Liposarcomas (LS) are the most frequent type of soft tissue sarcoma in adults.1 Their etiopathogenesis is unknown and, although they can develop in any adipose tissue, their primary location shows a predilection for certain anatomical regions.1
Occasionally, more than one synchronous or metachronous LS may present in a patient in non-visceral regions. The unusual peculiarity of the natural history of some LS has led us to ponder the possibility of a multifocal or multicentric origin (MLS). This has been and continues to be a question of controversy that is difficult to resolve because of the rarity of this entity. The main clinical interest lies in its therapeutic approach and prognosis.
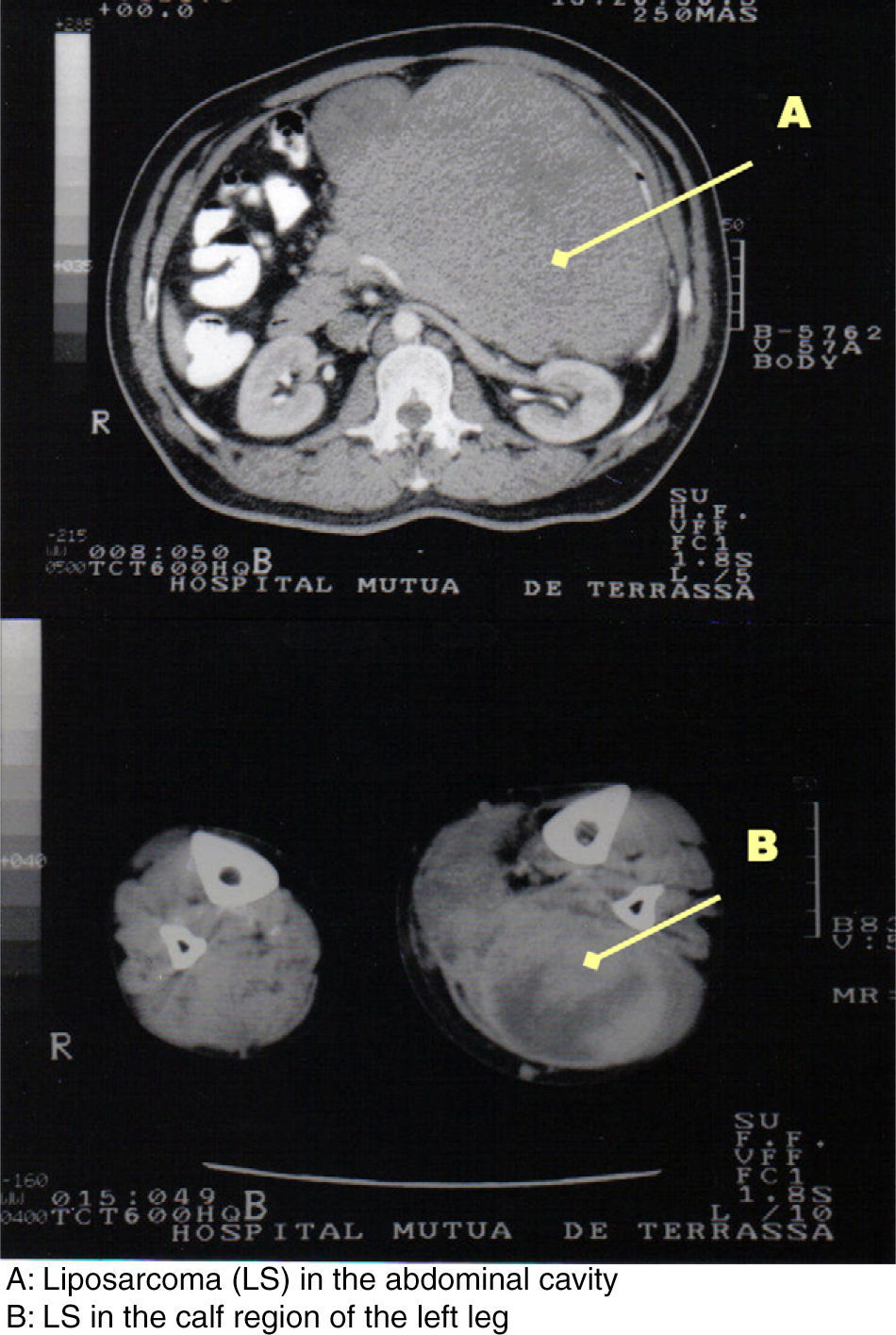
We present a new case of synchronous and metachronous MLS. The patient was a 57-year-old male, with no prior medical history of interest, who came to our Emergency Department due to progressive abdominal distension and general malaise that had been developing over the previous 5 months. He reported a simultaneous thickening of the left calf region. Physical examination revealed that the abdomen was occupied by a large mass. Likewise, the lower left extremity presented with an increased perimeter in the calf region, which was not painful but hard. CT confirmed an abdominal mass (Fig. 1) suggestive of LS and a tumor formation measuring 15cm in diameter in the left leg that was displacing the calf muscles (Fig. 1). Needle aspiration cytologies of both tumors were positive for LS.
The patient underwent resection of the tumor in the calf region as well as the abdominal tumor, which weighed 4100g and originated in the retroperitoneum. The pathology diagnosis of both tumors was myxoid liposarcoma. The surgical treatment was complemented with radiotherapy.
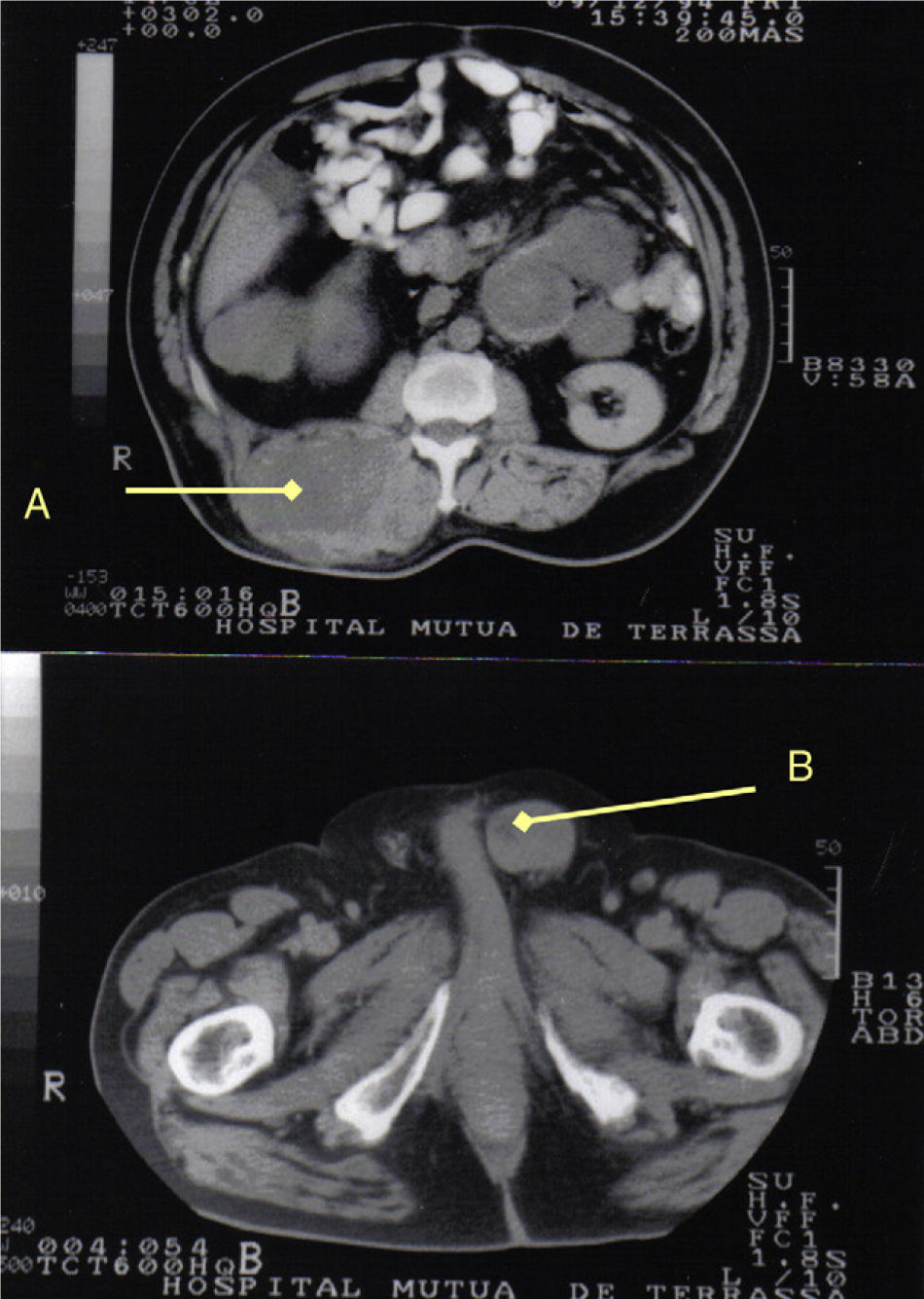
During the first six months of follow-up, the patient presented a myxoid LS in the right dorsolumbar region (Fig. 2), left spermatic cord (Fig. 2) and the left axillary, right scapular, subxiphoid, right inguinal, sub-mammary and right infraclavicular regions, which were treated surgically. One year later, there were recurrences in the dorsolumbar area and lower left leg, which were also removed. The cytogenetic study showed an XY karyotype with several chromosomal anomalies. The most frequent anomaly was the presence of a long-armed isochromosome of chromosome 7. Likewise, mutations were identified in chromosomes 1, 3, 6, 12, 16 and 19.
Three years after the initial intervention, 2 small nodules were identified in the left lung and one in the right, compatible with metastases. Several months later, recurrences were diagnosed in the abdomen and the left calf region, as well as new primary tumors in non-visceral regions whose tumor replication time was significantly shorter than that of the lung nodules. The patient died after 6 years follow-up.
DiscussionThe first case of multifocal synchronous LS in non-visceral regions was reported in 1934 and received the name of “sarcomatosis”.2 Ten years later, Ackerman presented a new case and referred to another 4, differentiating this entity with the name of “multicentric liposarcoma” (MLS).3 Case reports of MLS are rare. In a review of the literature from 1992, 35 cases were referenced and another new case was presented.4 Since then, we have witnessed the publication of sporadic cases,5,6 only one of which was found within the Spanish literature.7
The type of MLS that is most commonly identified is myxoid and expresses the chromosomal translocation t(12;16),8 a fact that was confirmed in the case that we present. The rarity of MLS makes it difficult to clarify whether they are synchronous or metachronous multicentric primary tumors, or whether it is metastatic disease, which involves disseminated neoplastic disease. Classically, in favor of the “multicentric” type, there has been emphasis made to the fact that synchronous or metachronous MLS appear in anatomical regions that are not commonly metastasized, generally in adipose tissue, and sometimes symmetrically. In addition, these areas usually coincide with the common locations of single LS: retroperitoneum, lower extremities and pectoral and pelvic girdles or even the spermatic cord.1,7 Since systemic metastatic dissemination requires us to consider lung involvement, a relevant fact has been the definition of MLS as LS whose presentation is evident in at least 2 different sites before pulmonary metastases.9 In the case we present, the tumor replication time of the pulmonary M1 has been clearly different than that of the non-visceral tumors, which could support the hypothesis of early subclinical microscopic lung disease. Recently, a clonal relationship in these tumors has been established, thus proving a common, and therefore metastatic, origin.10 Nonetheless, this does not explain why the anatomical locations of the metastases are areas where lung metastases are not usually located.
Please cite this article as: Vargas Pierola HJ, Muñoz Muñoz E, Sánchez Martínez A, González Pont G, Veloso Veloso E. Liposarcoma multicéntrico sincrónico y metacrónico. Cir Esp. 2014;92(6):441–443.