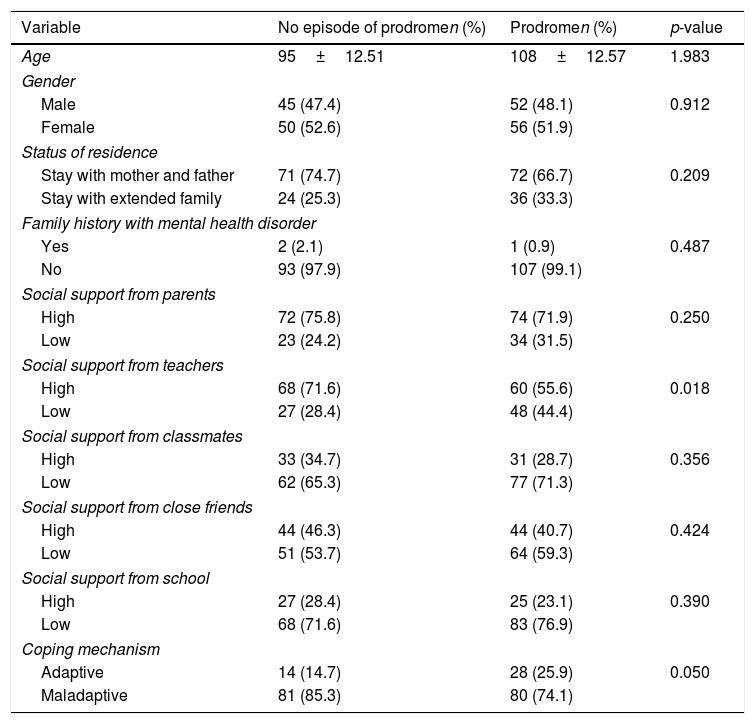
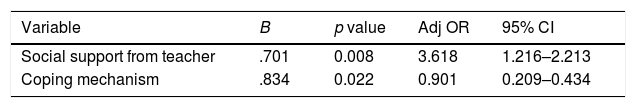
Maladaptive adjustments during adolescence could predispose to prodrome episodes such as anxiety, less confidence, worry, as well as inappropriate behaviors. This study is quantitative research with a cross-sectional design to identify factors associated with an episode of prodrome among junior high school students. The respondents were from Denpasar aged ≤15 years old and were collected through a random sampling technique, continued with sampling purposive technique to obtain 203 students. This study used questionnaires consisting of demography data, PQ 16, CASSS, and some of the coping mechanisms which in the last were analyzed statistically using chi-squared test and logistic regression analysis. Compared with other variables, this study assumed that low social support from teachers and teenagers’ maladaptive coping mechanism could become factors predisposing episode of prodrome in teenagers. Social support from teachers was the most influenced predisposing factor of prodrome episode with a value of 3.6% as well as coping mechanisms with a value of 0.9%. Therefore, teachers should give attention and support to teenagers to be able to develop adaptive coping mechanisms so that they could adapt to the stressors and are capable of responding appropriately when changes in the transitional stage from childhood to adulthood occur. Moreover, it is anticipated for teachers to help adolescents exploring their potential at schools. As a result, teenagers would spend their time mostly at school because it will help them to develop adaptive coping mechanisms.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora