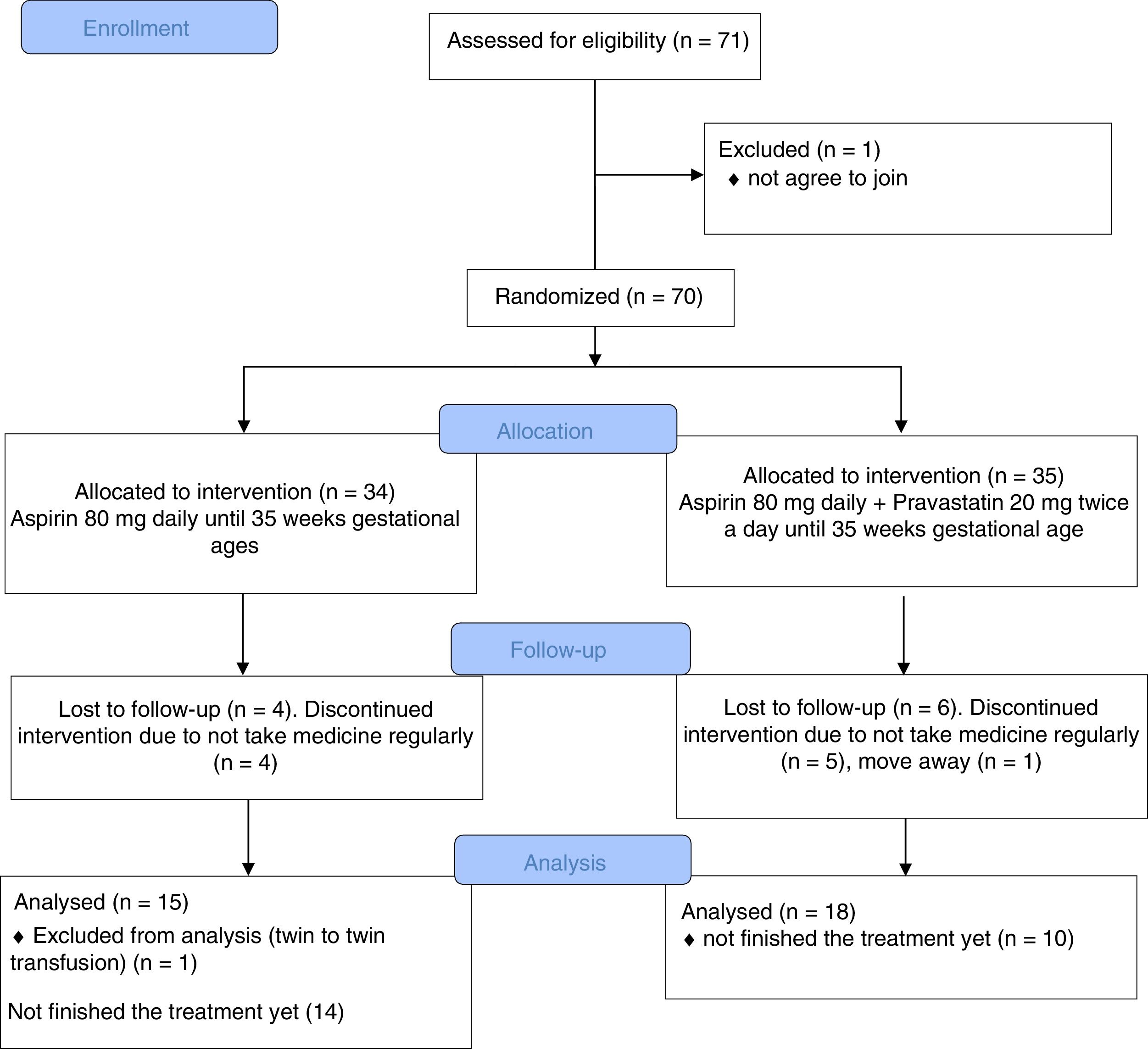
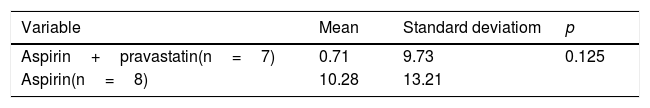
This study aimed to evaluate the effect of aspirin and pravastatin compared with aspirin on endothelin-1 levels, and the pregnancy outcome in pregnant women high risk for preeclampsia.
MethodsIt was a randomized clinical trial (RCT) analysis with block permutation. The sample divided into two groups. Group A as control has given aspirin 80mg and group B as an intervention group given aspirin 80mg plus pravastatin 20mg twice daily until 35 weeks gestation. Level of Endothelin-1 examined before and after treatment.
ResultsThere no differences found in endothelin-1 levels before and after being treated with aspirin or aspirin and pravastatin, as well as in the umbilical artery resistance index, fetal biometry, and the development of the fetus in two groups was typical at 28–32 weeks’ gestation. Similarly, no differences found in fetal outcomes such as preterm birth, fetal growth retardation, and the incidence of preeclampsia between the two groups.
ConclusionAs a conclusion, the administration of pravastatin, together with aspirin is no more effective than aspirin in preventing preeclampsia, to pregnancy outcome and decreasing endothelin-1 levels. No congenital abnormalities reported.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora