Papillary fibroelastomas are benign tumours, usually found on cardiac valves. They are attached to the aortic valve in 90% of cases. Even though benign and mostly asymptomatic, right-sided tumours can cause pulmonary embolism, while left-sided tumours can cause serious complications. We report a 76-year-old woman treated initially for a suspicious infective endocarditis of the aortic valve, in whom papillary fibroelastoma was histologically confirmed, with no evidence of infective endocarditis.
Los fibroelastomas papilares son tumores benignos que, generalmente, se encuentran en las válvulas cardiacas. El 90% de ellos están unidos a la válvula aórtica y, aunque estos sean tumores benignos, la mayoría pueden ser asintomáticos. Los del lado derecho pueden causar embolia pulmonar, mientras que los del lado izquierdo pueden ocasionar complicaciones graves. Presentamos el caso de una mujer de 76 años tratada por sospechas de endocarditis infecciosa de la válvula aórtica, a quien se le confirmó patológicamente el fibroelastoma papilar, sin evidencia de endocarditis infecciosa.
Papillary fibroelastomas are benign tumors that can develop on any endocardial surface.1,2 However, they are usually found on the cardiac valves, and most frequently on the aortic valve.3 Even though these tumors are categorized as benign and are usually asymptomatic, those in the right side of the heart can cause pulmonary embolism, while those in the left side can cause serious complications.4,5
Case reportWe report a case of a 76-year-old woman who had a permanent pacemaker since October 2018 for sinus node dysfunction, and who presented at a regional hospital with a one-week history of fever associated with palpitations. Her first transthoracic echocardiography showed an image of suspicious vegetation. And during her hospitalization she received a one-week course of antibiotics to treat a culture-negative endocarditis.
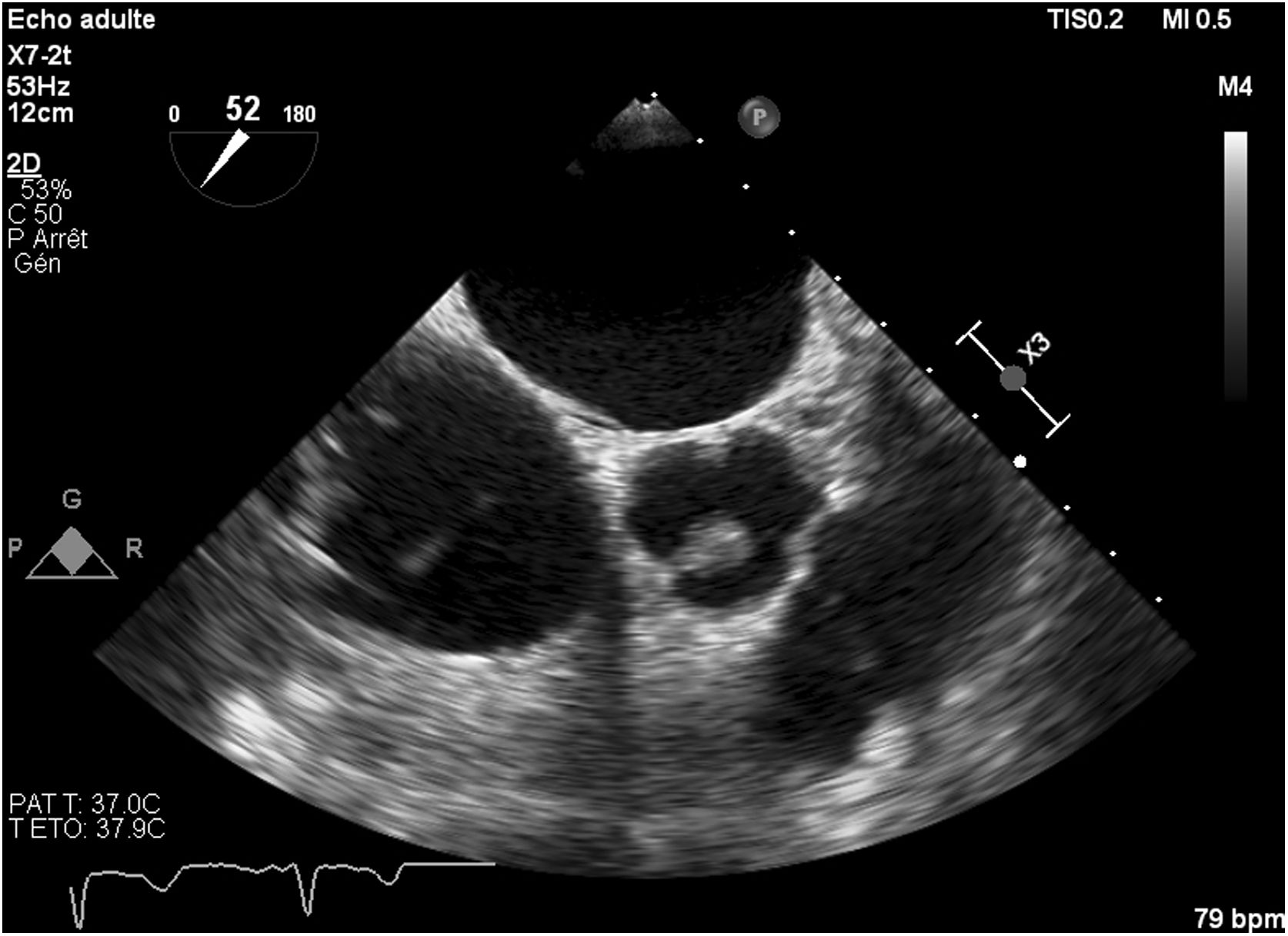
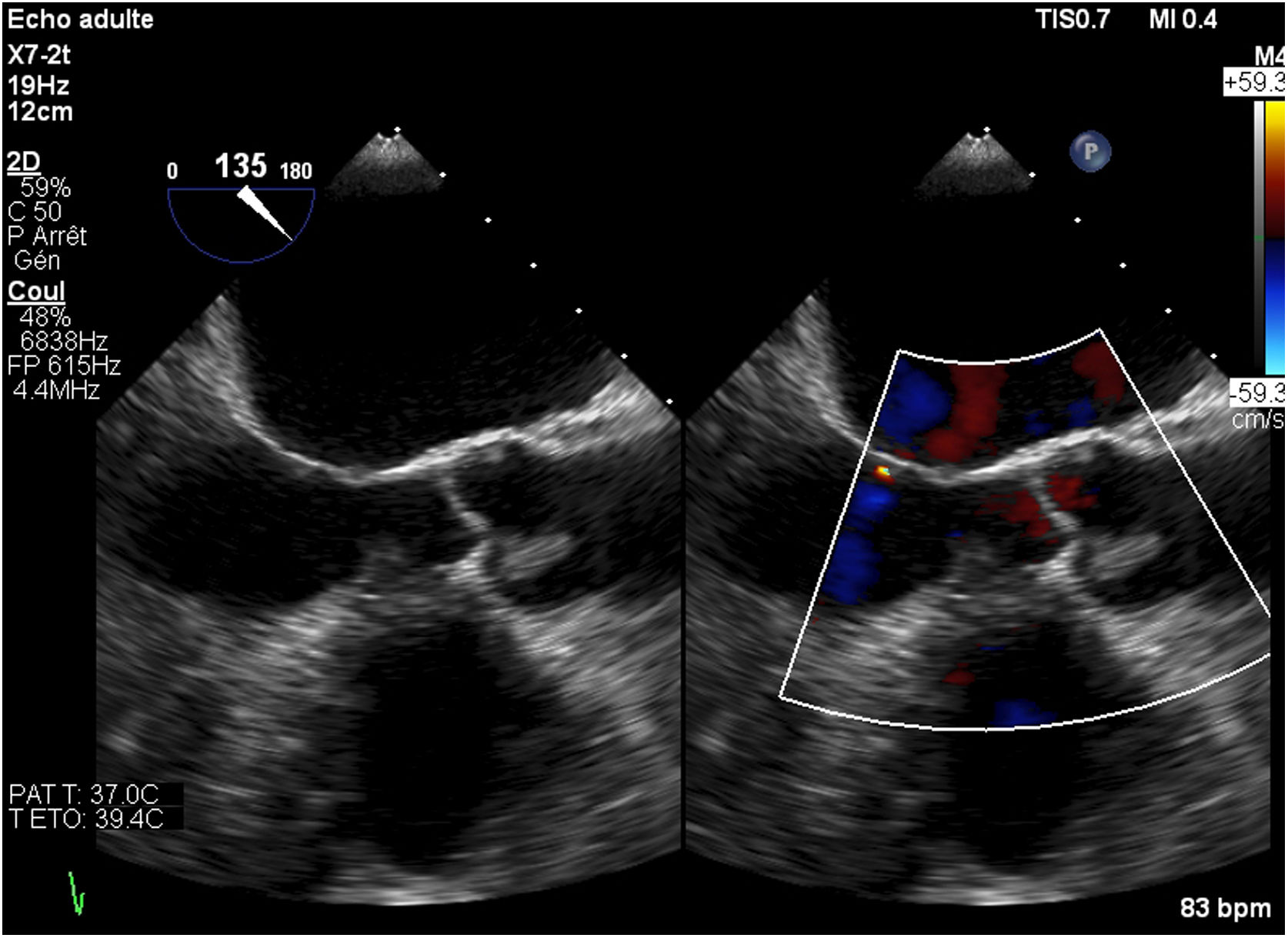
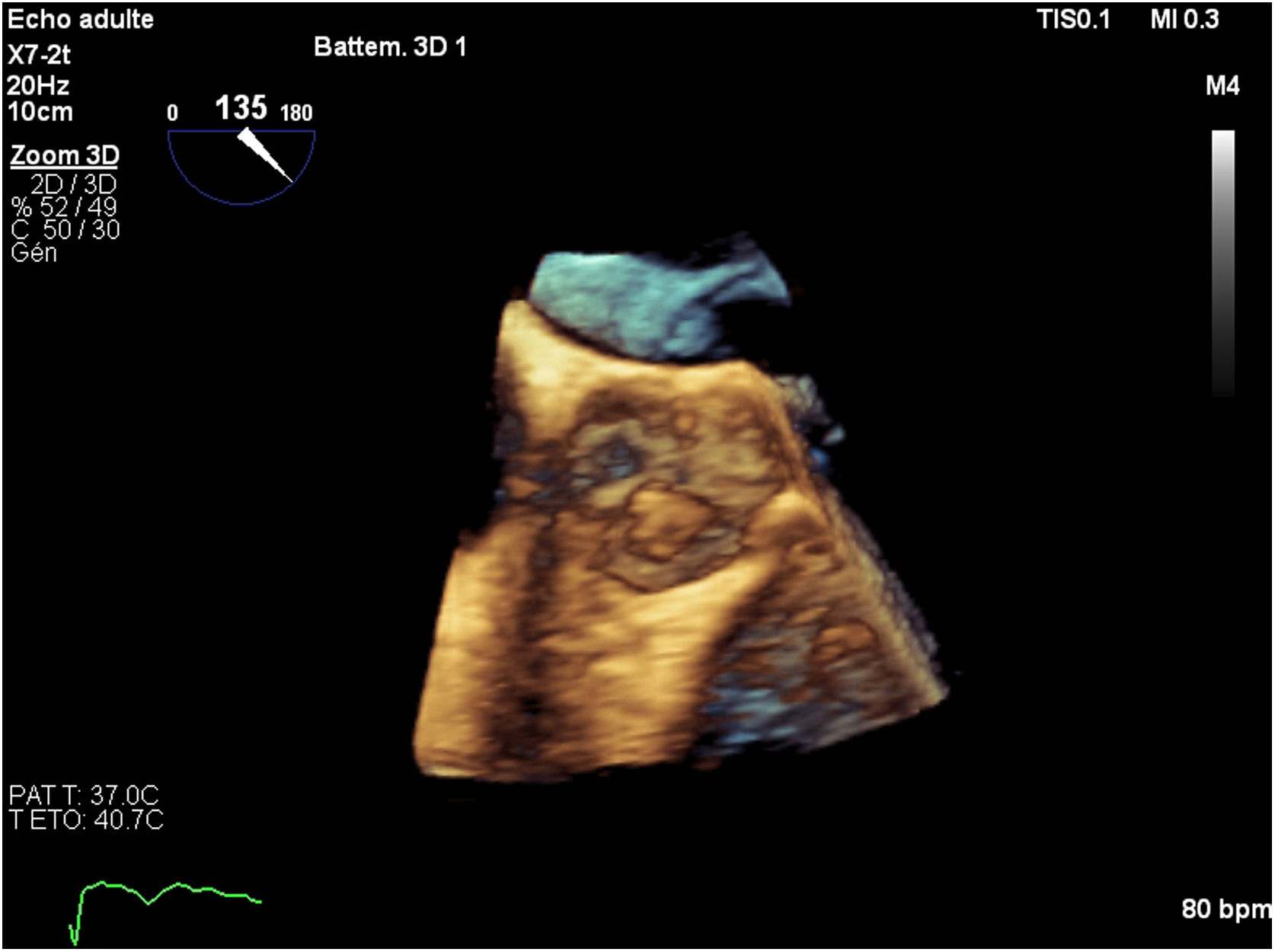
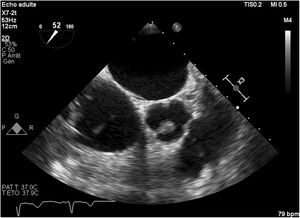
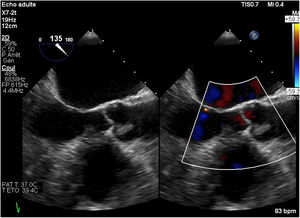
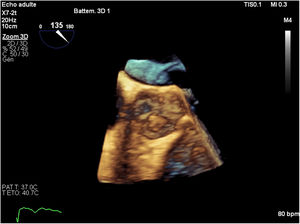
Then, she was transferred to our hospital for further investigations. In our department, the transesophageal echocardiography revealed a mobile, hypoechoic, heterogeneous mass, oval shaped, appended on the aortic surface of the right coronary cusp, measuring 14×8mm. This mass was compatible with both papillary fibroelastoma and vegetation (Figs. 1–3). Fortunately, no other mass was found on the leads of the pacemaker.
Based on medical history, clinical exam, echocardiographic image, negative blood cultures, and laboratory tests findings, the most likely diagnosis was a culture-negative endocarditis, a fibroelastoma of the aortic valve, or both.
In order to reduce the risk of embolism as well as to confirm an etiological diagnosis we scheduled an emergency surgical removal of the mass.
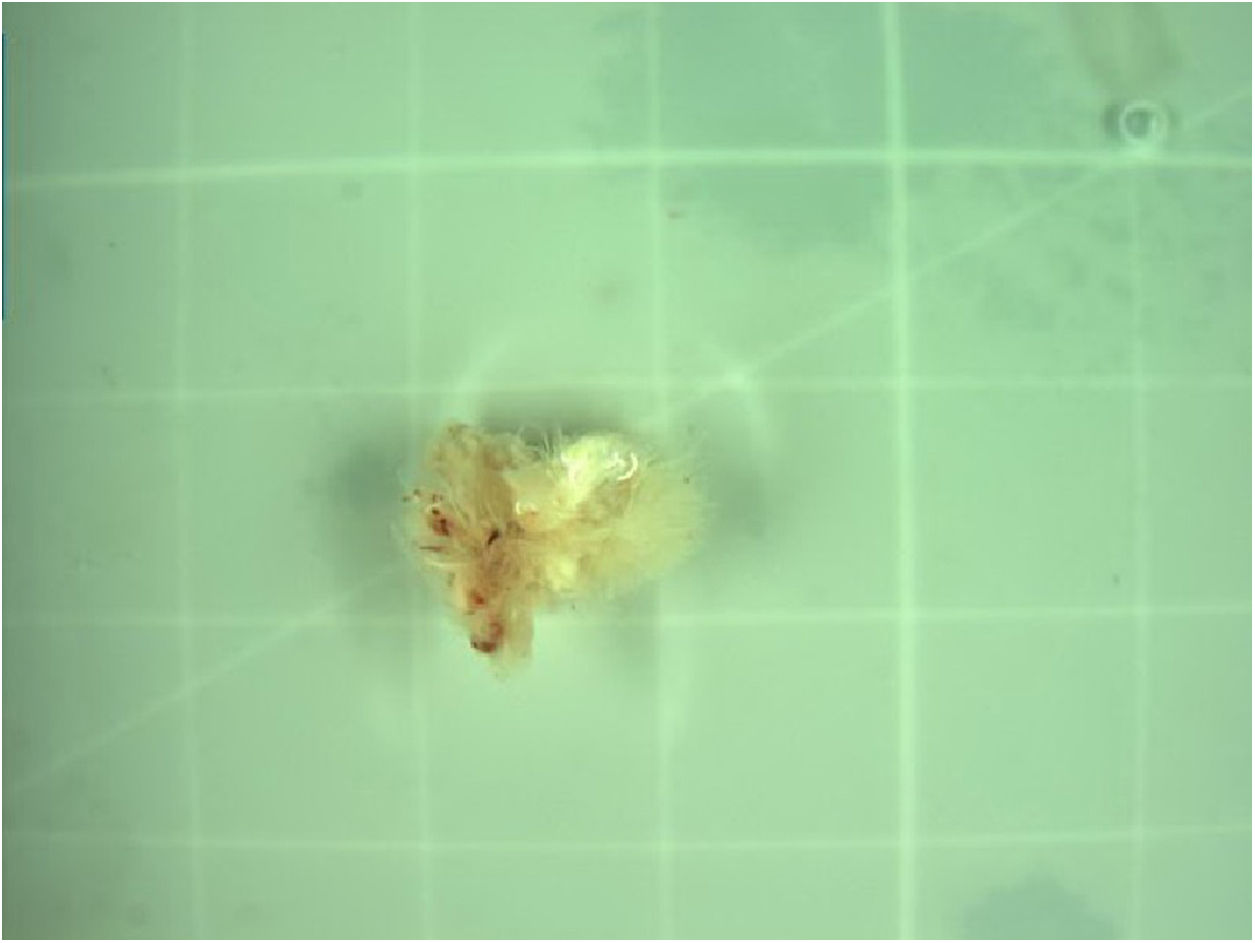
We initiated cardiopulmonary bypass by cannulating the distal ascending aorta and the right atrium with a dual stage venous cannula. After cross-clamping of the aorta, we injected a retrograde cold crystalloid cardioplegia, then we made a transverse aortotomy to expose the mass, which was soft, measuring 10mm and adhering to the free edge of the right coronary cusp of the aortic valve. We excised it carefully from the surface of the leaflet, ensuring that no mass was left behind. Then, we inspected the ascending aorta and the left ventricle for other tumors or vegetations.
The absence of aortic valve dysfunction was confirmed intraoperatively before the aortotomy was closed. After deairing maneuvers, we released the aortic cross-clamp. The patient's body was rewarmed, spontaneous cardiac contractility resumed with sinus pause as it was preoperatively, requiring the reactivation of the pacemaker, then the patient was successfully weaned from cardiopulmonary bypass.
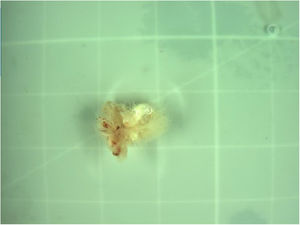
The intraoperative transesophageal echocardiography showed the absence of any residual mass, without any leakage of the aortic valve. Histological and microbiological investigations confirmed the nature of the papillary fibroelastoma of the mass, with no evidence of infective endocarditis (Fig. 4).
The follow-up was uneventful, and no residual or recurrent tumor had been seen in the follow-up transthoracic echocardiography.
DiscussionPapillary fibroelastomas are small benign tumors that represent 10% of all cardiac tumors,1 and measure 9–12mm.2 Histologically, their constituting layers have a similarity to those of the chordae tendineae.6 They can develop on any endocardial surface.7 90% of the cases are attached to the aortic valve.3 Even though they are categorized as benign tumors and in the majority of cases they are asymptomatic. Those in the right-side of the heart can cause pulmonary embolism, while those in the left-side can cause serious complications, such as systemic embolic events, stroke, and acute myocardial infarction.4,5
The mechanism of these complications could be either by the fragmentation of the papillary fibroelastoma, or by the disintegration of the thrombi that have adhered to the surface of these tumors. Also, there is another mechanism that is the prolapse of the tumor itself into any coronary ostium leading to an acute myocardial infarction.4,5,8
The transesophageal echocardiography is superior to the transthoracic one in the detection, the localization and the description of the cardiac masses and it has better visualization of valves and cardiac chambers.9 Typically, the papillary fibroelastoma is seen as2:
- -
Small round or oval tumor of 9–12mm in diameter.
- -
Homogeneous speckled texture.
- -
Stippling along its edges.
- -
Mobile if it has a pedicle.
- -
And 50% of them have small stalks.
Papillary fibroelastomas can be confused with other cardiac tumors, vegetations, thrombi, valvular calcifications, Libman–Sacks and Lambl's excrescences, leading to an incorrect therapeutic management.
Concerning cardiac tumors, there are several ones that can mimic papillary fibroelastomas, such as myxoma that is a multi-lobed one and that is located on the cardiac walls, mostly in the left atrium, and in the interatrial septum. Histologically, it has polygonal myxoma cells and multiple blood vessels within the papillae.10
The atrial thrombi are usually located in the atrial appendage, and mostly associated with atrial fibrillation, and atrial dilatation. However, the ventricular ones are typically located in the ventricular aneurysm, in the akinesis wall of the infarcted myocardium, and in any cardiac wall in case of the cardiomyopathy. In this case the echocardiography shows an irregular border, and the absence of a pedicle.
As in our case the principal differential diagnosis of papillary fibroelastoma was a vegetation, which made the therapeutic management challenging. It is known that vegetations are usually located in cardiac valves, and they are usually associated with valvular destruction.5 Also, there is a usual association between clinical signs of endocarditis and valvular destruction. Thus, the echocardiography may show a mass that changes in appearance over time and may reveal signs of valvular regurgitation.11 We should note that the fever identified in our patient during the preoperative period remained without any explanation, regardless of the tests that were done, however the association between the endocarditis and the papillary fibroelastoma was not totally excluded.
Surgical excision is the sole curative treatment of papillary fibroelastoma,12 which was performed for the first time by Lichtenstein in 1979.13 During the procedure all cardiac chambers and valves must be inspected to eliminate other localizations of the tumor, and sometimes to look for the association of a papillary fibroelastoma with vegetations. Furthermore, valvular regurgitation can be caused either by the tumor itself or by the surgeon after the excision. In this matter, the surgical procedure must be completed either by valvular repair, every time the valve is repairable, otherwise valvular replacement can be done.14
For symptomatic patients, surgery is highly recommended, whereas for asymptomatic patients, surgery should be done only if the papillary fibroelastoma is mobile. If not, a clinical and an echocardiographic follow-up for the patient is mandatory until the symptoms develop or the tumor becomes mobile. However, none of these recommendations are based on a randomized controlled study.2,14
ConclusionPapillary fibroelastoma of cardiac valves can mimic vegetation making it difficult to differentiate the two. Surgical removal of the mass is the only curative treatment. It reduces the risk of tumoral complications and confirms the etiological diagnosis.
Ethics approvalIRB and clinical trial registration approval are not required for case reports.
Constant of the use of medical data is obtained verbally and in written form from the patient.
FundingThe authors report no involvement in the research by the sponsor that could have influenced the outcome of this work.
Conflicts of interestThe authors certify that there is no conflict of interest with any financial organization regarding the material discussed in the manuscript.