4th International Conference for Global Health (ICGH) in conjunction with the 7th Asian International Conference in Humanized Health Care (AIC-HHC)
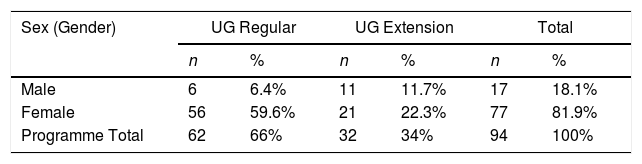
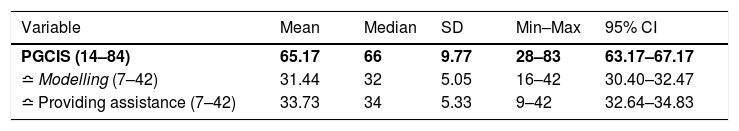
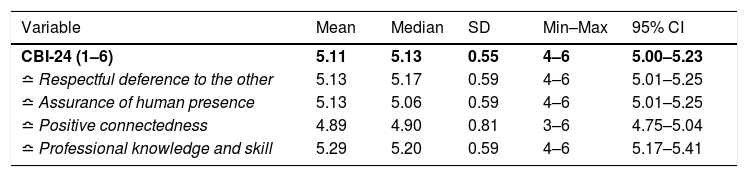
Más datosPeer is one of the contributing factors in developing nursing students’ caring behaviour. This research aims to determine the relationship between peers caring behaviour and nursing students’ caring behaviour. The cross-sectional study recruited 94 students from two nursing undergraduate programmes in Jakarta and Depok who selected using the simple random sampling technique. The study used the Peer-Group Caring Interaction Scale (PGCIS) and Caring Behaviours Inventory (CBI-24). Pearson test results showed a relationship between peer and student caring behaviours to patients (p<0.001) with a positive correlation (r=0.415). Therefore, better peer caring behaviour leads to an increased relationship between nursing internship students and patients. The study also found that modelling and positive connectedness needed to be improved in peer and student caring behaviour towards patients, respectively. Nursing education institutions needs to empower peers in developing a caring culture integrated with the curriculum and student activities.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora