This study aims to explore the experiences of TB-DM patients for the service barriers encountered in achieving the expected outcomes.
MethodA qualitative study was conducted between June-August 2019. TB-DM patients were identified from community health centers, and hospital TB registers Yogyakarta City, Indonesia. Fourteen adult TB-DM patients were purposively selected using criterion sampling. They were those who had been cured or already completed the intensive phase of TB treatment from 2018 to 2019. In-depth interviews were carried out using interview guides and tape-recorded. Thematic analysis was used to analyze the verbatim transcripts.
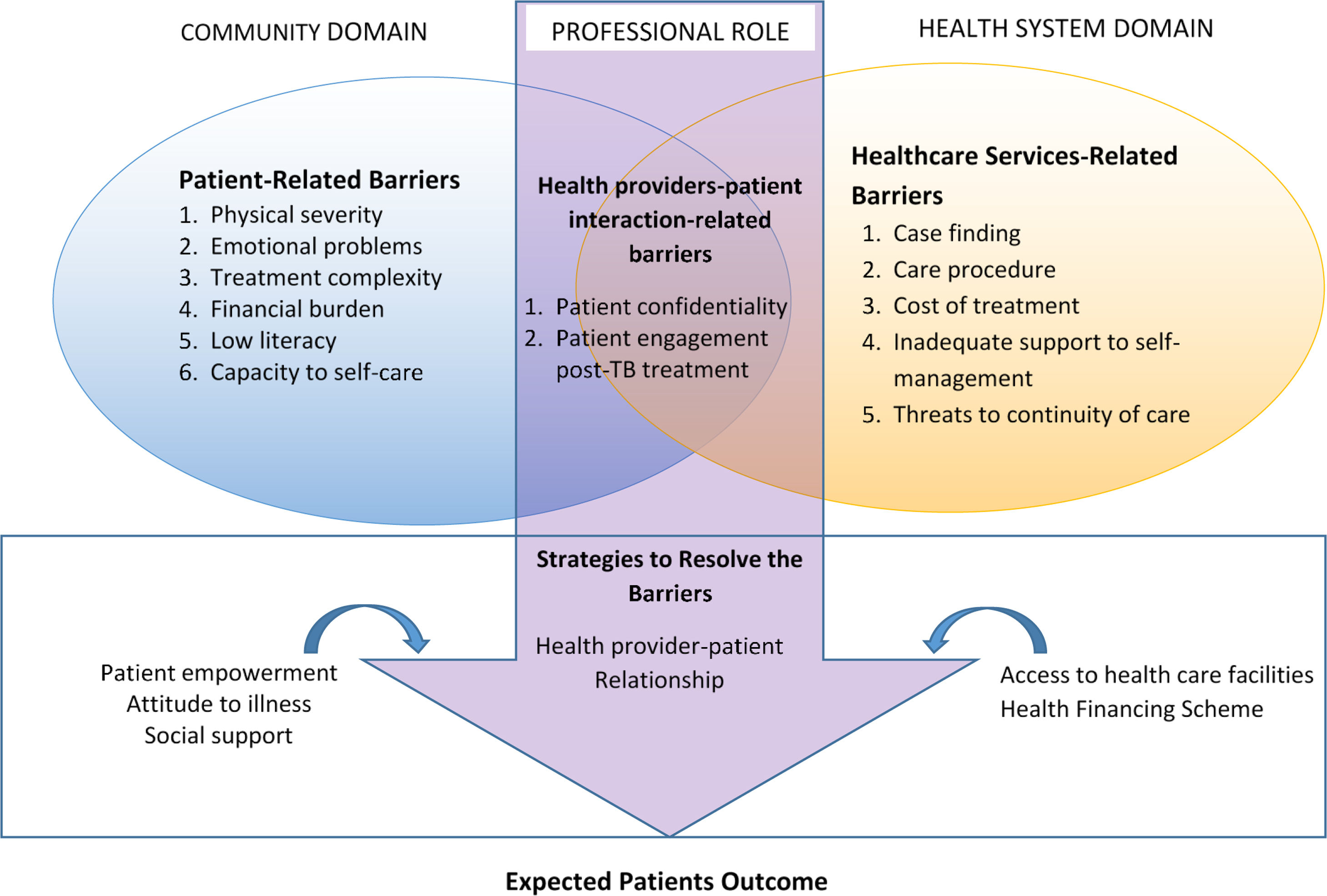
ResultsFour themes were identified: health services-related barriers, patient-related barriers, health provider-patients interaction-related barriers, and strategies to resolve the barriers.
ConclusionTB-DM patients faced a cascade of barriers with accessing TB-DM care and supports. Re-orienting the health care system for more integrated chronic care readiness and improving patients’ capacity is critical to improving the quality of care.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora