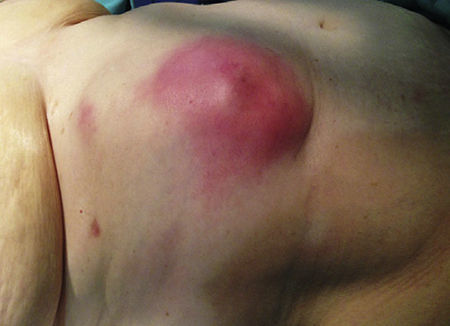
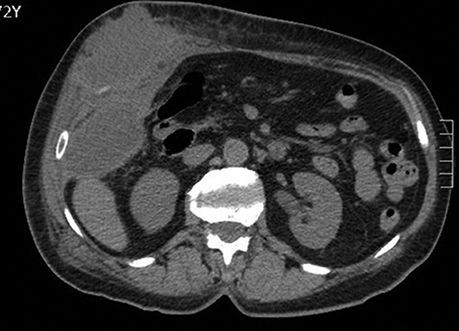
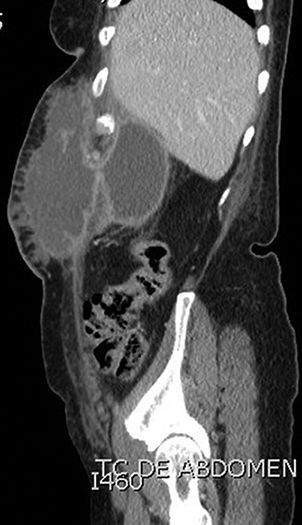
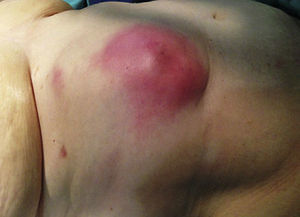
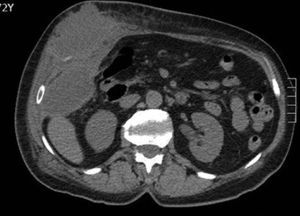
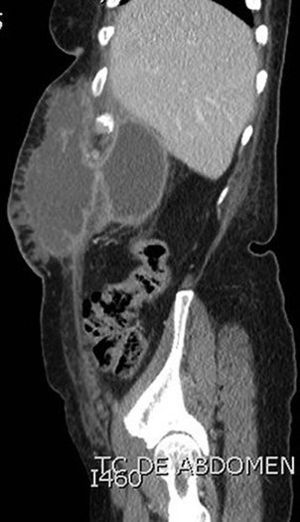
A 66-year-old woman presented with a subcutaneous abscess in the right hypochondrium (Fig. 1). CT scan showed a pericholecystic collection that reached the hepatorenal fossa (Fig. 2) and connected with another in the subcutaneous tissue, through the abdominal wall (Fig. 3).
Spontaneous cholecystic-cutaneous fistula with the formation of a subcutaneous abscess is a severe, uncommon complication of acute cholecystitis. It is confirmed by CT scan and/or fistulography, thus ruling out an erroneous diagnosis of a local cutaneous infectious process, pyogenic granuloma or metastasis.
Diagnosis: Perforated acute cholecystitis that fistulized through the abdominal wall, forming a subcutaneous abscess.
Please cite this article as: España Fuente L, Arias Pacheco RD, Bujarrabal Martínez J, Fernández Muñiz PI. Absceso subcutáneo. Presentación atípica de colecistitis aguda. Cir Esp. 2016;94:105.