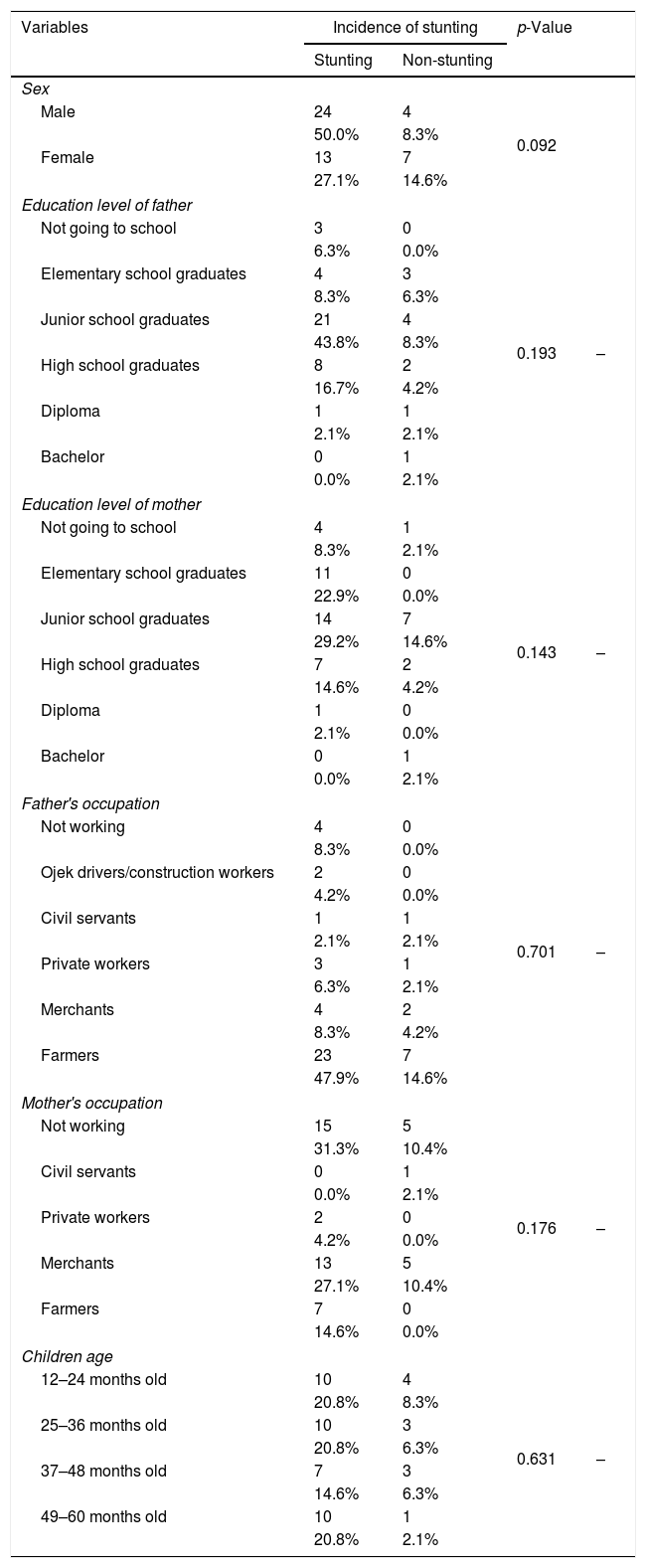
Stunting (dwarf) is a problem of chronic malnutrition, in which the children have smaller length or height for age. From the basic health research (Riskesdas) in 2018, the prevalence of stunting in the national scope was 30.8% and in Sigi is still above the national rate of 36.4%. This study aims to determinants the risk factor for stunting in the Kinovaro Sigi Health Center, Central Sulawesi.
MethodsThis study is a survey analytic method, with a cross sectional. The sampling technique used in this study was purposive sampling. The research data were analyzed using univariate, bivariate, and multivariate.
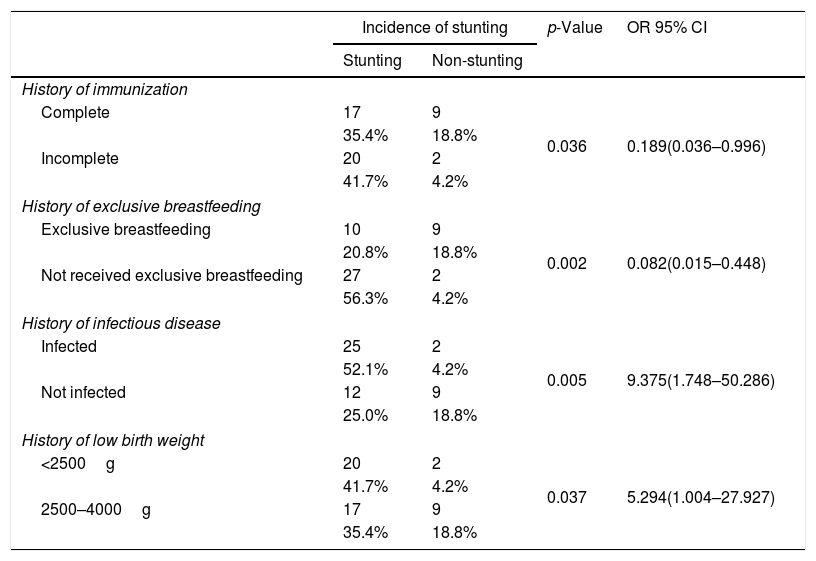
ResultsThe relationship between risk factor of immunization history and incidence of stunting events showed p-value=0.036 (OR 0.189 with 95% CI, 0.036–0.996), exclusive breastfeeding history showed p-value=0.002 (OR 0.082 with 95% CI, 0.015–0.448), history of infectious diseases showed p-value=0.005 (OR 9.375 with 95% CI, 1.748–50.286), and history of LBW showed p-value=0.037 (OR 5.294 with 95% CI, 1.004–27.927).
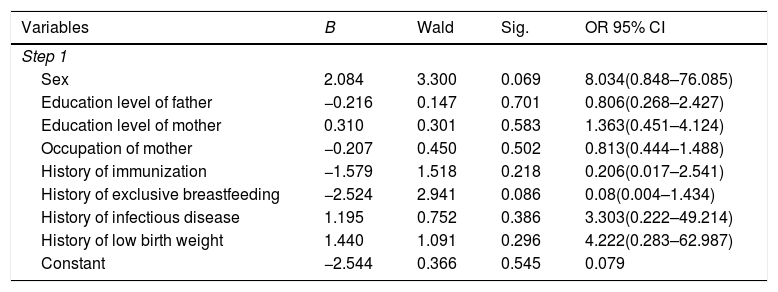
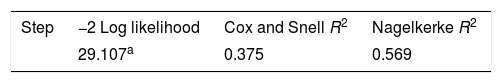
ConclusionThese risk factors are related to the incidence of stunting and contribute 56.9% in influencing the occurrence of stunting.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora