4th International Conference for Global Health (ICGH) in conjunction with the 7th Asian International Conference in Humanized Health Care (AIC-HHC)
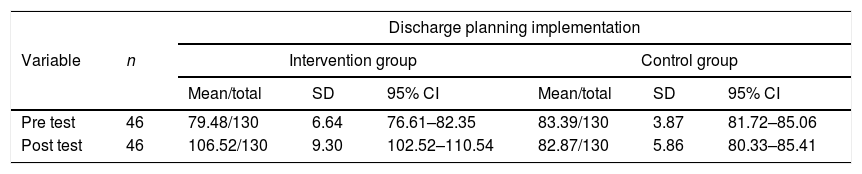
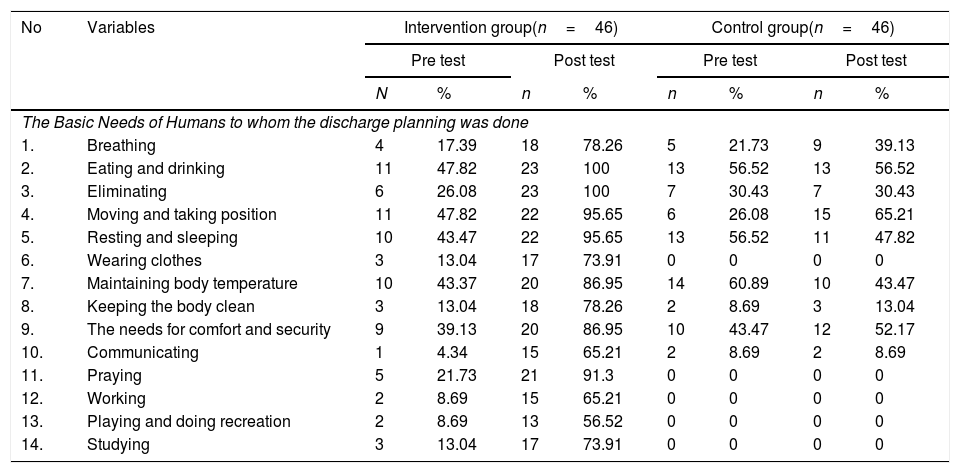
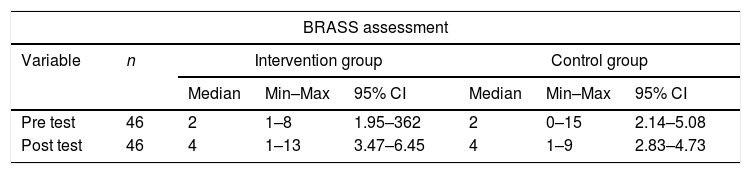
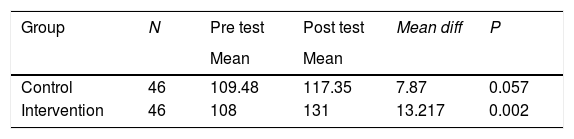
Más datosThe purpose of this study was to identify the effect of discharge planning management intervention on patient satisfaction and the role of nurses at the hospital. This study was a quasi-experimental study with 92 respondents. The intervention group was given a discharge planning management intervention by adding Blaylock Risk Assessment Screening Score (BRASS) and the control group was given discharge planning according to what was done in the hospital. Both groups measured patient satisfaction and role of nurses before and after the intervention. The results showed that discharge planning management intervention in the intervention group increasing patient satisfaction at the hospital (p=0.002) and the role of nurses especially in fulfilling 14 basic needs of humans (Henderson's Approach). Discharge Planning Management Intervention effectively increases patient satisfaction and the role of nurses.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora