Patients in palliative care are found in different places where care is provided, including the intensive care environment with important role of the nursing staff.
ObjectiveThe aim of this systematic review was to answer the following question: which nursing interventions are aimed to the palliative care patients who are in the intensive care unit (ICU).
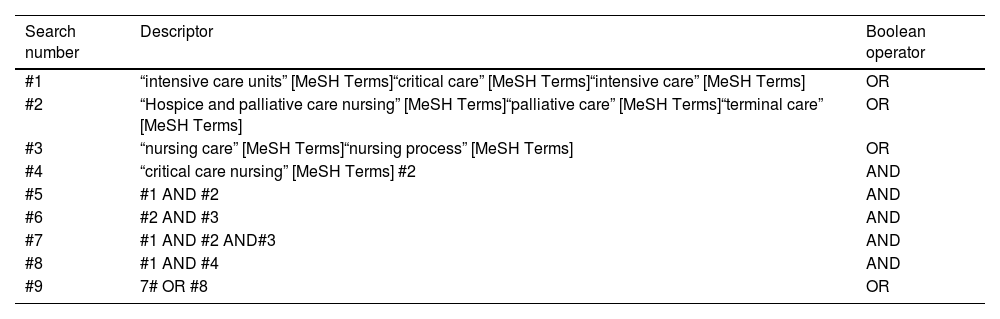
Data sourcesUS National Library of Medicine (PUBMED), Virtual Health Library (BVS), SciELO, The Cochrane Library (Cochrane) and Lilacs databases were used.
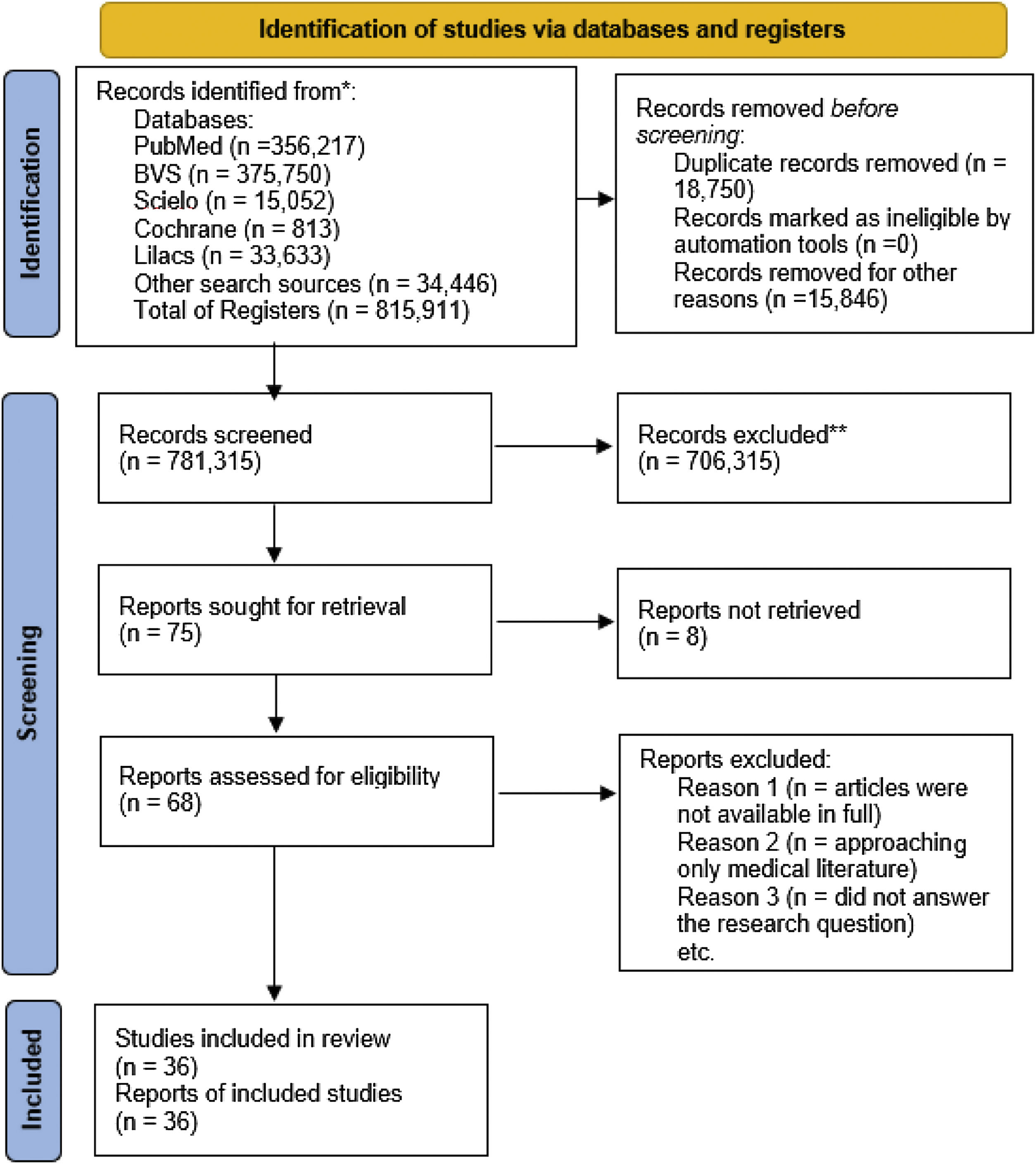
Data extractionAfter applying inclusion and exclusion criteria in accordance with the PRISMA method, a total of 36 entries published between 2010 and 2020 were used.
Data analysisThe records extracted were analyzed from a qualitative approach, so no statistical analysis was carried out.
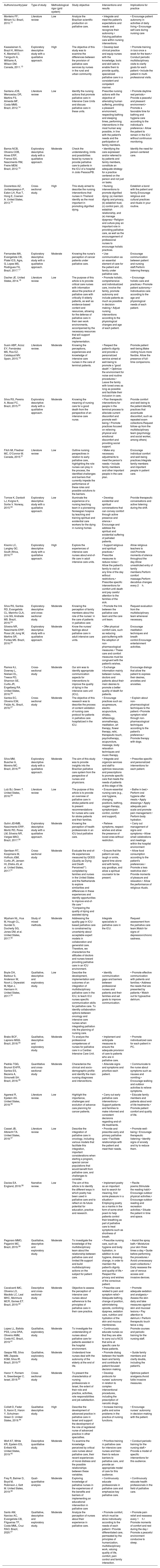
ResultsThe findings demonstrated that the interventions that focus on promoting the patient's autonomy and respect their needs on ICU involves effective communication, promoting shared decision with patient and family, individualize care for each patient including the family on the daily care and decisions, maintaining basic nursing care as hygiene and comfort and encouraging self-care, as well as the involvement of nursing palliative care specialists the care is important. Other interventions included promoting a continuing education program for the nursing staff and other professionals involved in caring for patients in palliative care at ICU.
ConclusionThis review highlighted the need for specific nursing interventions aimed at palliative care patients at ICU to promote patient autonomy and the focus on patient needs, always sharing decisions with the patient and family. However, it showed that there is a need for the continuous training of the nursing staff because factors such as the nurses’ lack of technical-scientific knowledge and, concomitantly, the absence of a standardized and specific intervention model linked to a bureaucratic system, make it difficult to carry out a specialized care for this type of patient.
Los pacientes en cuidados paliativos se encuentran en varios lugares, incluso en cuidados intensivos, y las enfermeras tienen un papel importante en el cuidado de este tipo de pacientes.
ObjetivoEsta revisión sistemática buscó responder a la siguiente pregunta: ¿Cuáles son las intervenciones de enfermería dirigidas a los pacientes en cuidados paliativos en la unidad de cuidados intensivos (UCI)?
Fuentes de datosBiblioteca Nacional de Medicina de EE. UU. (PUBMED), Biblioteca Virtual de Salud (BVS), SciELO, The Cochrane Library y Lilacs.
Extracción de datosAplicación de los criterios de inclusión y exclusión según el método PRISMA, totalizando 36 estudios publicados entre 2010 y 2020.
Análisis de datosLos datos extraídos se analizaron con un enfoque cualitativo, por lo que no se realizó ningún análisis estadístico.
ResultadosLas intervenciones que promueven la autonomía del paciente y respetan sus necesidades en la UCI involucran: comunicación efectiva, decisión compartida de individualizar el cuidado e incluir a la familia en el cuidado. Se debe mantener la higiene, el confort y la promoción del autocuidado, involucrando equipos de especialistas en cuidados paliativos, impulsando programas de educación continua para enfermeras de cuidados intensivos y otros profesionales implicados.
ConclusiónSon necesarias intervenciones enfermeras dirigidas a pacientes con cuidados paliativos en la UC para promover la autonomía y satisfacer las necesidades del paciente, compartiendo siempre las decisiones con el paciente y su familia, y asimismo es necesaria la formación continua de las enfermeras en factores como el desconocimiento técnico-científico de este colectivo y, concomitantemente, la ausencia de un modelo estandarizado de intervención vinculado a un sistema burocrático. Todo ello dificulta la atención especializada a este tipo de pacientes.
Artículo
Diríjase al área de socios de la web de la SEEIUC, (https://seeiuc.org/mi-cuenta/iniciar-sesion/) y autentifíquese.