Twenty percent of cases of cardiac tamponade are of malignant etiology, according to autopsy series. The most common cause is lung cancer, followed by breast and esophageal cancer, melanoma, lymphoma, and leukemia.
Papillary thyroid carcinoma is a very rare cause of malignant cardiac tamponade, and is even more exceptional as the first sign of the disease.
A 56-year-old female patient with nodular goiter since childhood who 30 years earlier had undergone left hemithyroidectomy for a 4.5cm×4.5cm toxic nodule is reported here. A pathological study revealed benign disease and nodular hyperplasia. Secondary hypothyroidism was subsequently treated with levothyroxine.
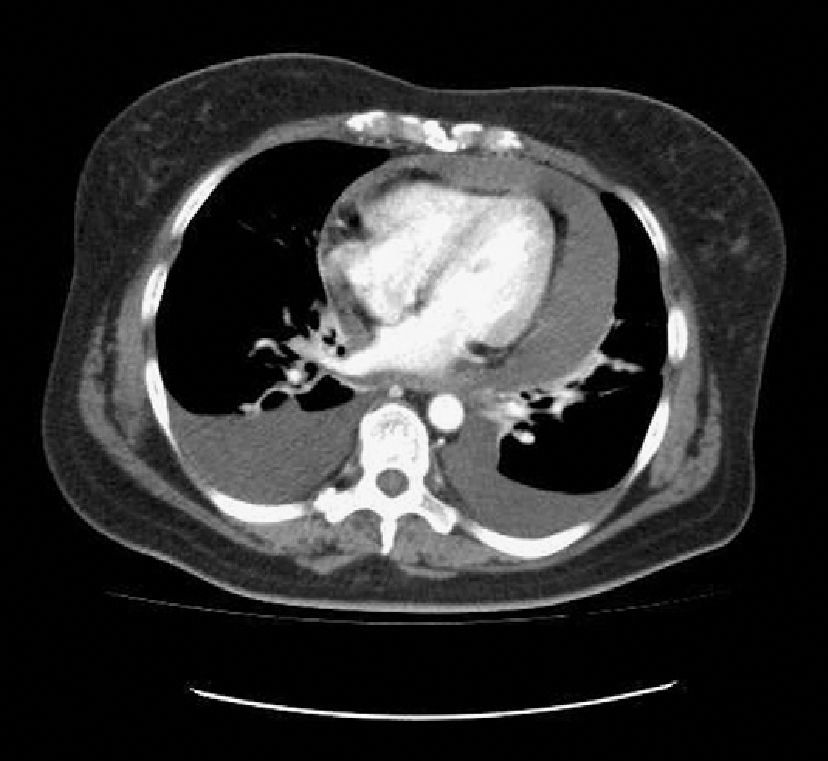
The patient attended the emergency room of her reference hospital reporting the occurrence during the previous month of asthenia, anorexia, weight loss, malaise, generalized pain, a progressive decrease in urine output, edema in the lower limbs, and progressive dyspnea in the preceding weeks with a sudden worsening to dyspnea at rest associated with dizziness and hypotension. Chest X-rays showed an increased cardiothoracic ratio with bilateral pleural effusion. A CT scan of the chest revealed pleuropericardial effusion (Fig. 1). The patient was referred to Hospital Central, where she was admitted with tachycardia of 115bpm, tachypnea of 28rpm, and poor perfusion. An electrocardiogram showed sinus rhythm with electric alternance, and an echocardiogram revealed pericardial effusion surrounding the cardiac silhouette. Pericardiocentesis was performed, with abundant fluid being drawn. The initial response was good, but a sudden impairment occurred two hours later, leading to cardiorespiratory arrest which did not respond to resuscitation maneuvers.
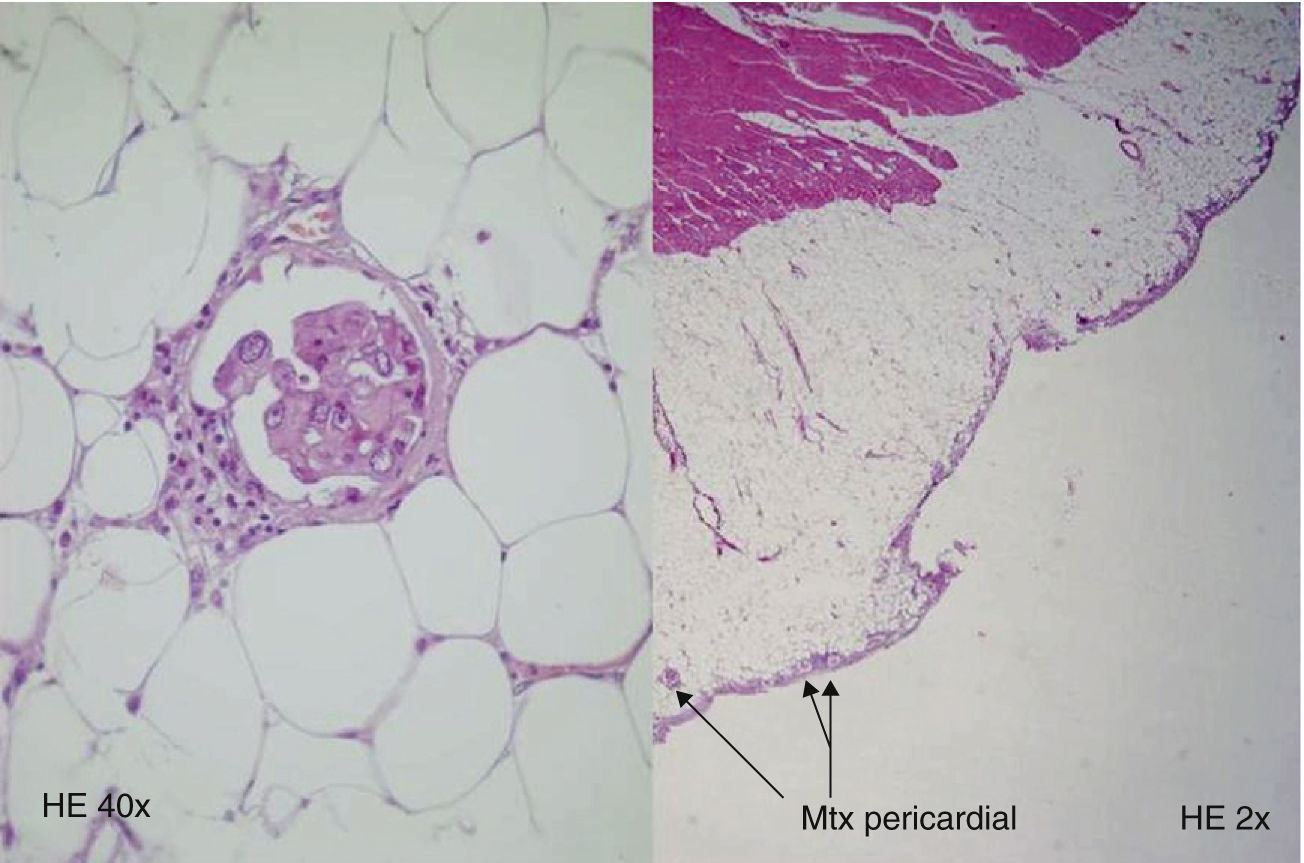
An autopsy was performed, leading to the diagnosis of a poorly differentiated thyroid carcinoma of papillary origin at the left thyroid bed, approximately 0.8cm at its largest size, with metastases in the lung, esophagus, pericardium, and mediastinal lymph nodes.
Cells of similar characteristics were seen in the hemithyroidectomy scar around suture residues (Fig. 2).
The incidence of papillary thyroid carcinoma has been increasing in recent years. In the United States, its incidence increased in the 1973–2002 period from 2.7 to 7.7/100,000 population.1,2 Although this increased incidence is probably due to a higher number of early diagnoses of subclinical thyroid carcinomas, an analysis made by the US National Cancer Institute found an increase in differentiated thyroid cancers of all sizes, including those greater than 4cm in size.3
Papillary thyroid carcinoma disseminates mainly by the lymphatic route to the regional lymph nodes. Only 2–10% of patients have distant metastases at diagnosis. Half of these metastases occur in the lung, one-fourth involve bone, and the remaining metastases are found in the brain, kidney, liver, and adrenal glands. Cardiac or pericardial metastases are very uncommon.4
Our patient had a poorly differentiated papillary carcinoma clinically occurring as a malignant cardiac tamponade. This is the seventh case reported in the literature to date.5–10
The pericardial fluid should be analyzed whenever effusion occurs, even if no malignancy is suspected.
As regards the reported case, the importance of comprehensive work-up of the thyroid nodule for the early diagnosis of thyroid cancer should also be emphasized because the malignant condition could probably have been detected earlier, thus preventing the dissemination of the disease.
Please cite this article as: Rodríguez Caballero MG, Suárez Gutiérrez L, Fernández Fernández L, Valdés Gallego N, Menéndez Torre E. Taponamiento cardíaco como primera manifestación de carcinoma papilar de tiroides. Endocrinol Nutr. 2013;60:e1–e2.