To determine the effect of thought stopping therapy (TS) and nursing intervention (NI) for changes in the ability to control negative thoughts associated with earthquakes.
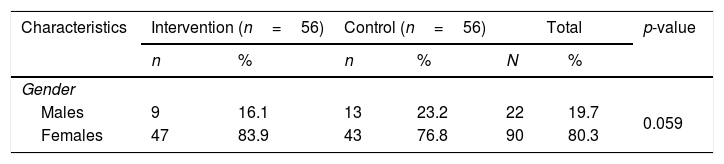
MethodThe design of this study was used a quasi-experimental study with pretest–posttest control groups and conducted in East Java-Indonesia. 112 respondents divided into intervention and control group. Intervention group were given NI and TS and control groups were given NI only. The questionnaire used in this study was valid and reliable.
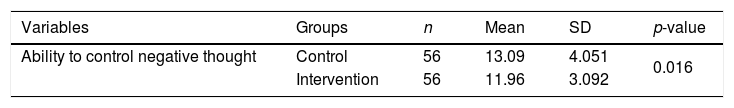
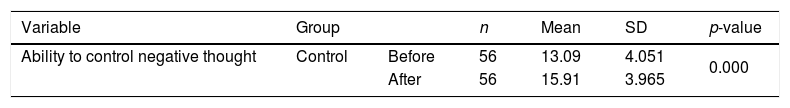
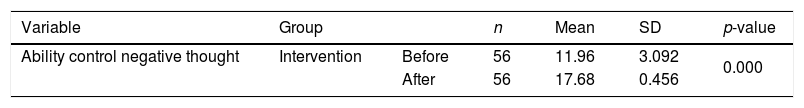
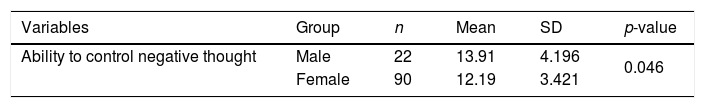
ResultData analysis included univariate and bivariate. There was a significant increase in the ability of adolescents to control negative thoughts related to earthquakes in both groups (control and intervention). The score of the ability to control negative thoughts in the intervention group increased 5.72 points while the control group only gained 2.82 points.
ConclusionNI and TS are recommended as effective strategy for controlling the adolescents negative thought related to earthquake.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora