Was to analyze the perception and self-care behavior of diabetic patients by using a nurse–patient transaction model based on the King's theory of the goal attainment.
MethodDescriptive analytical study design was used in this study. Fifty diabetics patients who met the inclusion criteria were recruited from three health center in Medan. Summary of Diabetes Self-Care Activities (SDSCA) and the assessment tool base on King's theory of goal attainment were used to measure of perception and self-care behavior. Distribution and frequentation were completed to describe perception and self-care behavior of diabetic patients.
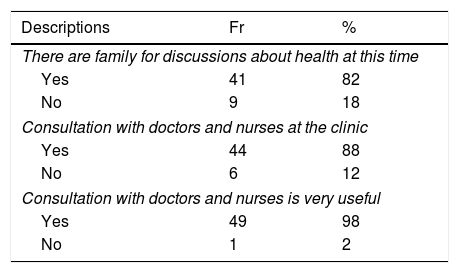
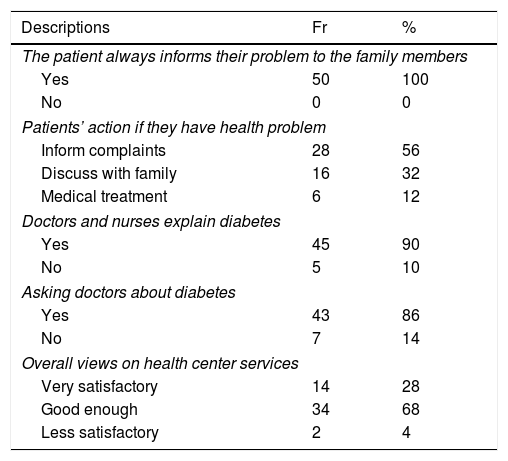
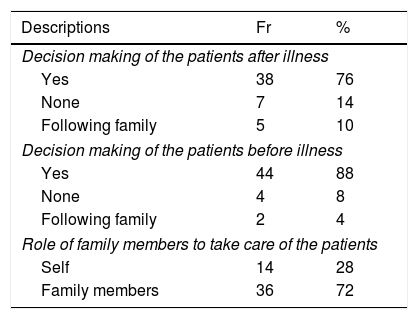
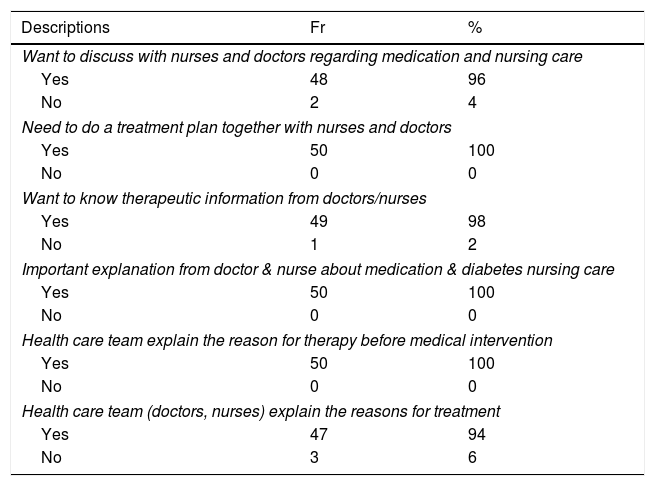
ResultsThere were 46% patients perceived that they are healthy, even though most of them have experienced complications. Most of the patients (98–100%) reported that interaction with others is needed to maintain their health. The following was a description of the patient's decision making related to diabetes 88% of the patients did before illness. The majority of respondents communicate and convey diabetes problems faced to the family (86–90%). The patient's transaction 96% want to discuss with nurses and doctors for treatment programs and therapy information (98%).
ConclusionThe nurse–patient transactions model based on King's could be appropriate to improve perception and self-care behavior of diabetic patients aged 21–59 years old in the primary care unit.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora