The existence of a conglomerate of lymph nodes in the periportal region can present in patients with haematological and abdominal neoplasms, or due to infectious causes.1,2 They usually do not cause symptoms, but they can lead to portal hypertension or obstructive jaundice.2–5 Diagnosis is complex and can require laparotomy.2 We present the case of a patient with HIV infection and Burkitt lymphoma who presented with periportal lymphadenopathies and fever caused by tuberculosis (TB).
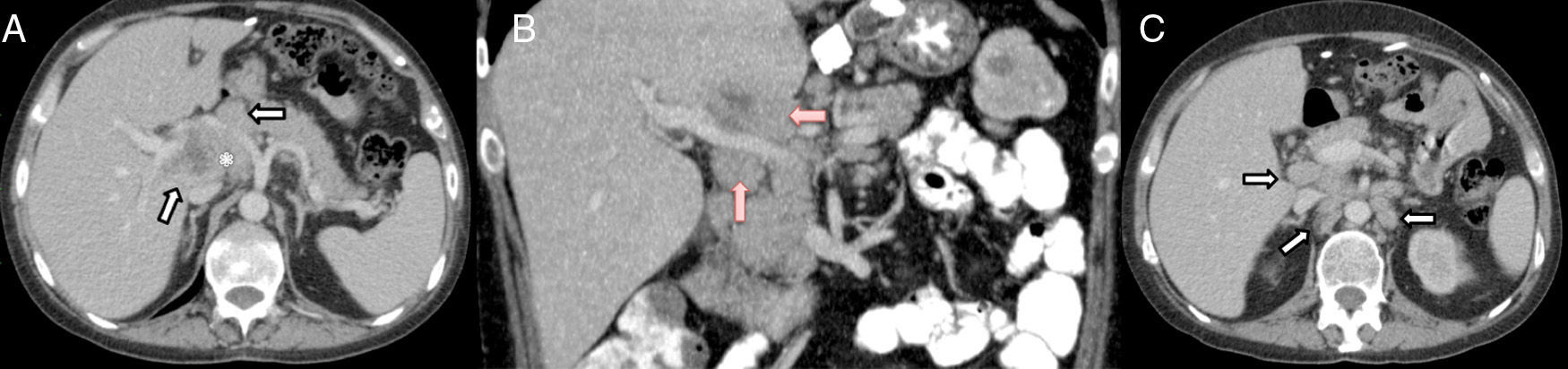
The patient is a 37-year-old male who underwent surgery for morbid obesity in 2012 at another hospital (gastric band). In April 2014, he was diagnosed with HIV infection and stage IV-B Burkitt lymphoma, which was treated with chemotherapy (R-CODOX-M/R-IVAC) from 24 April to 8 July 2014, which achieved complete remission. In October 2014, he presented with symptoms of fever (up to 39.5°C) and shivering that had been progressing over the course of 10 days, with no infectious focus. The patient had been treated with cefuroxime and later levofloxacin, which did not resolve the symptoms, so he was hospitalised. Physical examination was normal and no other symptoms were detected. Blood work showed: leukocytes 5700/mm,3 high percentage of polymorphonuclear cells, prothrombin activity 63% and platelets 84300μl. The biochemistry study was normal and the hepatic profile demonstrated levels of GGT 231U/L and alkaline phosphatase 171U/L. Abdominal computed tomography (CT) scan revealed a poorly defined lymph node conglomerate in the hepatic hilum, which surrounded the hepatic artery and portal vein. The central area was hypodense and compatible with an area of necrosis. There were also multiple lymphadenopathies in the hepatic hilum, the interaortocaval region and left lateral aortic area (Fig. 1). The blood culture and urine culture series were sterile. The transthoracic echocardiography and ophthalmoscopy were normal. As it was impossible to perform radiology-guided percutaneous needle biopsy due to the location of the lesions, a laparoscopic approach was initially decided upon, but, given the intraoperative findings (increased periportal circulation), a right subcostal laparotomy was done, which revealed multiple large periportal lymph nodes (>2cm). The largest (3cm) was compressing the posterior of the left portal vein in the region of the hepatic artery and celiac trunk. There was no ascites, and the liver parenchyma was normal. The 2cm lymph node in the left periportal area was resected (Group 12a). The postoperative period transpired without incident, although the patient's fever persisted.
Axial (A) and coronal (B) CT scan with IVC: poorly defined lymph node conglomerate in the hepatic hilum surrounding the hepatic artery (white arrows in A) and the portal vein (red arrows in B); hypodense central area corresponding with necrosis (asterisk in A). Axial CT scan with IVC (C): multiple lymphadenopathies in the hepatic hilum, interaortocaval region and left lateral aortic (arrows).
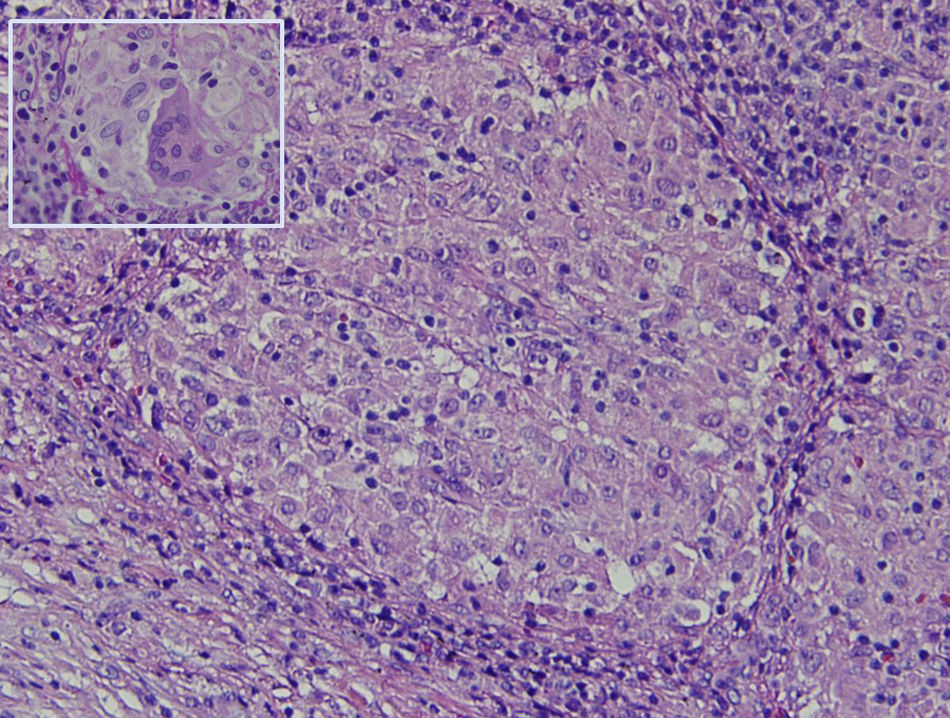
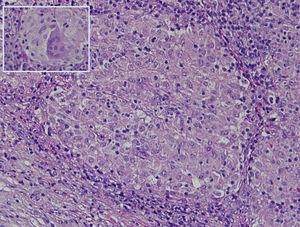
The histology study showed non-necrotising granulomatous lymphadenitis and the presence of mononucleated histiocytes of epithelioid cytoplasm outlining solid granulomas without central necrosis (Fig. 2). PAS, Grocott, Job-Fite and auramine techniques were negative. The immunohistochemistry study (CD79a, CD3, BCL-2, BCL-6, CD10 and Ki67) showed a limited lymph node population, mostly T cells, with no neoplastic lymph nodes and negative CD10. The lymph node immunophenotype confirmed that the lymphocytes were the predominant population (TCD4 and 8, and NK lymphocytes), and no B cells. In the microbiological study of the resected lymph node, growth of Stenotrophormona maltophila was observed. PCR of the lymph node biopsy showed amplification for Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Treatment was initiated with rifampicin, isoniazid, pyrazinamide and ethambutol, and the fever disappeared. At follow-up office visits, complete resolution of the symptoms was confirmed.
TB is an infectious disease that primarily affects the respiratory system but can also affect other organs: gastrointestinal system, peritoneum, lymph nodes, etc.2,3,6–8 Its incidence has been increasing due to the appearance of treatment-resistant strains and infections of HIV-positive patients.7,9 Intraabdominal TB represents 1%–3% of all TB cases; out of these, only 15% have concomitant pulmonary TB, although this rate is higher in HIV-positive patients, and 2/3 present lymph node involvement.2,6,7 Hepatobiliopancreatic TB is rare and usually occurs in patients with miliary TB.3,4 Isolated periportal tuberculous lymphadenitis (PTL) only occurs in 20% of patients with hepatobiliopancreatic TB.3–5,7
PTL can spread from neighbouring organs, or by means of lymphatic, intestinal or hematogenous pathways.2–4,7,9 It is suspected that, when there are no active TB foci in the surrounding areas or miliary involvement, its appearance can be due to the reactivation of latent TB foci in the periportal lymph nodes.4
The most frequent signs and symptoms that patients with PTL present are epigastric pain, fever, weight loss, fatigue and abdominal mass.2,3,7,9 PTL can occasionally cause extrahepatic portal hypertension and, in extreme cases, lead to portal thrombosis.4–6,10 In our case, the patient presented thrombocytopenia and splenomegaly as indirect signs of portal hypertension. The association of HIV infection, PTL and portal hypertension is very uncommon.10 PTL can also cause obstructive jaundice due to direct compression.2,6–9
The diagnosis of PTL is difficult and is rarely made preoperatively.3,5,7 CT is the most sensitive imaging method, although ultrasound and abdominal magnetic resonance imaging have also been used.2,7 On CT, the lymph nodes are observed to be large and heterogeneous, with no calcifications, poorly defined margins, and a higher frequency of presentation as a conglomerate.1,2,7,9 If contrast material is administered, peripheral enhancement is observed with a central area of low density, although this does not occur in AIDS or immunosuppressed patients as they present a smaller reduction in inflammatory reaction.1,2,7 The disappearance of lymphadenopathies after tuberculosis treatment is also considered diagnostic.5
The differential diagnosis of PTL should above all include intraabdominal lymphomas.1 In these patients, the lymph nodes are more homogeneous, show no peripheral enhancement, and there is typically vascular involvment.2,7 The mesenteric and periportal lymph nodes are more frequently affected in patients with TB.1 Other diseases that should be ruled out are the presence of metastatic lymphadenopathies or infectious diseases, such as Whipple disease.2
If it is possible to carry out an ultrasound or CT-guided needle aspiration of the periportal lymph nodes, a diagnosis of PTL can be reached with a sensitivity close to 80%.2,5,9 But, when the sample is insufficient or the location is close to large vessels and puncture is risky, surgery is required to reach a diagnosis.2 This has also been done by laparoscopy, but this technique can be very complex and carries risks.2
The histological study of the periportal lymph nodes in PTL usually shows chronic granulomatous inflammation with central necrosis.4 Once the diagnosis is reached, the establishment of adequate tuberculosis treatment usually resolves the symptoms, with a significant reduction of the periportal lymph nodes.2
In conclusion, PTL is an entity that is difficult to diagnose in the absence of other tuberculous foci, especially is it occurs in a patient previously diagnosed with Burkitt lymphoma. Needle aspiration of the periportal lymph nodes can avoid laparotomy, but this is often not feasible and requires surgical intervention. Tuberculosis treatment usually leads to the regression of the lesions.
Please cite this article as: Ramia JM, Diaz-Morfa M, Caminoa A, Gijón L, de la Plaza R. Linfadenitis periportal tuberculosa: un reto diagnóstico. Cir Esp. 2016;94:194–196.