Adrenal carcinoma (AC) is a rare neoplasm with an incidence of 0.5–2 cases/million population per year.1 Women are more frequently affected, mostly in the 5th decade of life. AC shows an aggressive behavior, with a survival in metastatic disease less than 10% at 5 years and 32–48% in patients who underwent complete resection,2 which is the treatment of choice.
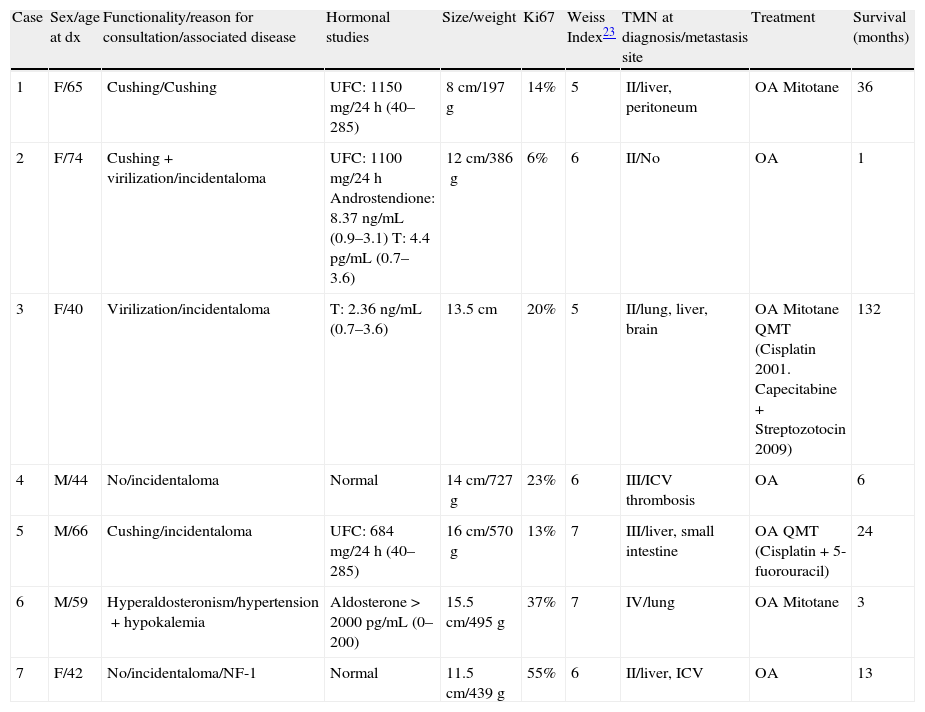
We present 7 patients with AC treated in our hospital between 1993 and 2010, whose clinical and histological characteristics and treatment received are summarized in Table 1.
Patients characteristics.
| Case | Sex/age at dx | Functionality/reason for consultation/associated disease | Hormonal studies | Size/weight | Ki67 | Weiss Index23 | TMN at diagnosis/metastasis site | Treatment | Survival (months) |
| 1 | F/65 | Cushing/Cushing | UFC: 1150mg/24h (40–285) | 8cm/197g | 14% | 5 | II/liver, peritoneum | OA Mitotane | 36 |
| 2 | F/74 | Cushing+virilization/incidentaloma | UFC: 1100mg/24h Androstendione: 8.37ng/mL (0.9–3.1) T: 4.4pg/mL (0.7–3.6) | 12cm/386g | 6% | 6 | II/No | OA | 1 |
| 3 | F/40 | Virilization/incidentaloma | T: 2.36ng/mL (0.7–3.6) | 13.5cm | 20% | 5 | II/lung, liver, brain | OA Mitotane QMT (Cisplatin 2001. Capecitabine+Streptozotocin 2009) | 132 |
| 4 | M/44 | No/incidentaloma | Normal | 14cm/727g | 23% | 6 | III/ICV thrombosis | OA | 6 |
| 5 | M/66 | Cushing/incidentaloma | UFC: 684mg/24h (40–285) | 16cm/570g | 13% | 7 | III/liver, small intestine | OA QMT (Cisplatin+5-fuorouracil) | 24 |
| 6 | M/59 | Hyperaldosteronism/hypertension+hypokalemia | Aldosterone>2000pg/mL (0–200) | 15.5cm/495g | 37% | 7 | IV/lung | OA Mitotane | 3 |
| 7 | F/42 | No/incidentaloma/NF-1 | Normal | 11.5cm/439g | 55% | 6 | II/liver, ICV | OA | 13 |
dx: diagnosis; F: female; M: male; NF-1: neurofibromatosis 1; UFC: urinary free cortisol; T: testosterone; ICV: inferior cava vein; QMT: chemotherapy; OA: open adrenalectomy.
AC is usually a sporadic tumor, but it may appear in familial syndromes such as Li-Fraumeni syndrome, Gardner syndrome, multiple endocrine neoplasia 1, Carney complex or neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF-1). Until 2005 only four cases of AC associated with NF-1 had been described.3 They are usually functioning tumors (∼60%) and Cushing's syndrome is the most frequent (45%); functioning tumors can present with Cushing and androgens overproduction (30%) or with virilization alone (10%).4 The overproduction of mineralocorticoids is uncommon4; it causes hypertension and hypokalemia and is generally associated with an aggressive behavior,5 as in our case 6. Patients with non-functioning tumors may have abdominal pain or may be detected as incidentalomas.5 In fact, in a review of Barzon et al., ACs represent 4.4% of adrenal incidentalomas.6
Survival depends on the stage: at 5 years it is 82% for stage I, 61% in stage II, 50%in stage III and 13% in stage IV, according to staging of ENSAT 2008.5 This classification has a superior prognostic value than the UICC staging system.7 Other factors associated with poor prognosis are: advanced age, hypersecretion of cortisol, tumor size and a high Ki67 proliferation index.1,8 Other molecular markers have been proposed as IGF2 gene and IGF1 receptor gene and more recently the steroidogenic factor 1 (SF-1) (transcription factor associated with the development and synthesis of steroidogenic tissues) which has been correlated with a poorer prognosis.9
Complete resection is the only curative option and the most important prognostic factor, especially in stages I–III.8 There is not a standard type of surgery, but some of the authors10 suggest that to reduce local recurrence and improve disease-free survival and overall survival, adrenalectomy should be accompanied by regional lymphadenectomy (including celiac, renal hilum and ipsilateral lateroaortic ganglia). The technique of choice for adrenalectomy is open surgery, although some of the authors propose laparoscopic surgery for tumors<10cm without evidence of invasive disease; but this surgery should only be performed by experienced surgeons.11,12 In stage IV, cytoreductive surgery can be considered for hormonal control and/or to facilitate radiofrequency ablation.
Radiotherapy (RDT) has traditionally been considered ineffective in AC. However, a retrospective study of 58 patients showed that adjuvant RDT significantly reduced the risk of local recurrence (but not affected overall survival).13 Some of the authors recommend adjuvant RDT for AC in patients with (1) macroscopic incomplete (R1) or uncertain (Rx) resection, (2) in patients with stage III or (3) in tumors with complete resection (R0), size>8cm, vascular invasion and Ki67>10%.4 RDT may also be beneficial when surgery is not feasible. These recommendations are recent, so none of our patients received RDT.
Mitotane is an inhibitor of the cortisol synthesis and an adrenal cytotoxic agent. Its use as adjuvant therapy after surgery has been controversial because there are no randomized studies, but it is the only drug formally approved for AC. A retrospective nonrandomized multicenter study14 showed that adjuvant mitotane was associated with a lower recurrence rate (49% in the German mitotane group versus 73% in the Italian and 91% in the German non-mitotane groups). After this study, an international panel of experts15 proposed administration of adjuvant mitotane in patients with R1 or Rx and/or Ki67>10%, but it would not be mandatory in the following situations: stage I or II (classification ENSAT 2008), radical resection R0 and Ki67≤10%. There is an ongoing multinational randomized trial comparing adjuvant treatment with mitotane versus only monitoring (ADIUVO trial) for patients with low/moderate recurrence risk (stages I–III without residual microscopic disease). Side effects of mitotane may limit its use, the most frequent being neurological and gastrointestinal. There is no consensus on the duration of treatment, but it varies between 2 and 5 years. The initial dose could be 1–2g/day and it should be increased gradually, and according to tolerability, to obtain plasma levels between 14 and 20mg/L,16 values that are predictors of greater therapeutic response. Some of the authors propose an initial dose of 4–6g/day.17 Mitotane can induce adrenal insufficiency, so replacement therapy with hydrocortisone is necessary. A dose of 50mg/day may be required.16
There are some factors that seem to influence the response to mitotane. Volante et al.18 have found that RRM1 (ribonucleotide reductase large subunit 1) gene expression is associated with mitotane response: in patients with a low gene expression, adjuvant mitotane showed an improved disease-free survival but it did not occur with a high RRM1 expression.
Most of our patients received mitotane generally for short periods (maximum 6 months) because of adverse neurological effects, or sudden death in the days after the surgery (case 2) or because it was diagnosed initially as pheochromocytoma (case 7).
If there is hypercortisolism, mitotane must be combined with fast-acting drugs, because of its slowness to reach therapeutic levels such as ketoconazole (or metyrapone) or, if oral intolerance, intravenous etomidate.
Chemotherapy (QMT) is reserved for advanced CA in progression despite mitotane. Recently, the result of the first randomized international trial, the FIRM-ACT,19 which compared the two more frequently used antineoplastic regimens, has been published. The results showed that the combination of mitotane with etoposide, doxorubicin and cisplatin (M-EDP) achieved a greater objective tumor response rate than the combination of mitotane with streptozotocin (23% versus 9%, p<0.001), an increase in free survival progression also significant (5.3 months versus 2, p<0.001) and a higher percentage of patients without progression within 12 months (26% versus 7%). However, overall survival was no significantly different between both groups (14.8 months in M-EDP group versus 12 in patients with mitotane and streptozotocin, p=0.07), although these results could be influenced by the change of therapy in case of if progression.
If these two regimens fail, then salvage treatment with gemcitabine and metronomic fluoropyrimidines (fluorouracil intravenous or oral capecitabine) is recommended. This option has showed stabilization of the disease. Another treatment that has been proposed is capecitabine with the monoclonal antibody against VEGF (Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor) bevacizumab, but the results have been unsatisfactory.
In our series, only two cases were treated with QMT and they achieved a longer survival (cases 3 and 5). Cases 2 and 6 died prematurely, cases 1 and 4 were seen before 1998, the year when M-EDP regimen was published and case 7 was initially diagnosed as malignant pheochromocytoma. Sometimes, the histopathological differential diagnosis between malignant pheochromocytoma and AC is difficult and the inmunohistochemical study is necessary. The tumor cell positivity for inhibin, melan A and calretinin suggests adrenal cortical tumor, while chromogranin A is only positive in pheochromocytoma.
In recent years, different antineoplastic targeted drugs (imatinib, gefitinib, sorafenib) have been tested with poor results. The best results, although modest, were obtained with antiangiogenic multikinase inhibitor sunitinib (SU). In a recent phase II trial in refractory CA, SU achieved stable disease in 5 out of 35 patients, although these results could be negatively influenced by the inducing effect on cytochrome p450-3A4 of mitotane, causing lower plasma levels of SU and therefore, less effectiveness.20
Other future therapeutic option is radiopharmaceutical therapy with iodine-metomidate (131I-IMTO), which is very selective for adrenocortical tissue. In patients with advanced ACC when radical surgery is not possible and the uptake of 131I-IMTO is high, it has been seen that in patients who respond to treatment, median progression-free survival is 14 months.21 Other options are IGF-1R inhibitors and SF-1 inhibitors.22