The 3rd International Nursing & Health Sciences Students & Health Care Professionals Conference (INHSP) 2019
Más datosThis research aimed to assess the effectiveness of honey and chlorhexidine in reducing halitosis of stroke patients.
MethodPretest–posttest randomized control group design was used to obtain the data in 102 patients at RSUD Dr. Soedarso. The present study compared the effectiveness of different mouthwash liquids; chlorhexidine and honey. The data were analyzed using univariate and bivariate analysis.
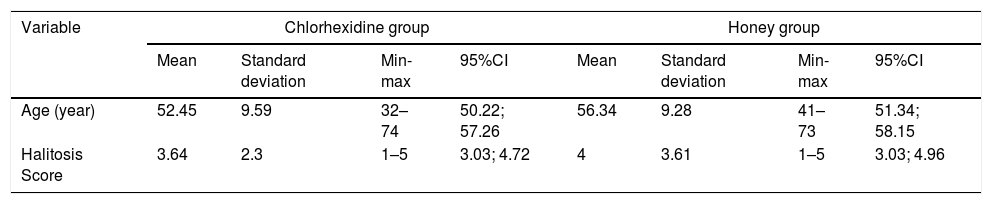
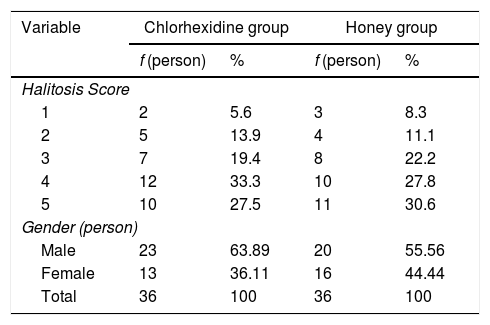
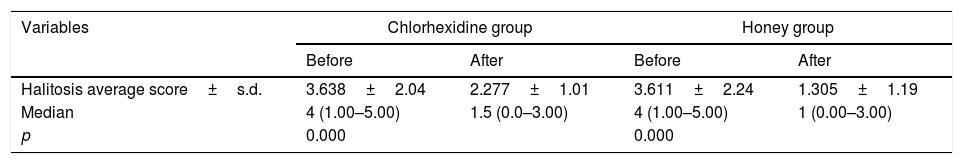
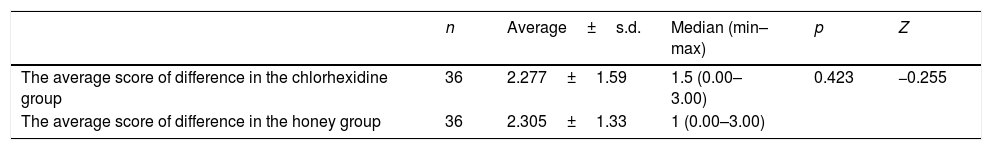
ResultMost of the halitosis cases were observed in male patients at the age of >54 years old. The mean halitosis score of the patients before treatment was 4 (estimated by using Tanita Breath Checker). After the treatment, both chlorhexidine and honey showed a positive result in reducing halitosis. The average Halitosis score before treatment in the chlorhexidine group was 4 and changed into 1.5 post-treatment. In honey group, the mean Halitosis score before treatment was 4 and changed into 1 after treatment. The average score of halitosis in the group treated with chlorhexidine and in a group treated with honey was not really significant. In the chlorhexidine group, the average score was 2.377 while in the honey group, the average score was 2.277. It meant that both liquids have a similar impact in reducing halitosis.
ConclusionHoney and chlorhexidine are effective in reducing halitosis. Moreover, honey was better in improving halitosis in stroke patients compared to chlorhexidine.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora