4th International Conference for Global Health (ICGH) in conjunction with the 7th Asian International Conference in Humanized Health Care (AIC-HHC)
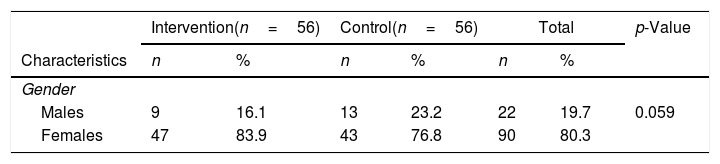
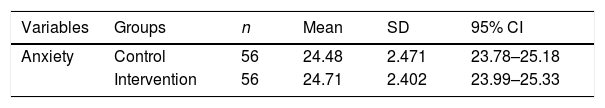
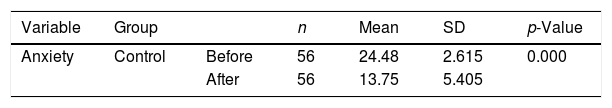
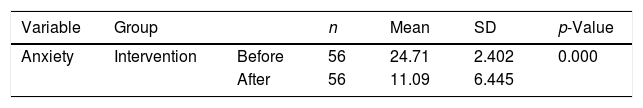
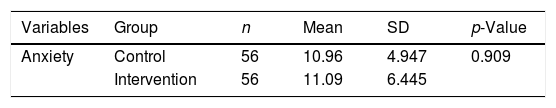
Más datosThe objective of the study is to determine the effect of thought-stopping therapy on anxiety levels in adolescents living in earthquake-prone areas. This study used quasi-experiment pre-post test with control group, conducted in one of the earthquake-prone areas city in East Java. 112 respondents (the control and the intervention group) were included in the research. Both groups received nursing intervention. In addition to the nursing intervention, the intervention group was asked to use thought-stopping techniques. The HAM-A questionnaire was used to determine anxiety levels. A significant decrease in anxiety in both the control and intervention groups was demonstrated in the present study after the intervention. The intervention group experienced a decrease in the anxiety rating of 5.54, compared to the corresponding decrease in the control group of 2.79. Nursing intervention and thought-stopping are recommended as effective in reducing anxiety in adolescents living in earthquake-prone areas.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora