3rd Aceh International Nursing Conference (AINC) “Strengthening Resilience from Pandemic Crisis Through Multidisciplinary Approaches
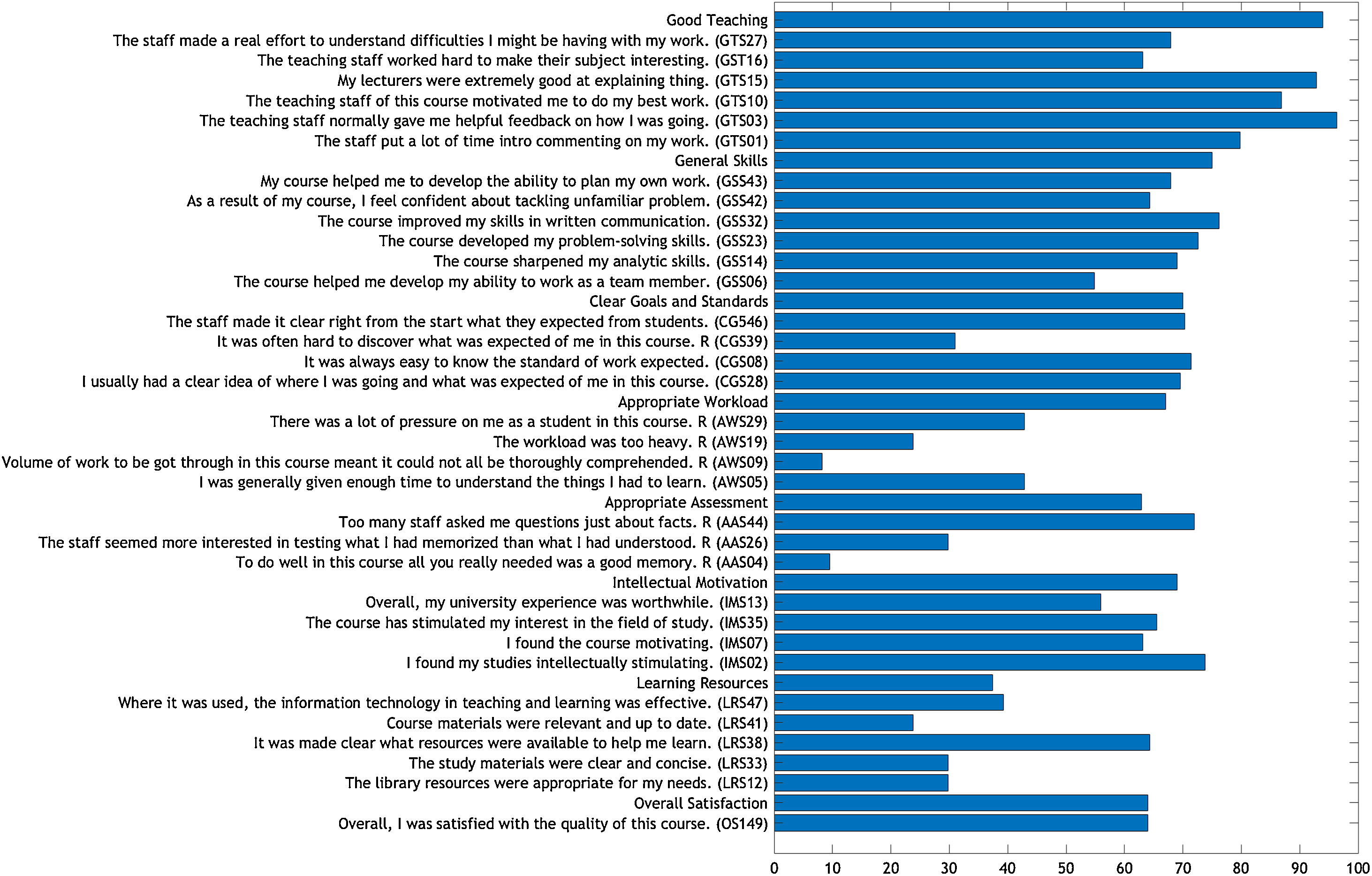
Más datosNursing students in Universitas Syiah Kuala using Problem Based Learning (PBL) worked in small groups to achieve learning outcomes by solving case studies in seven PBL steps. Although PBL is a popular educational method in the health profession, its effectiveness in helping students solve problems is debatable. The aim of this study is to assess the nursing students’ perception of teaching quality and their course satisfaction using the PBL approach. By using the proportional random sampling technique, a total of 84 students participated in this study. The Course Experience Questionnaire (CEQ) was employed. The CEQ consisted of 33 items which are grouped into eight domains of students’ teaching and learning experiences. For statistical data analysis, mean percentage agreement is counted from the Likert scale score. The results indicate that when the LRS components are negative, the GTS, GSS, CGS, AWS, ASS, and IMS are all positive. The GTS element has the highest mean percentage score of the eight CEQ elements. Two-thirds of PBL participants were satisfied with the PBL approach. Nevertheless, there are still some defects in the learning process, such as students’ perceptions that they don’t have enough time to understand a topic. Also, when learning topics are related to field facts, students are not ready to discuss them. The learning resources are severely limited. The use of e-learning must be properly managed, and students must be regulated in order to have the ability to find effective learning resources and share them with their peers.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora