Testosterone is the hormone responsible for secondary sexual characteristics in men, in whom the serum concentration is 10 times higher than in women. A raised testosterone concentration in women may be due to various diseases, such as polycystic ovary syndrome, congenital adrenal hyperplasia, and adrenal or ovarian tumors, among other ovarian or adrenal disorders.
In the absence of clinical symptoms, a testosterone concentration above the reference interval may be due to interference in the immunoassay1-4.
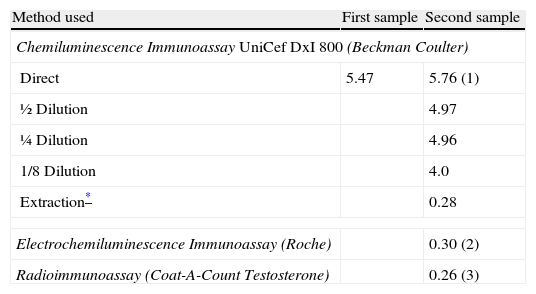
Case reportA 51-year-old woman who started her menopause a year previously, in good general health and not on any medication, had goiter as the only medical history of interest, for which periodical thyroid hormone monitoring was performed. In december 2008, her testosterone concentration was studied fortuitously, with a value of 5.47 ng/mL (table 1) (reference interval 0.2-0.8 ng/mL). The testosterone level was measured in an UniCel DxI 800 autoanalyzer (Beckman Coulter®, CA USA), an automated chemiluminescence immunoassay system. To confirm this value, the analysis was repeated and the same result was obtained. A new sample was requested, which was processed in the same autoanalyzer. A testosterone concentration of 5.76 ng/mL was found (table 1). The concentration of other androgens and hypophyseal hormones was studied for a possible subclinical disorder. The results obtained were as follows: androstenedione 1.1 ng/mL (0.4-4.5); dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate (DHEA-S) 900 ng/mL (700-3,900); sex hormone binding globulin 40 nmol/L (11-124); 17OH-progesterone 0.67 ng/mL (<4); cortisol 13.4μg/dL (8-25); thyroid stimulating hormone 2.4μU/mL (0.3-4.8); FSH 61.9 mU/mL (42-126); luteinizing hormone 31.9 mU/mL (11-50); prolactin 4.7 ng/mL (6.0-29.9).
Testosterone concentration (ng/mL) found in distinct samples and with different methods
| Method used | First sample | Second sample |
| Chemiluminescence Immunoassay UniCef DxI 800 (Beckman Coulter) | ||
| Direct | 5.47 | 5.76 (1) |
| ½ Dilution | 4.97 | |
| ¼ Dilution | 4.96 | |
| 1/8 Dilution | 4.0 | |
| Extraction* | 0.28 | |
| Electrochemiluminescence Immunoassay (Roche) | 0.30 (2) | |
| Radioimmunoassay (Coat-A-Count Testosterone) | 0.26 (3) | |
Reference values (1): 0.2-0.8; (2): 0.06-0.82; (3): 0.04-0.62 ng/mL.
To rule out possible interferences in the immunoassay, serial dilutions5 were performed with the Access Testosterone Calibrator 0, at 1:1; 1:2; 1:4 and 1:8, with the following results: 5.62 ng/mL; 4.97 ng/mL; 4.96 ng/mL and 4 ng/mL respectively (table 1).
To rule out any possible artefacts in the chemiluminescence system, various parameters (TSH, FT4, AFP, CEA, cortisol and testosterone) were determined in the same autoanalyzer. All the results, except those for testosterone, fell within the reference interval.
Alternatively, the sample was processed in the Modular E170 (Roche® Diagnostics GmbH, Mannheim), an automated electrochemiluminescence immunoassay system. A testosterone concentration of 0.30 ng/mL was found (reference interval 0.06-0.82 ng/mL) (table 1). The sample was also processed by radioimmunoassay in the solid phase, Coat-A-Count Testosterone Total (Siemens®, CA USA), and a concentration of 0.26 ng/mL was found (0.04 -0.62) (table 1).
Finally, extraction with diethyl ether was performed, prior to immunoassay2, and the testosterone concentration was measured in the same autoanalyzer. A result of 0.28 ng/mL (table 1) was found.
In view of the absence of clinical symptoms compatible with hyperandrogenism, a raised testosterone concentration in a woman when other androgen concentrations are normal suggests interference in the immunoassay used6,7.
Direct immunoassay of testosterone in women is subject to various types of interference, which tend to result in overestimation of the true concentration8. Cross-reactions due to drugs are common, but not in our patient since she was not taking any medication. DHEA-S, when found at high concentrations, may produce interference due to cross-reaction in the testosterone analysis9. The analysis performed in our patient showed normal values of this hormone.
The interference was eliminated by extraction with diethyl ether prior to the analysis, demonstrating that the cause was a hydrosoluble substance that may provoke a cross-reaction in some competitive immunoassays2,3.
The reference method for determining testosterone and other steroids is liquid chromatography followed by mass spectrometry10. Improved specificity of these methods will lead to more reliable and meaningful testosterone results in female patients. Until these methods are available in clinical laboratories, both laboratorians and clinicians should be aware of the possibility of interference in immunoassays.
Conclusions: When unusual steroid results are found in immunoassays, we recommend the following: (a) the use of a different method to process the sample and (b) extraction with ethyl ether before immunoassay. The latter is useful to eliminate interference by hydrophilic substances and is essential when a raised testosterone concentration is found in a woman.
We are grateful to Dr. Javier Lugo for testosterone determination using the Roche Diagnostics autoanalyzer.