Analizar la influencia en la unidad familiar de la existencia de un hijo en edad infantil o adolescente, con discapacidad intelectual.
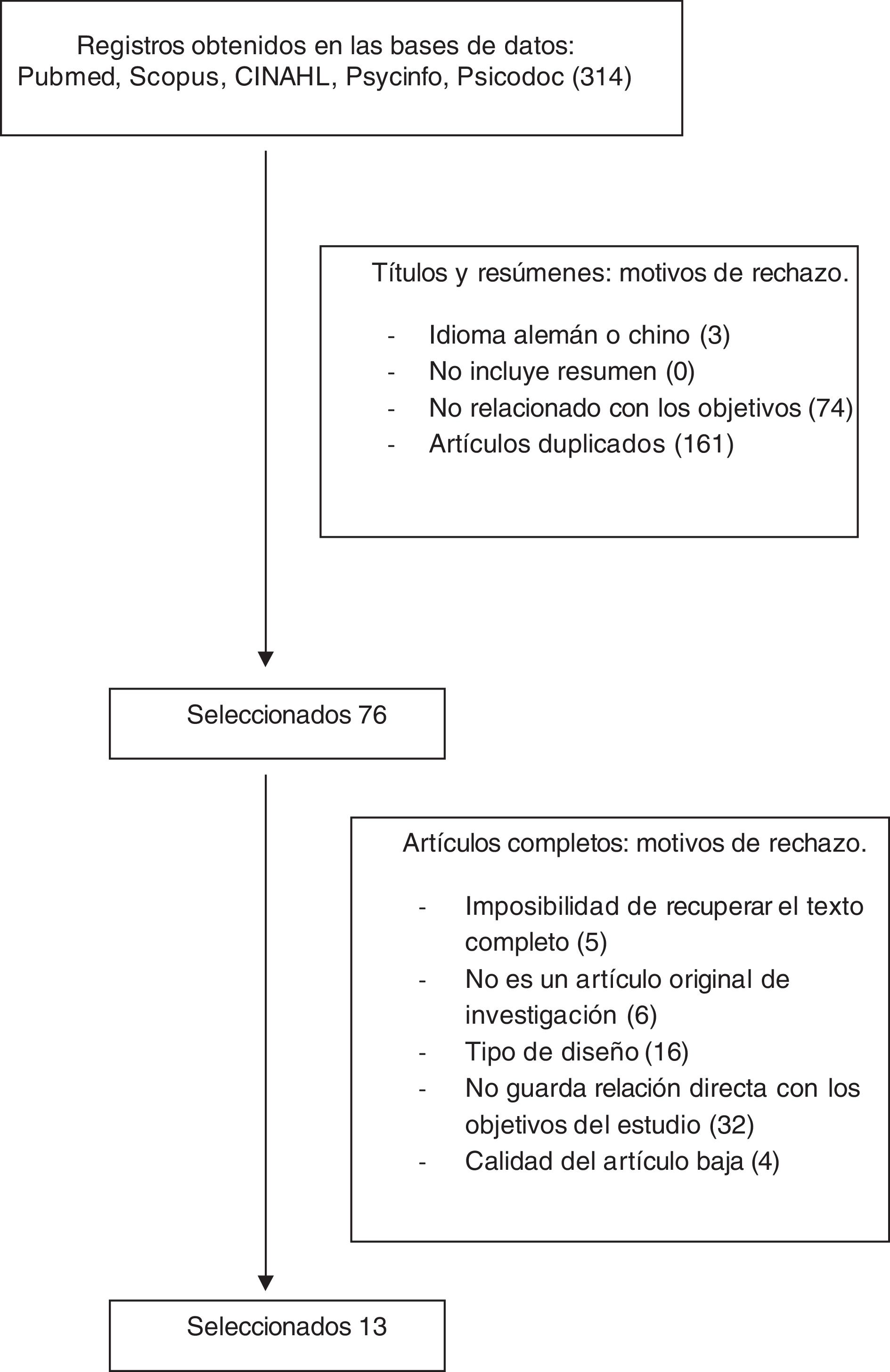
MétodoRevisión sistemática de la literatura, siguiendo las recomendaciones de la declaración PRISMA, en PubMed, Scopus, CINAHL, PsycINFO y Psicodoc. Se localizaron artículos originales, publicados en los últimos 5 años, en español, inglés, portugués, italiano o francés, con resumen y texto completo y calidad metodológica satisfactoria o buena. Dos investigadores independientes consensuaron decisiones.
ResultadosGeneralmente el cuidado se presta en la familia, asumiendo las madres la mayor responsabilidad, presentando menor bienestar que los padres. El apoyo del cónyuge mejora su calidad de vida. El subsistema fraternal puede afectarse en la calidez de la relación, el estatus/poder y los problemas comportamentales. La salud familiar puede afectarse en todas sus dimensiones: clima y funcionamiento familiar por las mayores demandas y modificaciones en la organización y distribución de roles; resistencia y afrontamiento familiares por el aumento de gastos y disminución de recursos; la integridad familiar puede reforzarse al fortalecerse los lazos familiares. El apoyo emocional favorece la calidad de vida familiar.
ConclusionesEstas familias pueden necesitar atención diferenciada por su mayor demanda de cuidados, disminución de recursos o problemas de salud familiar. Las enfermeras, desde un enfoque de atención centrado en la familia, pueden identificarlas y ayudarlas a normalizar su situación, fomentando la salud familiar y el bienestar de sus miembros.
To examine the influence of a child or adolescent with intellectual disabilities on the family unit.
MethodA systematic review of the literature, following the recommendations of the PRISMA statement, was carried out on the PubMed, Scopus, CINAHL, PsycINFO and Psicodoc databases. Original articles were found, published in the last 5 years, in Spanish, English, Portuguese, Italian or French, with summary and full text and satisfactory or good methodological quality. Two independent researchers agreed on their decisions.
ResultsIn general, care is provided in the family, mothers assume the greater responsibility, and their wellbeing is lower than that of fathers. Having the support of the husband improves their quality of life. The fraternal subsystem can be affected, with regard to the warmth and the status/power of the relationship, and behavioural problems. Family health may be affected in all its dimensions: family functioning and atmosphere due to increased demands and changes in the organisation and distribution of roles; family resilience and family coping, due to rising costs and dwindling resources; family integrity could be strengthened by strengthened family ties. Quality of family life is enhanced by emotional support.
ConclusionsThese families may need individualised attention due to the increased demand for care, diminishing resources or other family health problems. Nurses using a family-centred care approach can identify these families and help them to normalise their situation by promoting their family health and the well-being of its members.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora