The 3rd International Nursing & Health Sciences Students & Health Care Professionals Conference (INHSP) 2019
Más datosThis study aims to determine the predictors of the patient safety culture outcomes in Jambi Province.
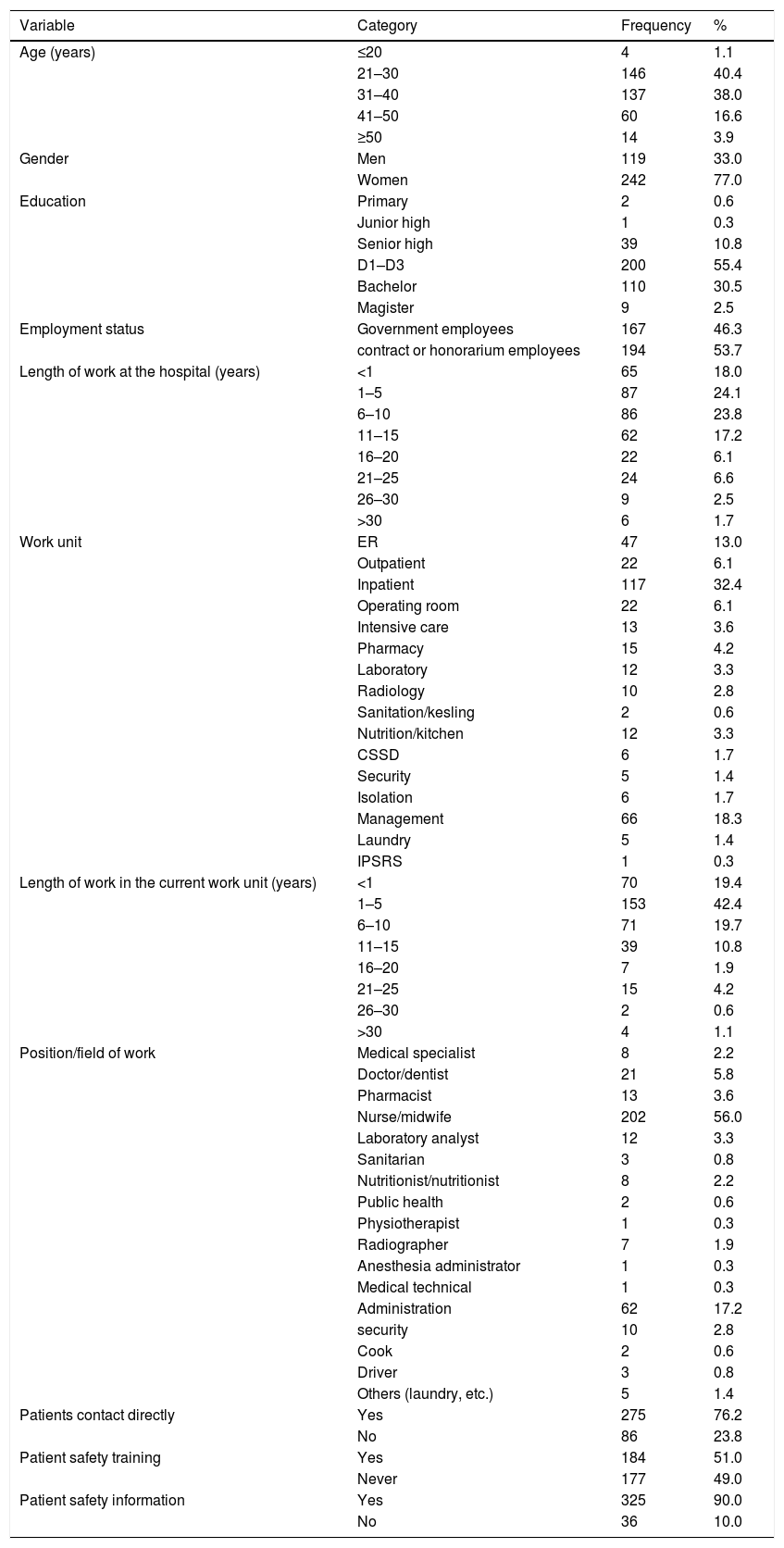
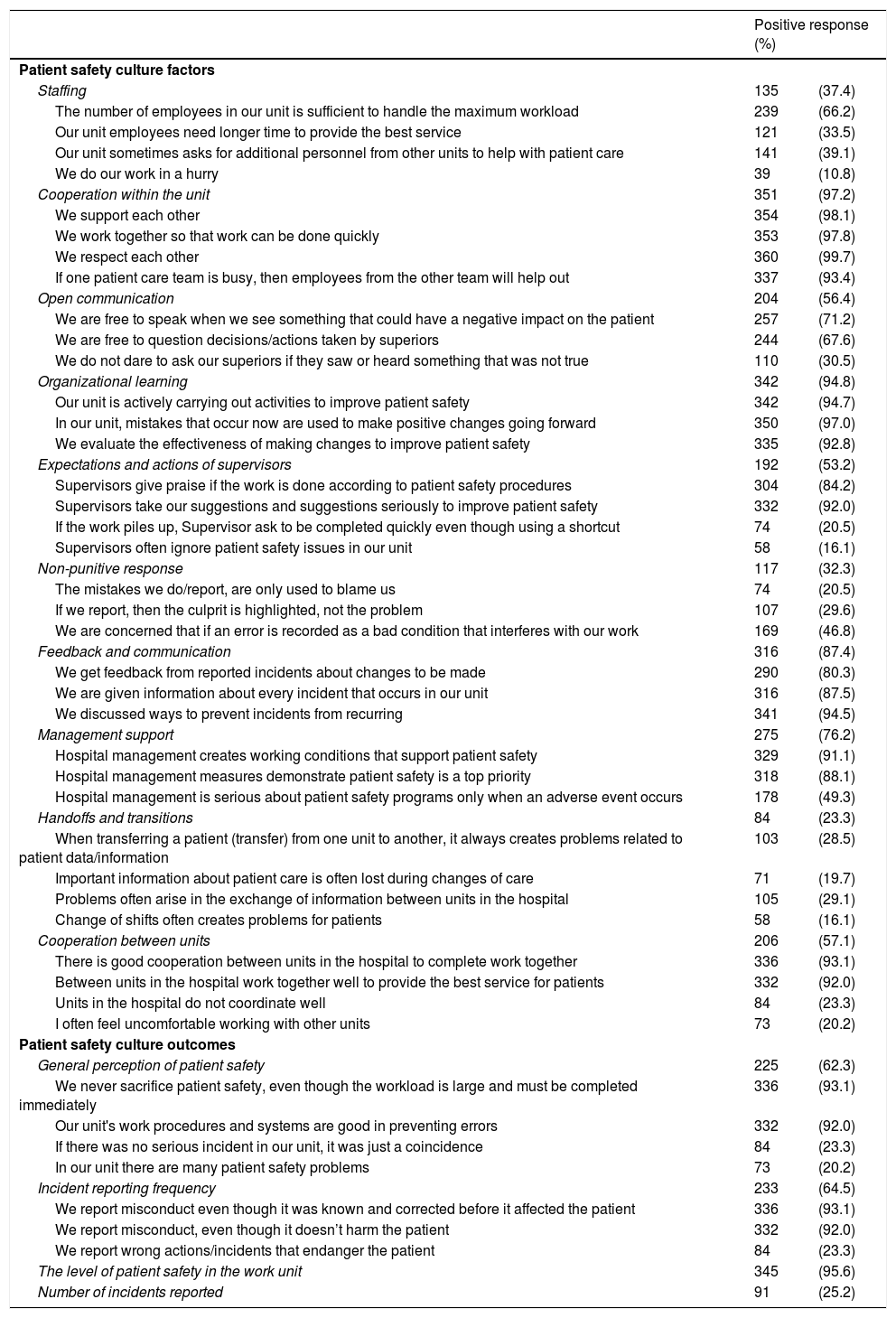
MethodsThe study design was cross-sectional through a survey using the Hospital Survey on Patient Safety Culture (HSOPSC) instrument developed by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ) on 361 samples, namely hospital employees ranging from doctors to administrative staff selected by proportional random sampling at two government hospitals in Jambi Province. This study analyzes factors including staffing, cooperation within units, open communication, organizational learning, supervisor expectations and actions, non-punitive responses, feedback and communication, management support, handovers and transitions, and collaboration between units in predicting outcomes. patient safety culture. Data analysis through Chi-square and multiple logistic regression.
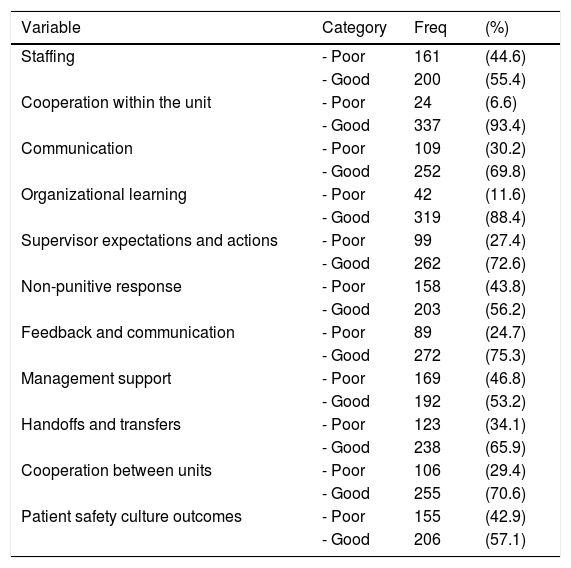
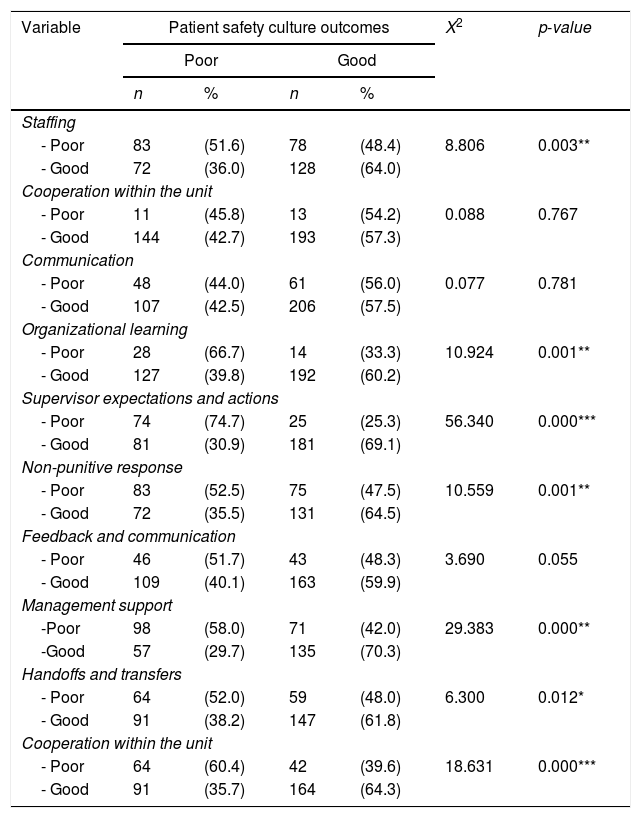
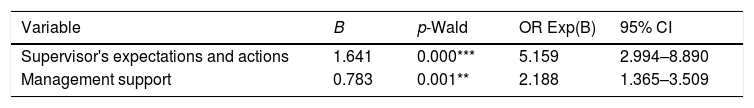
ResultsThis study found a good hospital patient safety culture outcome of 57.1%. Simultaneously, the factors that predict the outcome of the hospital patient safety culture are supervisor expectations and actions (OR=5.159, 95% CI=2.994–8.890) and management support (OR=2.188, 95% CI=1.365–3.509). Expectation factors and supervisor/manager actions are the main predictors of hospital patient safety culture in Jambi province.
ConclusionsMeasuring safety culture is an important means of designing and implementing patient safety improvement programs. The role of the supervisor must be further enhanced through providing motivation, education, consultation, monitoring and evaluation related to the implementation of patient safety programs in hospitals.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora