Vulvovaginal candidiasis affects women of reproductive age, which represents approximately 15–25% of vaginitis cases. The present study aimed to isolate and characterize yeast from the patients irrespective of the presentation of clinical symptoms. The isolates were subjected to in vitro susceptibility profile and characterization by molecular markers, which intended to assess the distribution of species. A total of 40 isolates were obtained and identified through the CHROMagar, API20aux and by ITS and D1/D2 regions sequencing of DNAr gene. Candida albicans strains were genotyped by the ABC system and the isolates were divided into two genotypic groups. The identity of the C. albicans, C. glabrata, C. guilliermondii, C. kefyr and Saccharomyces cerevisiae isolates was confirmed by the multilocus analysis. The strains of Candida, isolated from patients with complications, were found to be resistant to nystatin but sensitive to fluconazole, amphotericin B and ketoconazole, as observed by in vitro sensitivity profile. The isolates from asymptomatic patients, i.e., the colonized group, showed a dose-dependent sensitivity to the anti-fungal agents, fluconazole and amphotericin B. However, the isolates of C. albicans that belong to distinct genotypic groups showed the same in vitro susceptibility profile.
Vulvovaginal candidiasis (VVC) is a primary opportunistic mycosis or secondary with endogenous or exogenous characteristics. It is also classified as a sexually transmitted disease (STD) and is caused by different species of Candida.1,2 The disease is characterized by inflammation of the genital mucosa as a response to the yeast proliferation.3
The genus Candida includes approximately 300 heterogeneous species with different morphological and functional features, and is currently found as a part of the normal flora in skin, digestive tract and mucous membrane, including the human genito-urinary tract.4 Predominantly, VVC is caused by C. albicans and its prevalence can reach 85–95%.1 However, infections caused by other species such as C. tropicalis, C. glabrata, C. krusei, C. parapsilosis, C. kefyr and C. lusitaniae have been reported as well.1,4,5 According to literature these species are part of the vaginal mucous microbiota and they are present in 20–80% of healthy adult population, with clinical manifestations in 10% of pre-menopausal patients, 5–10% in menopausal and 30% of pregnant women.6,7
Vulvovaginal infection, caused by Candida spp., affects women of reproductive age representing approximately 15–25% of the vaginitis cases.8 These microorganisms usually remain hosted in the vaginal mucous only as colonizers; however, under inappropriate conditions the yeast reproduction increases inducing expression of virulence factors, which subsequently affects the mucous membrane, characteristic of the symptomatic VVC.9
Identification of strains that are isolated from VVC is crucial to clarify the distribution of C. albicans in relation to other species of Candida genus in different populations with manifestations of the infection. In clinical practice, the yeast identification is based on morphological and biochemical markers, including the automated methods.10,11 However, not all the species are precisely identified by such procedures. Therefore, molecular markers based on the sequencing of variable domain (D1/D2) from the 26S region and internal transcribed spacers (ITS) of the RNA gene were utilized in the present study to enable identification and detection of various strains.12
VVC is not a notified disease and generally the drug treatment is recommended based on the clinical diagnosis. Epidemiological molecular studies are relevant in context of establishment of species prevalence, elucidation of virulence factors and mechanisms of drug resistance so as to support the treatment protocols.13
A few studies have focused on the correlation of antifungal susceptibility with clinical results in VVC.14 In spite of a considerable enhancement in the resistance profile among the various Candida species, fluconazole is still widely used for treatment of VVC.1 Since it has been noticed that C. albicans displays a variable sensitivity to azoles derivatives, it seems crucial to identify its sensitivity profile against various drugs for a better therapeutic conduct.15
In view of such grounds, the current work aimed to evaluate in vitro susceptibility and molecular characterization of yeast from genus Candida that were isolated from the patients with infection and the patients with no clinical symptoms, for elucidation of epidemiological aspects of vulvovaginal candidiasis.
Materials and methodsTest organismThe present study analyzed vaginal material isolates from the patients assisted by an outpatient clinic of Toco-gynecology at the Clinical Hospital/UFPR, Paraná (Table 1). The study was conducted from November 2011 to October 2012. The research work was approved by the Ethical Committee of Federal University of Paraná Clinical. Samples from 133 women were collected with their consent.
List of reference strains and the clinical isolates.
| Name | Number of reference | Substrate | Geographical indication | GenBank access | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ITS | D1/D1 | ||||
| Candida albicans | CBS 562 | Clinical isolate | Australia | EF567995 | U45776 |
| Candida dubliniensis | CBS 7987 | Clinical isolate | Japan | AB035589 | U57685 |
| Candida inconspícua | CBS 180 | Clinical isolate | Australia | AJ853766 | U71062 |
| Candida intermedia | CBS 572 | Clinical isolate | Australia | EF568011 | U44809 |
| Candida glabrata | CBS 138 | – | Ireland | AY198398 | U44808 |
| Candida haemulonii | CBS 5149 | – | Spain | JX459660 | U44812 |
| Candida tropicalis | CBS 94 | Clinical isolate | Japan | AB437068 | U45749 |
| Clavispora lusitaniae | CBS 6986 | Urine | Bulgaria | EF568049 | U44817 |
| Debaryomyces carsonii | CBS 2285 | Clinical isolate | USA | AJ853767 | U45743 |
| Kluyveromyces marxianus | CBS 712 | Clinical isolate | Australia | EF568057 | U94924 |
| Kluyveromyces lactis | CECT1961 | Environmental | USA | AJ401704 | U94922 |
| Meyerozyma guilliermondii | CBS 2030 | Clinical isolate | Australia | EF568003 | U45709 |
| Pichia fermentans | L1B | Environmental isolates | UK | FJ713081 | U75726 |
| Pichia membranifaciens | 23 | – | Spain | JQ410476 | AJ508586 |
| Pichia segobiensis | CECT 10-210 | – | Spain | DQ409166 | U45742 |
| Torulaspora delbrueckii | CBS 1146 | Clinical isolate | Australia | EF568083 | AJ508558 |
| Saccharomyces cerevisiae | NRRL Y-12632 | – | USA | AM900404 | AY048154 |
| Schizosaccharomyces pombe | NRRL Y-12796 | – | USA | AY251633 | U40085 |
| Candida glabrata | HC01 | Cervicovaginal contents | Brazil | KJ651873 | KJ624025 |
| Saccharomyces cerevisiae | HC02 | Cervicovaginal contents | Brazil | – | KJ624026 |
| Candida albicans | HC03 | Cervicovaginal contents | Brazil | KJ651903 | KJ624027 |
| Candida albicans | HC04 | Cervicovaginal contents | Brazil | KJ651904 | KJ624028 |
| Candida albicans | HC05 | Cervicovaginal contents | Brazil | KJ651905 | KJ624029 |
| Candida albicans | HC06 | Cervicovaginal contents | Brazil | KJ651906 | KJ624030 |
| Candida glabrata | HC07 | Cervicovaginal contents | Brazil | KJ651907 | KJ624031 |
| Candida guilliermondii | HC08 | Cervicovaginal contents | Brazil | KJ651908 | KJ624032 |
| Candida kefyr | HC09 | Cervicovaginal contents | Brazil | KJ651909 | KJ624033 |
| Candida glabrata | HC10 | Cervicovaginal contents | Brazil | KJ651910 | KJ624034 |
| Candida albicans | HC11 | Cervicovaginal contents | Brazil | KJ651874 | KJ624035 |
| Candida albicans | HC12 | Cervicovaginal contents | Brazil | KJ651875 | KJ624036 |
| Candida albicans | HC13 | Cervicovaginal contents | Brazil | – | KJ624037 |
| Candida albicans | HC14 | Cervicovaginal contents | Brazil | KJ651876 | KJ624038 |
| Candida albicans | HC15 | Cervicovaginal contents | Brazil | KJ651877 | KJ624039 |
| Candida albicans | HC16 | Cervicovaginal contents | Brazil | KJ651878 | KJ624040 |
| Candida albicans | HC17 | Cervicovaginal contents | Brazil | KJ651879 | KJ624041 |
| Candida albicans | HC18 | Cervicovaginal contents | Brazil | KJ651880 | KJ624042 |
| Candida albicans | HC19 | Cervicovaginal contents | Brazil | KJ651881 | KJ624043 |
| Candida albicans | HC20 | Cervicovaginal contents | Brazil | KJ651882 | KJ624044 |
| Candida albicans | HC01IC | Cervicovaginal contents | Brazil | KJ651883 | KJ624045 |
| Candida albicans | HC02IC | Cervicovaginal contents | Brazil | KJ651884 | KJ624046 |
| Candida dubliniensis | HC03IC | Cervicovaginal contents | Brazil | KJ651885 | KJ624047 |
| Candida albicans | HC04IC | Cervicovaginal contents | Brazil | KJ651886 | KJ624048 |
| Candida albicans | HC05IC | Cervicovaginal contents | Brazil | KJ651887 | KJ624049 |
| Candida albicans | HC06IC | Cervicovaginal contents | Brazil | KJ651888 | KJ624050 |
| Candida albicans | HC07IC | Cervicovaginal contents | Brazil | KJ651889 | KJ624051 |
| Candida albicans | HC08IC | Cervicovaginal contents | Brazil | KJ651890 | KJ624052 |
| Candida albicans | HC09IC | Cervicovaginal contents | Brazil | KJ651891 | KJ624053 |
| Candida albicans | HC10IC | Cervicovaginal contents | Brazil | KJ651892 | KJ624054 |
| Candida albicans | HC11IC | Cervicovaginal contents | Brazil | KJ651893 | KJ624055 |
| Candida albicans | HC01INC | Cervicovaginal contents | Brazil | KJ651894 | KJ624056 |
| Candida albicans | HC02INC | Cervicovaginal contents | Brazil | KJ651895 | KJ624057 |
| Candida albicans | HC03INC | Cervicovaginal contents | Brazil | KJ651896 | KJ624058 |
| Candida albicans | HC04INC | Cervicovaginal contents | Brazil | KJ651897 | KJ624059 |
| Candida albicans | HC05INC | Cervicovaginal contents | Brazil | KJ651898 | KJ624060 |
| Candida albicans | HC06INC | Cervicovaginal contents | Brazil | KJ651899 | KJ624061 |
| Candida albicans | HC07INC | Cervicovaginal contents | Brazil | KJ651900 | KJ624062 |
| Candida albicans | HC08INC | Cervicovaginal contents | Brazil | KJ651901 | KJ624063 |
| Candida albicans | HC09INC | Cervicovaginal contents | Brazil | KJ651902 | KJ624064 |
(–) data not provided; HC: clinical hospital/UFPR; C: colonized; IC: complicated infection; INC: non-complicated infection.
The study enrolled women, who were aged between 18 and 56 years, with or without VVC clinical symptoms, and who had not been administered any drug treatment in the last six months before collection of the samples. The patients were divided into two groups: colonized patients (without clinical symptoms) and infected patients.1 The infected patients presented three or more of the following clinical symptoms: typical discharge, vaginal itching, vulvovaginal burning, dysuria and dyspareunia. Infected patient group was sub-divided into two sub-groups: (i) complicated – which included women with a history of recurrence infection; and (ii) uncomplicated – patients with sporadic episodes of the infection. The exclusion criteria were age (under 18 and over 56), pregnancy and women with immunosuppressive diseases and under treatment.
Collection, isolation and phenotypic identificationThe samples were collected by swabs, and each sample was sowed on Sabouraud Dextrose Agar medium followed by incubation at ±30°C for a period of 48–120h as per the growth parameters of each isolate. A presumptive identification of isolates was done by CHROMagar at 37°C for 48h.16 Some of the isolates were identified by the API 20 AUX system (BioMérieux, France).
Molecular characterization of Candida isolatesDNA from the isolates was extracted by physical maceration of the samples in a mixture of silica/celite (2:1) in CTAB (cetyltrimethylammonium bromide). The isolated DNA was precipitated by CIA (acidic solution of chloroform-isoamyl alcohol) followed by sequencing on ABI3500 sequencer.17 For ITS sequencing, the following primers were used: ITS1 (5′-TCCGTAGGTGAACCTGCGG-3′) and ITS4 (5′-TCCTCCGCTTATTGATATGC-3′) and the reaction conditions of sequencing were as follows18: one cycle at 94°C for 2min, followed by 30 cycles at (94°C for 30s, 56°C for 1min, 72°C for 1min) and a final extension at 72°C for 3min.17 For amplification of D1/D2 region, the primers NL-1 (5′-GCATATCAATAAGCGGAGGAAAAG-3′) and NL-4 (5′-GGTCCGTGTTTCAAGACGG-3′) were used following the same reaction conditions, as listed above.19
For ABC genotyping of C. albicans, the primers CA-int-L (5′-ATAAGGGAAGTCGGCAAAATAGATCCGTAA-3′) and CA-int-R (5′-CCTTGGCTGTGGTTTCGCTAGATAGTAGAT-3′) were used.20 The genotyping was based on the presence or absence of a DNA insert, which codes for the ribosomal 26S RNA, dividing C. albicans in four groups20: A (C. albicans – 450bp), B (C. albicans – 840bp), C (C. stellatoidea – 840bp) and D (C. dubliniensis – 1080bp).
Alignment and phylogenetic constructionThe obtained sequences were edited using the Staden program version 1.6, and were compared by the BLAST program for detection of the similarities using reference sequences available in the data bank (NCBI, National Center for Biotechnology Information – http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/).21,22 The Mafft program (http://mafft.cbrc.jp/alignment/server/) was used for the alignment; and visual inspection was done by MEGA 5.1 version.23 Forty sequences of Candida isolates were submitted for phylogenetic analysis using Schizosaccharomyces pombe strain U40085 as outgroup.20 The Maximum Likelihood phylogenetic tree was built with 100 bootstraps, based on the evolutionary model Tamura-3 parameters with using 5.1 version of the MEGA software for final editing.23
In vitro susceptibility testsThe in vitro susceptibility tests were done by micro-dilution method of broth, as per the Norm M27-A3 recommendations provided by the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute.24 The antifungals used were amphotericin B (Sigma–Aldrich 110 Química, Madrid, Spain), ketoconazole (Pharma Nostra, Brazil), itraconazole (Fragon), fluconazole (Pfizer, Madrid, Spain) and nystatin (Pharma Nostra, Brazil). The samples were diluted in RPMI (Roswell Park Memorial Institute Medium)-1640 medium (Sigma) and incubated at 37°C for 48h. According to the CLSI criteria, the sensitivity profile is classified as sensitive, dose-dependent sensitivity and resistant.
ResultsA total of 40 isolates were obtained from 133 cervicovaginal samples, which were previously identified by CHROMagar and API 20AUX systems. On the basis of ITS and D1/D2 sequences, the isolates could be attributed to the genera Candida and Saccharomyces (Table 1). Among the isolates studied, 20 belonged to the colonized group, 11 were from the complicated infection group and 9 were from the uncomplicated infection group.
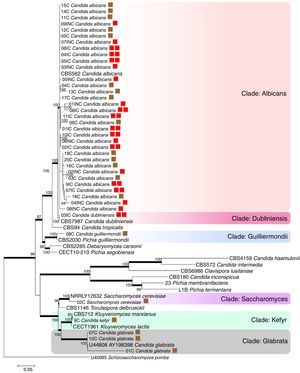
A tree was constructed using maximum likelihood analysis and the evolutionary model Kimura 2-parameter with 100 bootstraps. A total of 1959 sites were evaluated, of which, 786 were conserved sites, 1092 were variable sites, 712 sites provided parsimonious information (pi), and 361 were unique sites. The empirical basis frequencies were pi (A): 0.225836 pi (C): 0.283009 pi (G): 0.238533, pi (t) 0.252622. The phylogenetic tree was generated by using 18 strains as references, which included various types of strains of Candida species, Kluyveromyces marxianus, K. lactis, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Torulaspora delbrueckii, keeping Schizosaccharomyces pombe as an outgroup.
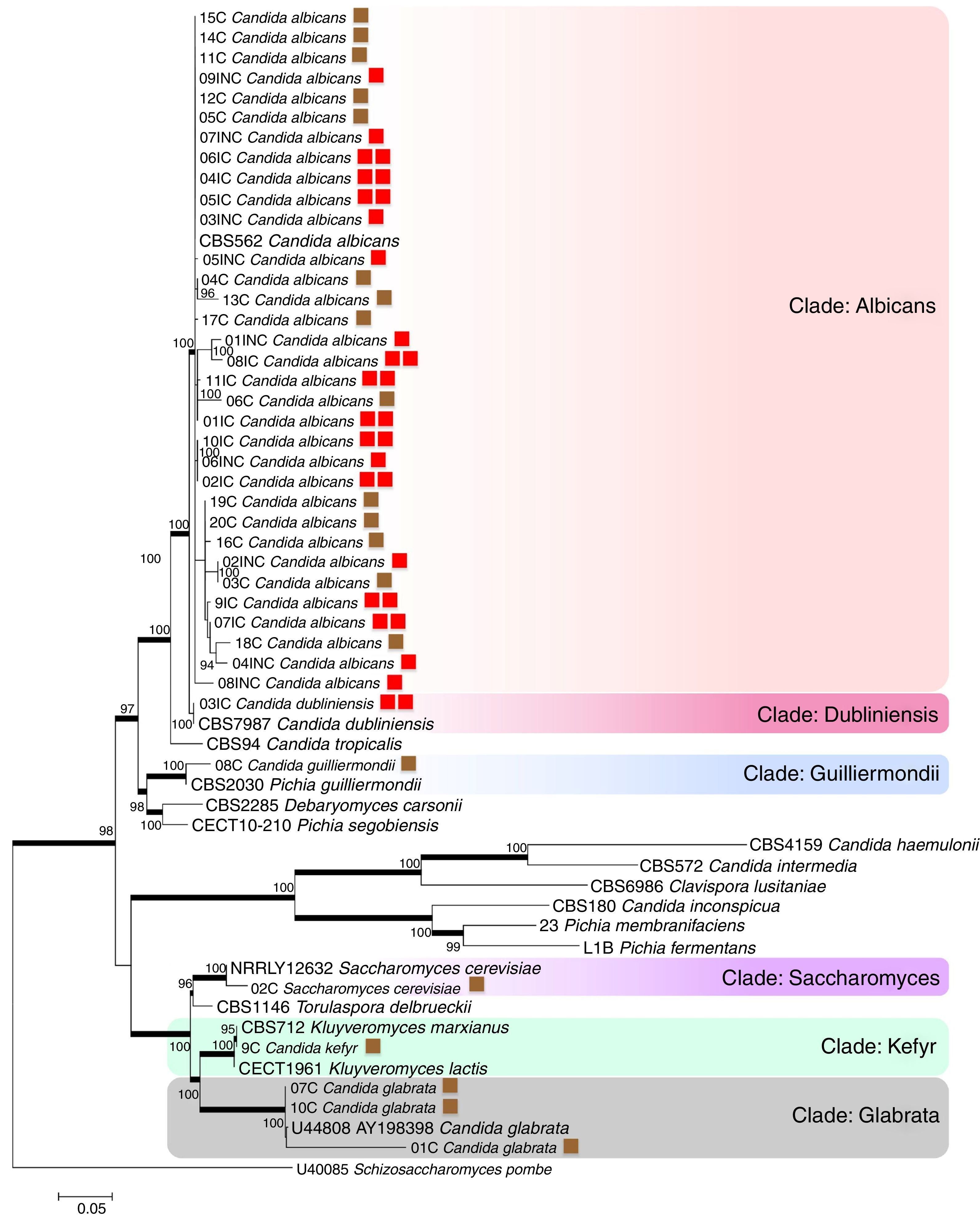
The evaluated VVC isolates were identified to be C. albicans, C. dubliniensis, C. guilliermondii, C. kefyr, Saccharomyces cerevisiae and C. glabrata and were found to be distributed into six clades supported by bootstrap values (Fig. 1). The phylogenetic data corroborated with the biochemical data, except for the HC03IC isolate that was identified as C. albicans by the API 20AUX system, but as C. dubliniensis by the phylogenetic analysis (Fig. 1).
The phylogenetic tree of maximum likelihood based on the alignment of the entire region of its1/its2 and D1/D2 was built using 100 bootstrap, using the evolutionary model Tamura-3 parameters with program Mega version 5.1. Schizosaccharomyces pombe was used as an outgroup. The tree showed 6 clades (Albicans; Dubliniensis; Guilliermondii, Saccharomyces; Kefyr; Glabrata) diversified according to the isolated species. For a thorough understanding, the evaluated groups in this study are represented by colored squares for discernment: the brown square refers to the colonized group; one red square indicates isolates from the uncomplicated infection group; the two red squares represent the group with complicated infection.
According to the tree, most of the analyzed clinical isolates were identified to be C. albicans, with 33 isolates clustered in Albicans clade (bs, 100%). Analysis revealed that C. albicans isolates could not be separated according to the studied groups, i.e., colonized, complicated, and uncomplicated infection groups. In Guilliermondii clade (bs, 99%), the clinical isolate (HC08C) and P. guilliermondii (NRRL Y-2075) type strain were grouped. The isolate (HC02C) from the colonized group and Saccharomyces cerevisiae type were clustered in Saccharomyces clade (bs, 100%). Kefyr clade consisted of Kluyveromyces marxianus (NRRL Y-8281), Candida kefyr teleomorph strain CBS 712, K. marxianus var. Kluyveromyces lactis strain NRRL Y-8279 and HC09C isolate of C. kefyr. Three isolates were classified into the Glabrata clade (HC01C, HC07C and HC10C), belonging to the colonized group and C. glabrata type (5478) with 100% bootstrap.
Based on the molecular data, amidst the 40 isolates that were obtained from vaginal samples, the most prevalent species was C. albicans (82.5%), followed by C. glabrata (7.5%), C. guilliermondii (2.5%), C. kefyr (2.5%), C. dubliniensis (2.5%) and Saccharomyces cerevisiae (2.5%). Among the colonized group alone, a total of 20 isolates belonging to five different species C. albicans (60%), C. glabrata (25%), C. guilliermondii (5%), C. kefyr (5%) and Saccharomyces cerevisiae (5%) were identified. A total of 9 isolates obtained from the uncomplicated infection group were C. albicans (100%). In the complicated infection group, 11 isolates were from two different Candida species: C. dubliniensis (9.1%) and C albicans (90.9%).
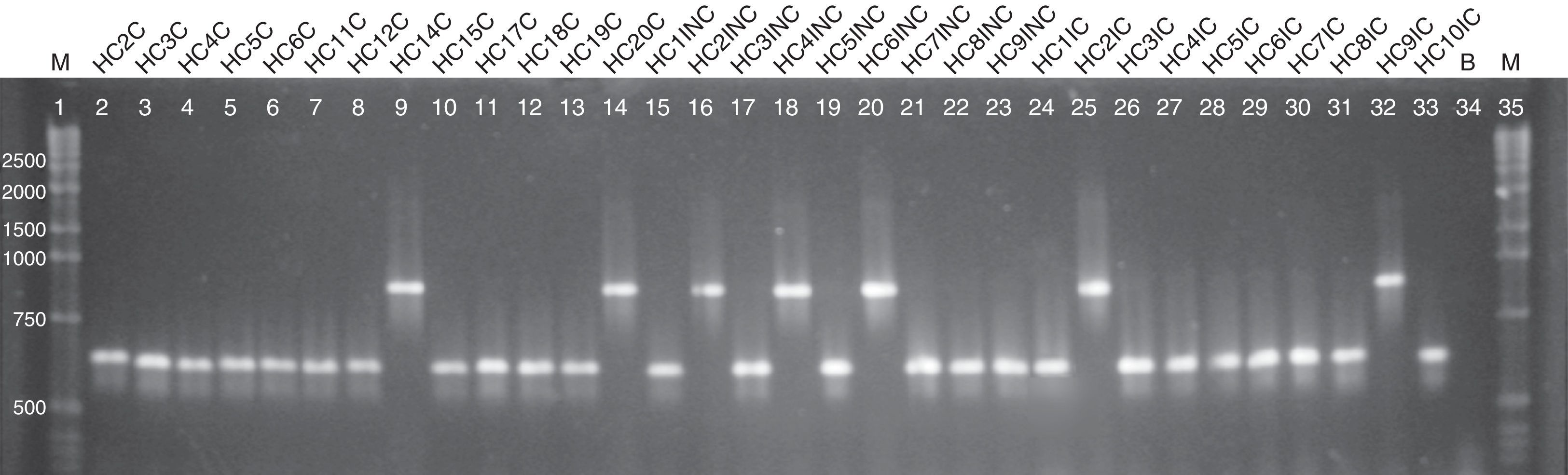
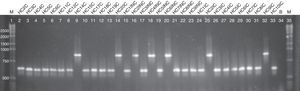
Regarding the ABC genotyping of C. albicans, at least two different genotypes (A and B) were observed, although 25 isolates belonged to type A and 7 isolates to type B, it was not possible to establish a correlation amidst the genotypes identified and the susceptibility profile of the tested drugs (Fig. 2).
Agarose electrophoresis ABC genotyping of the C. albicans from the different studied groups, genotype A (C. albicans – 450bp) and B (C. albicans – 840bp). The lanes 2–14 correspond to the colonized group; 15–23 to the uncomplicated infection group and 24–33 to the complicated infection group. Lane 34 represents a blank; the lanes 1 and 35 indicate standard 1kb molecular weight markers (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, Ca, USA).
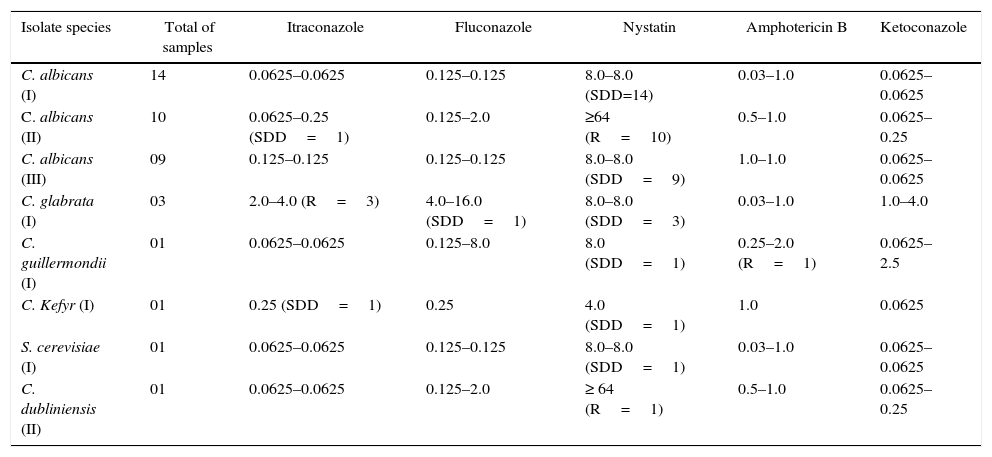
The susceptibility testing results of the studied isolates from different patient groups are summarized in Table 2. In the colonized group (I), all isolates of C. albicans (n=14) showed a dose-dependent sensitivity (SDD) to nystatin (8.0μg/mL) and sensitivity (S) to itraconazole (0.0625μg/mL), fluconazole (0.125μg/mL), amphotericin B (0.03–1.0μg/mL) and ketoconazole (0.0625μg/mL). Three C. glabrata isolates (HC01C, HC02C and HC07C) were resistant (R) to itraconazole (4.0μg/mL), SDD for the fluconazole (4.0–16μg/mL), nystatin (8.0μg/mL) and sensitive to amphotericin B (0.03–1.0μg/mL) and ketoconazole (1.0–4.0μg/mL). The isolate of C. guilliermondii (HC16C) showed SDD to nystatin (8.0μg/mL), resistance to amphotericin B (2.0μg/mL), sensitivity to itraconazole (0.0625μg/mL), fluconazole (0.125μg/mL), and ketoconazole (0.0625μg/mL). C. kefyr (HC09C) presented SDD to itraconazole (0.25), nystatin (4.0μg/mL), and sensitivity for fluconazole (0.25μg/mL), amphotericin B (1.0μg/mL) and ketoconazole (0.0625μg/mL). Furthermore, S. cerevisiae isolate (HC02C) was SDD to nystatin (8.0μg/mL) and sensitive to itraconazole (0.0625μg/mL), fluconazole (0.125μg/mL), amphotericin B (0.03–1.0μg/mL) and ketoconazole (0.0625μg/mL).
Variations in the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of antifungals for the different study groups.
| Isolate species | Total of samples | Itraconazole | Fluconazole | Nystatin | Amphotericin B | Ketoconazole |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C. albicans (I) | 14 | 0.0625–0.0625 | 0.125–0.125 | 8.0–8.0 (SDD=14) | 0.03–1.0 | 0.0625–0.0625 |
| C. albicans (II) | 10 | 0.0625–0.25 (SDD=1) | 0.125–2.0 | ≥64 (R=10) | 0.5–1.0 | 0.0625–0.25 |
| C. albicans (III) | 09 | 0.125–0.125 | 0.125–0.125 | 8.0–8.0 (SDD=9) | 1.0–1.0 | 0.0625–0.0625 |
| C. glabrata (I) | 03 | 2.0–4.0 (R=3) | 4.0–16.0 (SDD=1) | 8.0–8.0 (SDD=3) | 0.03–1.0 | 1.0–4.0 |
| C. guillermondii (I) | 01 | 0.0625–0.0625 | 0.125–8.0 | 8.0 (SDD=1) | 0.25–2.0 (R=1) | 0.0625–2.5 |
| C. Kefyr (I) | 01 | 0.25 (SDD=1) | 0.25 | 4.0 (SDD=1) | 1.0 | 0.0625 |
| S. cerevisiae (I) | 01 | 0.0625–0.0625 | 0.125–0.125 | 8.0–8.0 (SDD=1) | 0.03–1.0 | 0.0625–0.0625 |
| C. dubliniensis (II) | 01 | 0.0625–0.0625 | 0.125–2.0 | ≥ 64 (R=1) | 0.5–1.0 | 0.0625–0.25 |
SDD: sensitivity dose dependent; R: resistant; S: sensitivity; I: colonized group; II: complicated infection group; III: uncomplicated group.
In the complicated infection group (II), one strain of C. albicans isolate (HC01IC) was found to be SDD to itraconazole (0.0625–0.25μg/mL); all isolates (n=10) were resistant to nystatin (≥64μg/mL) and sensitive to fluconazole (0.125–2.0μg/mL), amphotericin B (1.0μg/mL) and ketoconazole (0.0625μg/mL). C. dubliniensis isolate (HC03IC) was resistant to nystatin (≥64μg/mL) and presented sensitivity toward the itraconazole (0.0625μg/mL), fluconazole (0.125–2.0μg/mL), amphotericin B (0.5–1.0μg/mL) and ketoconazole (0.0625μg/mL). Finally, in the uncomplicated infections group (III), all the isolates (n=9) of C. albicans were SDD to nystatin (8.0μg/mL) and sensitive toward itraconazole (0.0625μg/ml), fluconazole (0.125–2.0μg/mL), amphotericin B (0.5–1.0μg/mL) and ketoconazole (0.0625μg/mL).
DiscussionIdentification of Candida species that causes VVC is highly desirable in microbiological practice, as it may help in clarifying the prevalence and incidence of species that affects the susceptible population. Moreover, determination of susceptibility of Candida to the antifungal drugs may be crucial in context of the recurrent clinical forms of VVC. Several studies have demonstrated the occurrence of vulvovaginitis due to Candida species, indicating heterogeneity among isolates from different geographical regions. In the present study, the prevalent species were3,25–27C. albicans, followed by C. glabrata, C. guilliermondii, C. kefyr, C. dubliniensis and Saccharomyces cerevisiae, thereby suggesting an increase of infection by non-albicans Candida. An increase in infections that are caused by non-albicans Candida has been registered, although C. albicans is still the most isolated species in VVC clinical cases.13,28–31 Furthermore, the cultural and ethnic differences may also influence the isolation rate of yeast from vulvovaginitis samples.32,33 The lack of data on epidemiology and genetic variability reinforces the importance of epidemiological studies by molecular methods.6,27,34–36
The colonized group investigated in the current study presented a wide diversity of species such as C. albicans, C. glabrata, C. guilliermondii, C. kefyr and Saccharomyces cerevisiae. In addition, C. albicans was found to be prevalent (n=19) in the infection group and C. dubliniensis (n=1) isolates were observed only in the complicated infection group (Table 2). The microbiota species found in colonized women are the same as reported in VVC.1,4,27,30,35 Vaginitis caused by S. cerevisiae is rare and it has been isolated from an asymptomatic patient.37,38 This corroborates with the findings of the present study.
The VVC Candida albicans isolates, analyzed by us, were clustered into a single clade, indicating a monophyletic group (Fig. 1), which is in concordance with the data already reported by several authors.31,39 The strain, identified as C. albicans (HC03IC) by biochemical test, proved to be C. dubliniensis according to the phylogenetic analysis. A lack of correlation between the phenotypic and molecular identification of the samples can be justified by the limitations of the commercial identification system, which do not allow distinguishing the yeast species, which have minor phenotypic differences.40,41 Therefore, multilocus analyses are needed in order to identify Candida species.31 In the ABC genotyping, two different genotypes among C. albicans isolates were detected. The genotype A was observed in 75.7% of the isolates, and the isolates of genotype B were present in all the analyzed groups. However, it had a higher occurrence in the uncomplicated infected group (Fig. 2). It has been reported that the candidiasis that is caused by C. albicans of genotype B has a higher tendency for persistent infections, though further studies with larger populations for a better assessment are required.36
In the current analysis, all the C. albicans isolates from the complicated group, regardless of genotype, were resistant to nystatin and susceptible to other tested antifungals, except for the isolate HC04IC that showed SDD to fluconazole. In the uncomplicated infections group, the isolates of C. albicans were SDD to nystatin and susceptible to other tested antifungals. The same was observed in the isolates from the group of colonized patients. Concerning the non-albicans Candida species, the isolate of C. dubliniensis was resistant only to nystatin, the C. glabrata isolates were resistant to itraconazole and SDD to fluconazole and nystatin. These results contrast from the previous reports that regarded C. glabrata isolates as resistant and SDD to fluconazole.42 Besides, C. kefyr strain presented SDD to itraconazole and nystatin, and a similar susceptibility profile was previously reported.10 In other studies, similar results were obtained, reporting that VVC species strains of genus Candida presented resistance and also a high frequency of SDD for nystatin and sensitivity to others tested drugs.26,35,43
The isolate of C. guilliermondii showed SDD to nystatin and resistance to amphotericin B. According to the literature, the treatment is problematical due to a low sensitivity for some antifungal classes, especially for fluconazole, itraconazole and amphotericin B; and VVC infections caused by C. guilliermondii are rare.2 Furthermore, we obtained an isolate of S. cerevisiae SDD to nystatin, which differed from the data previously reported for this species, which demonstrated that S. cerevisiae isolates were resistant to fluconazole, posaconazole, and itraconazole.44
There are several factors that can influence the clinical response to treatment of VVC, as evident from different reports showing variation in the in vitro susceptibility and in vivo response to the drug.39,45 Through in vitro susceptibility testing, it was observed that all the isolates were sensitive to ketoconazole, although fluconazole remains the drug of choice for VVC treatment. Such results indicate that the susceptibility profile for the isolates may not be a factor related to the recurrence of the disease. Therefore, it may be concluded that the molecular analysis provides accurate identification of Candida species isolated from patients with VVC. Hence, our findings demonstrated the importance of molecular tools for identification of the isolates and also to elucidate the epidemiology of VVC.
Conflicts of interestThe authors declare no conflicts of interest.
We would like to thank the staff of the Diagnostic Unit of Clinical Hospital and the Microbiology and Molecular Biology laboratory at UFPR for their technical assistance and the financial support provided by the Brazilian Federal Agencies: CAPES (Brazilian Federal Agency for Support and Evaluation of Graduate), CNPq (National Counsel of Technological and Scientific Development) and the Parana's state agency Fundação Araucaria.