The 3rd International Nursing & Health Sciences Students & Health Care Professionals Conference (INHSP) 2019
Más datosThis study aimed to evaluate the effectiveness of antiseptic soaps in reducing bacterial colonization in patients with a diabetic foot ulcer (DFU).
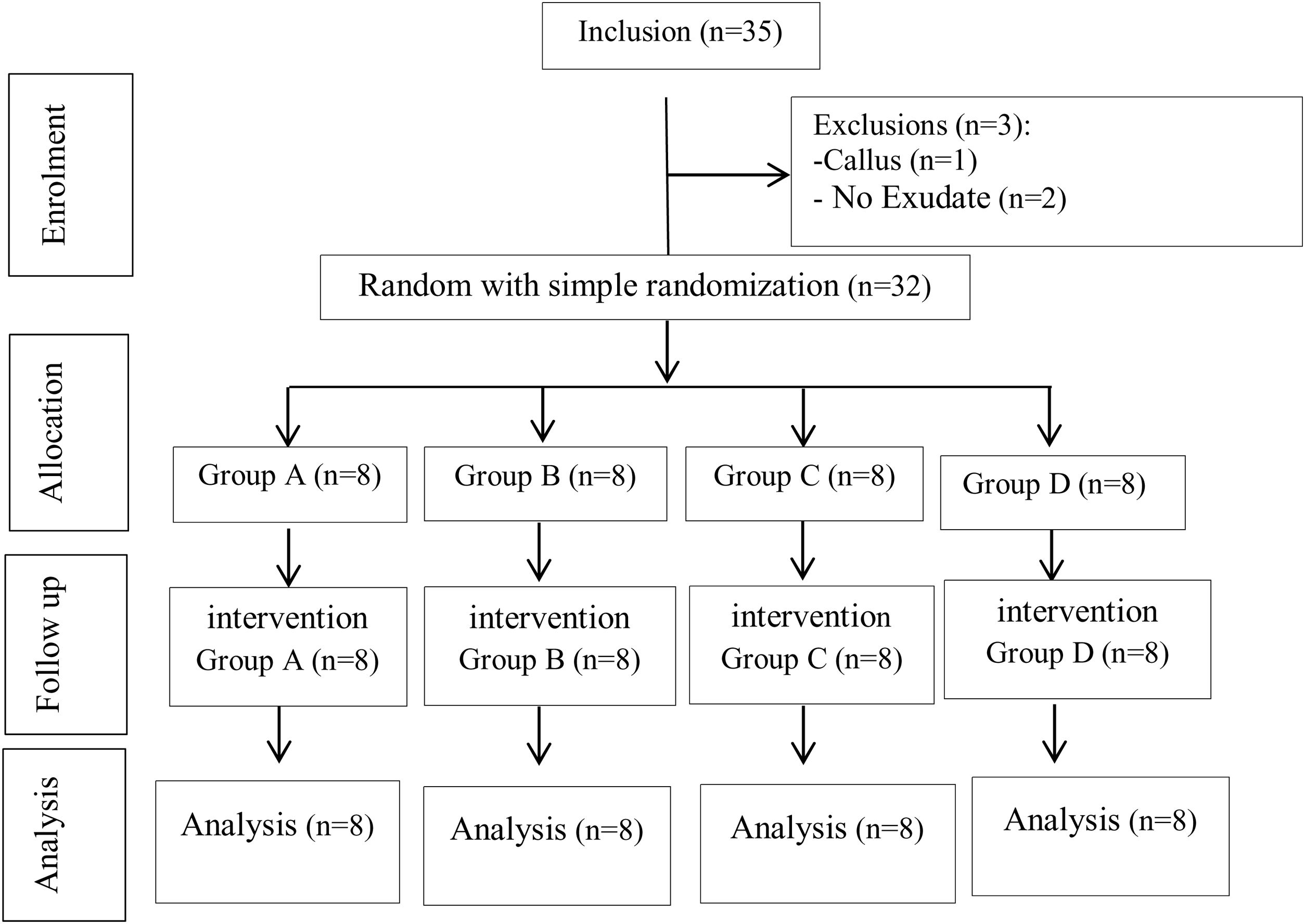
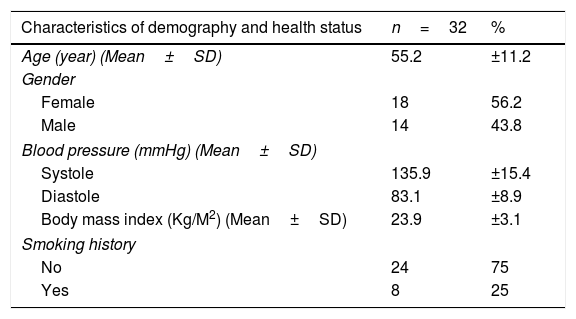
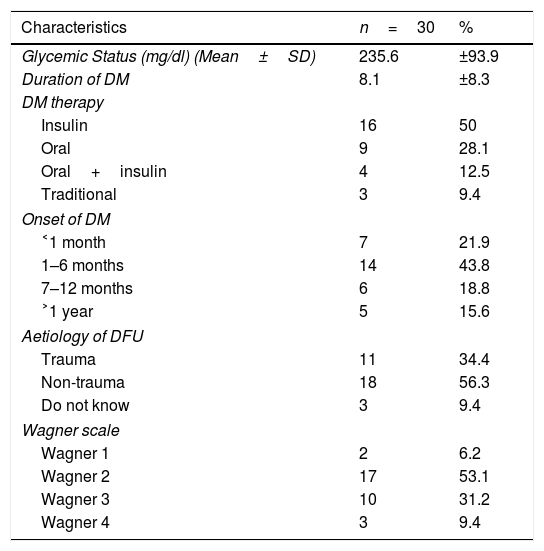
MethodsThis was a quasi-experimental study conducted in Makassar, South Sulawesi, Indonesia. Data were collected from 32 participants, and those who met the inclusion criteria were grouped into four groups. Wilcoxon and Kruskal–Wallis post hoc tests were used for data analyses.
