The presence of substantial evidence regarding the association between dietary niacin intake and cognitive impairment among the elderly remains limited, with inconsistent findings. Thus, the objective of this study was to assess the aforementioned relationship, utilizing data obtained from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES).
MethodsThis cross-sectional study analyzed 2255 participants aged ≥60 years from NHANES 2011–2014.The assessment of dietary niacin intake was conducted through two 24-hour dietary recalls, while cognitive function was evaluated using a battery of five tests. Multivariable logistic regression models and generalized additive model (GAM) was utilized to investigate the association between dietary niacin intake and cognitive impairment. Furthermore, subgroup analysis was conducted to assess the robustness of the primary findings.
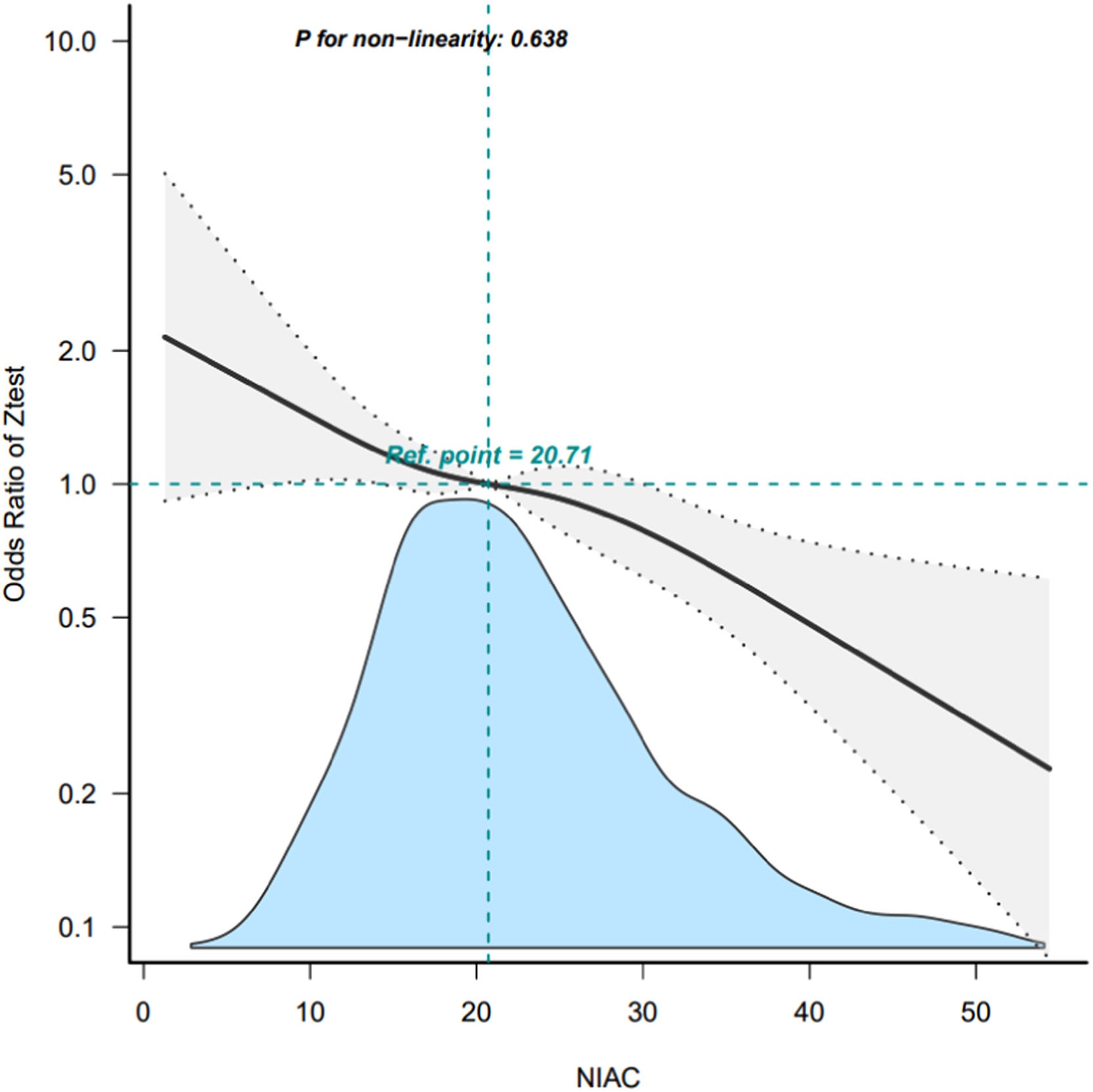
ResultsA total of 2255 old adults were included in this study, of whom 47.9% were male. In the fully adjusted model, we observed a significant inverse association between dietary niacin intake and cognitive decline [as a quartile variable, Q4 vs. Q1, odds ratio (OR):0.5 and 95% confidence interval (CI): (0.35∼0.72), p < 0.001; as a continuous variable, per 1 mg/day increment, OR (95%CI):0.97(0.95∼0.98), p < 0.001].The smooth curve fitting results revealed that A linear relationship was found between niacin intake and cognitive impairment in elderly people. The results of the sensitivity analysis remained stable.
ConclusionsDietary niacin intakes might be inversely associated with the prevalence of cognitive impairment. Further research is required to confirm this association.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora