setback of this methodology, compared to the other two evaluated in this study, is the time needed for the final result, considering that at least 6h are necessary for a proper growth of the carbapenem-susceptible E. coli, which is mandatory for the test interpretation. On the other hand, the CIM seems to be the simplest test, considering that no special reagents are necessary for its execution.
The difficulty for detection of isolates harboring OXA-48-like is probably related to the least expressive hydrolytic capacity of class D carbapenemases.20 Also, it is still not clear if OXA-370 (a variant of OXA-48) is a true carbapenemase, considering that low carbapenem MIC values are usually observed in clinical samples presenting this enzyme. In this matter, the detection of imipenem hydrolysis, in which the tests are based, is even harder. If OXA-370 producing isolates were not included in this study, the sensitivity for CarbaNP test would be of 83.8% and of 96.7% for CIM. However, the OXA-370 seems to be the variant of OXA-48 that is prevalent in Brazil and, therefore, it is important that the rapid tests be evaluated against these isolates.
Noteworthy, minimal color changes, yielded by lower carbapenem hydrolysis levels, were easier to observe using the Blue-Carba test, considering that blue-green changes are easier to observe, compared to red-orange ones. In some cases, especially regarding OXA-370- and GES-5-producing isolates, the interpretation of tests results were challenging, and a second opinion was requested. Thus, the correct interpretation relies on capacitated technicians.
The global spread of carbapenemases highlights the importance of their rapid detection. Considering that carbapenems are the last resort for serious Enterobacteriaceae infections, controlling the dissemination of the mechanisms of resistance to these antibiotics is mandatory.22 Although PCR is considered the gold standard for carbapenemase detection,16 most laboratories are not able to perform this methodology due to costs and the special equipment required. The methodologies evaluated in this study provide reliable results in a single workday. The carbapenemase detection might also be done directly from clinical samples, as described by Dortet et al.18
In summary, the Blue-Carba presented the highest sensitivity and, therefore, can be considered the best test to be used as a screening phenotypic methodology, considering that the misdetection of carbapenemase producers has a greater impact for clinicians than a false positive result, and differences observed between sensitivity values are much greater than the differences observed in specificity. On the other hand, CIM might be the easiest test to perform, as it does not require any special reagent and it is easier to be interpreted. The early detection of carbapenemases helps to establish infection control measures and may prevent carbapenemases to spread reducing the risk of healthcare associated infections and therapeutic failure.
Conflicts of interestThe authors declare no conflicts of interest.