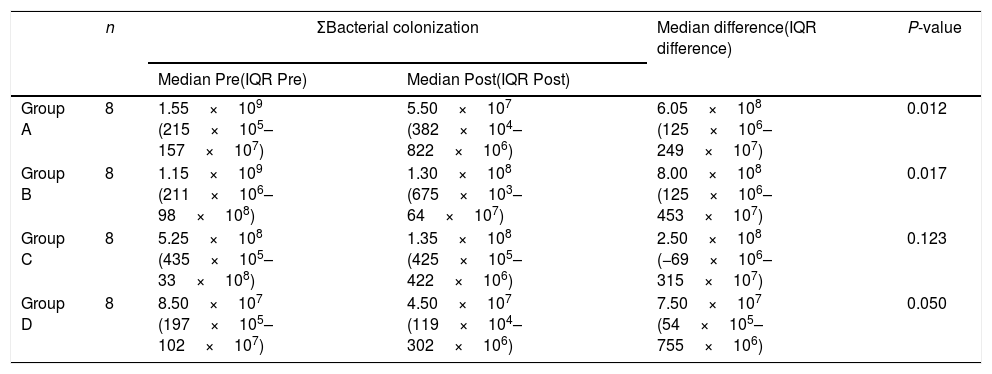
ResultsThe decrease in bacterial colonies was not statistically significant when the wounds were cleansed with soaps made of chlorhexidine, parchlorometxylenol (PCMX)/chloroxylenol, tymol, and silver as well as those made of TCC and triclosan, with a P-value of = 0.546 (P>0.05).
ConclusionAntiseptic soaps containing chlorhexidine, parachlorometxylenol/chloroxylenol, TCC, and triclosan all were equally effective in reducing wound bacteria.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora