Supporting the neurodevelopmental model of schizophrenia, minor physical anomalies (MPAs) are markers of abnormalities in early fetal development. The mouth seems to be a common region for the occurrence of MPAs in patients with schizophrenia. This study aimed to compare the palatal rugae patterns, according to their length, shape, and orientation, between patients with schizophrenia and controls in a blinded fashion. The palatal rugae patterns were also evaluated by sex, as its effect on neurodevelopment was relevant.
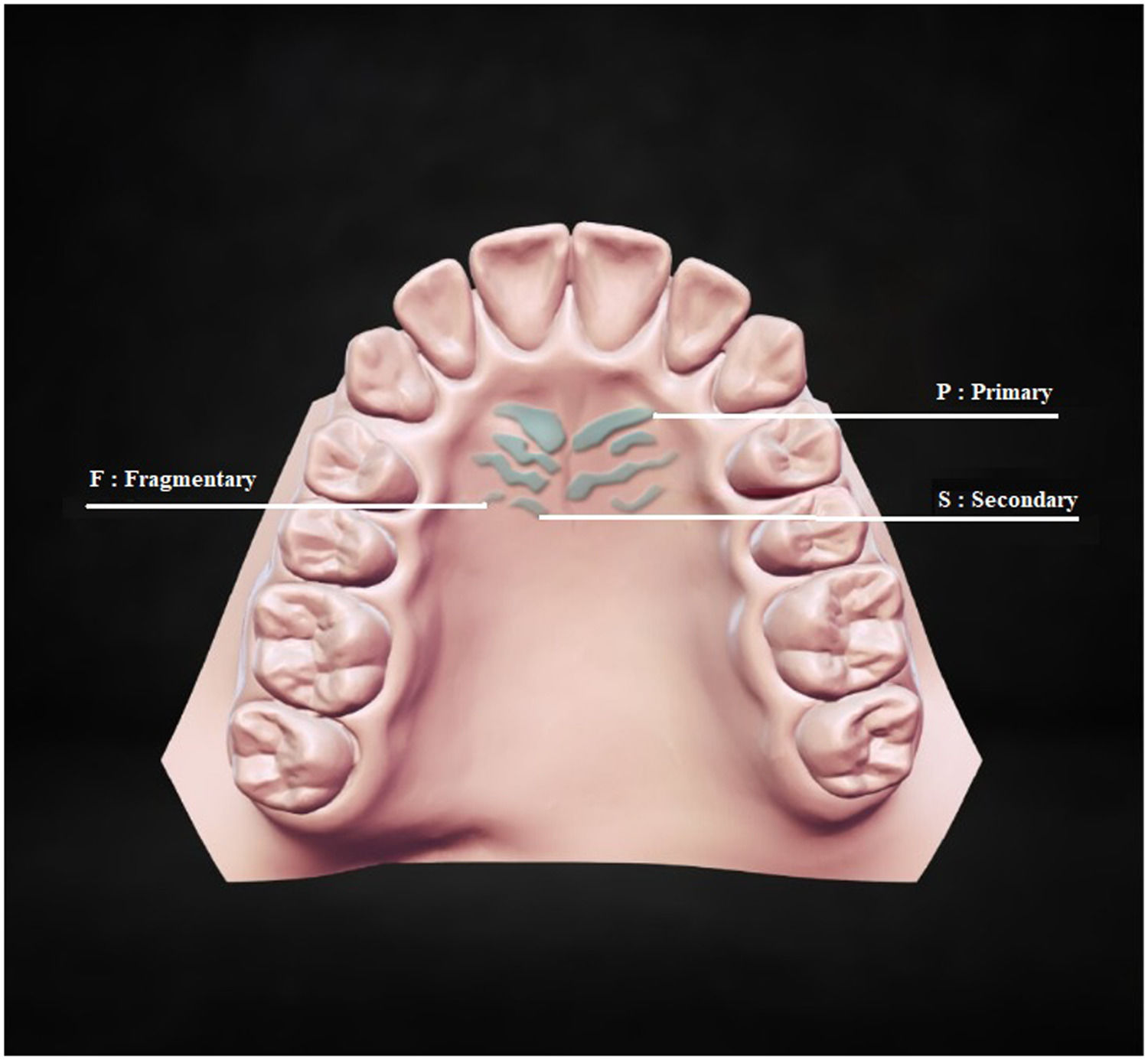
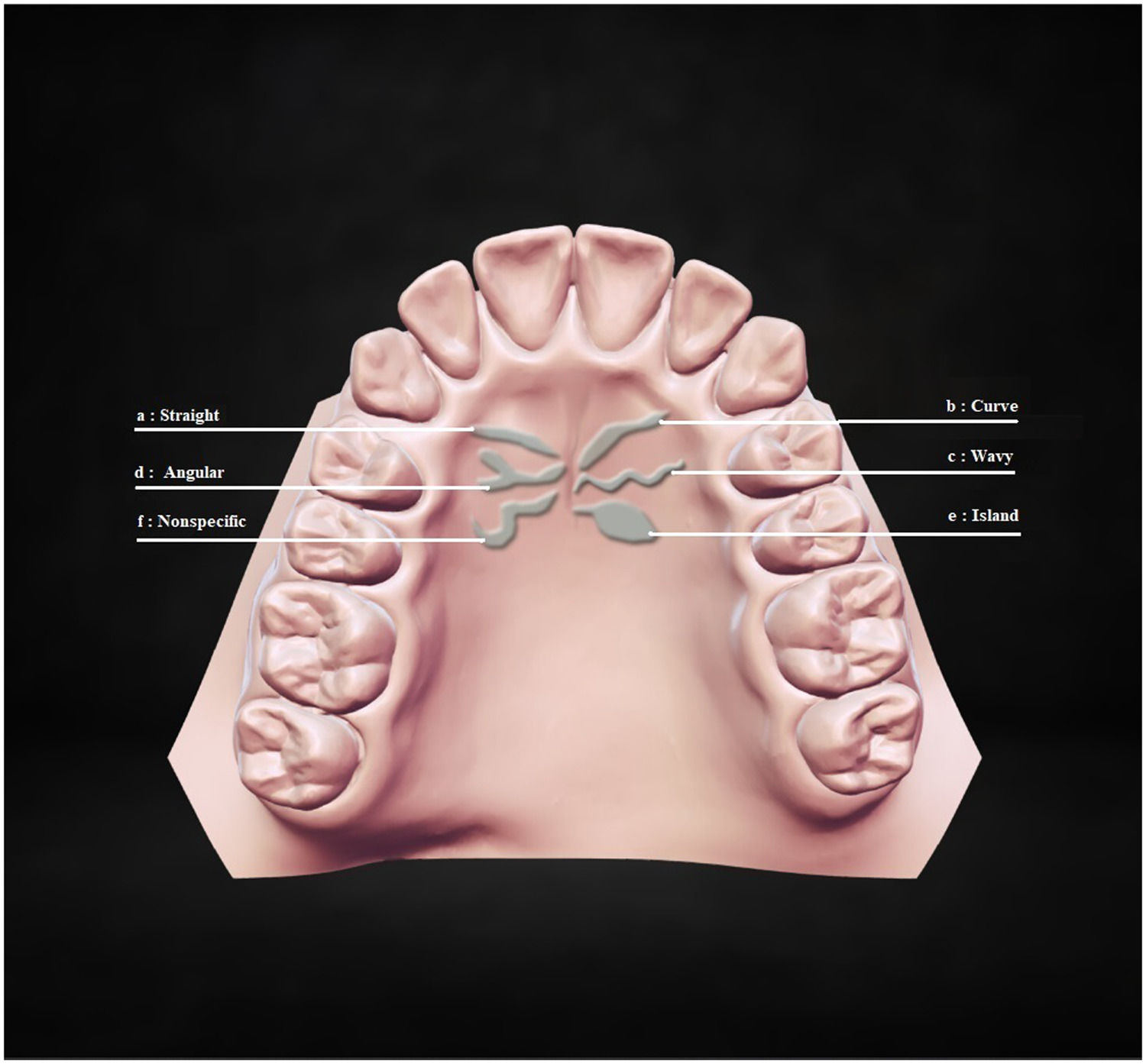
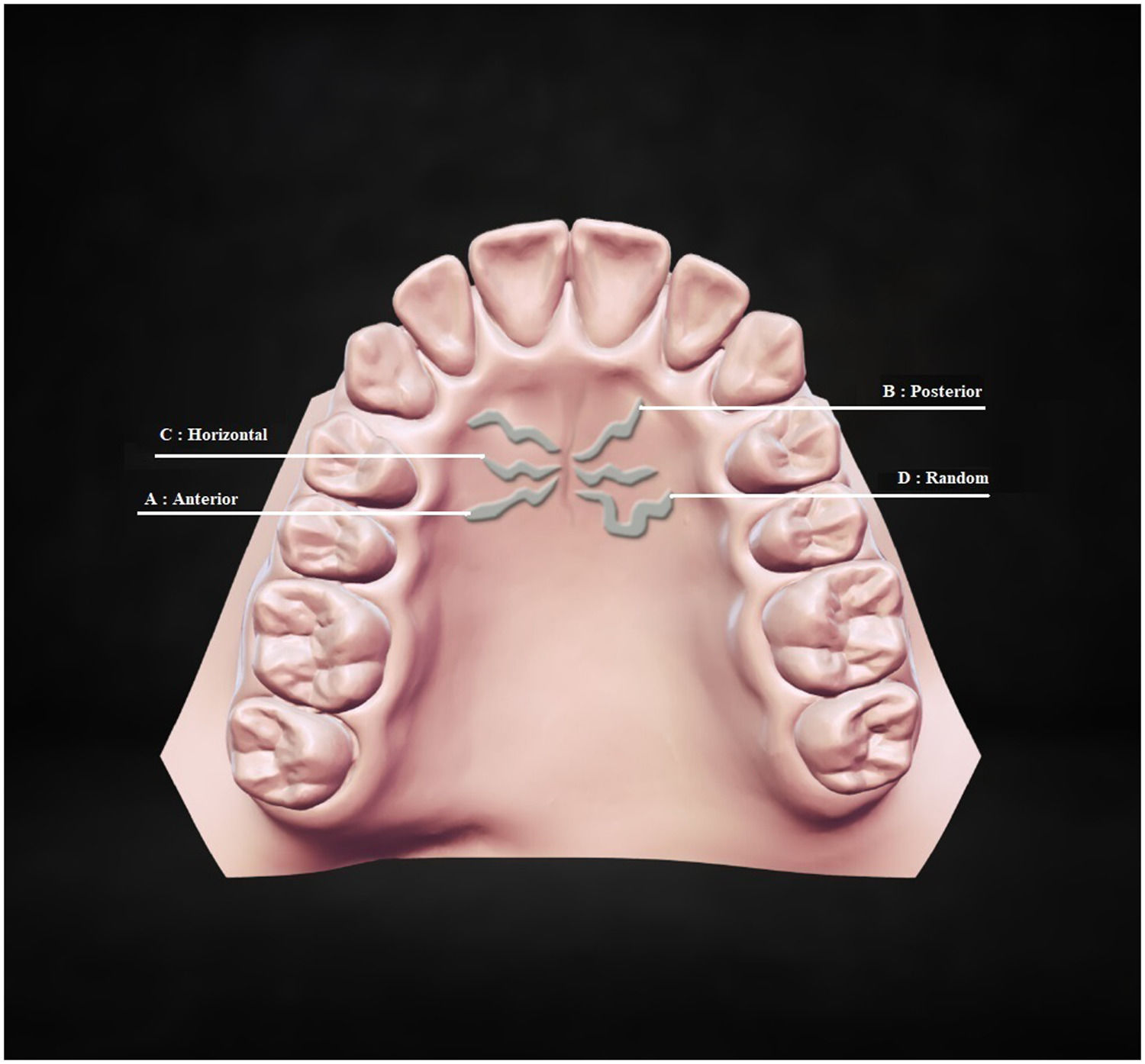
MethodsDental stone models were fabricated from maxilla impressions of patients with schizophrenia (N = 105) and controls (N = 105). Based on their lengths, three types of palatal rugae were classified; primary, secondary, and fragmentary. Primary rugae were further categorized according to their shape and direction.
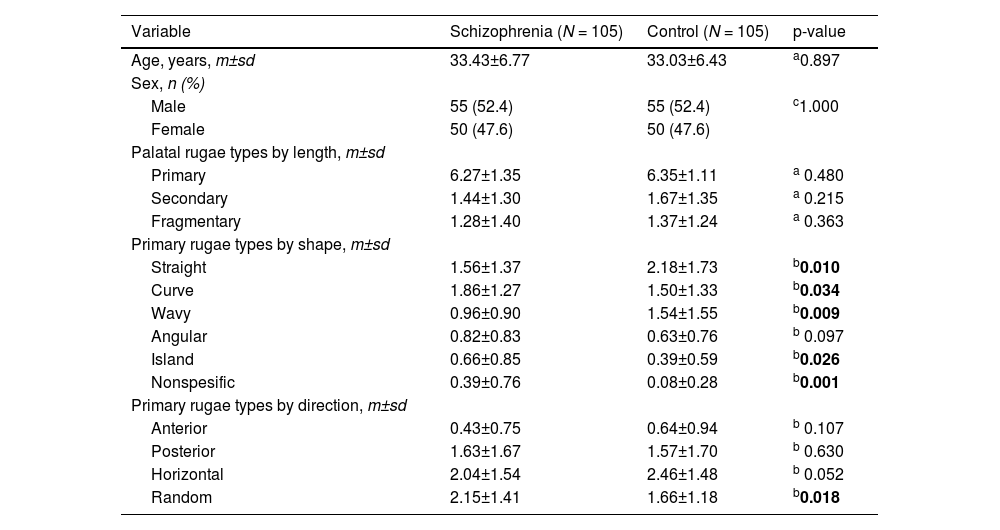
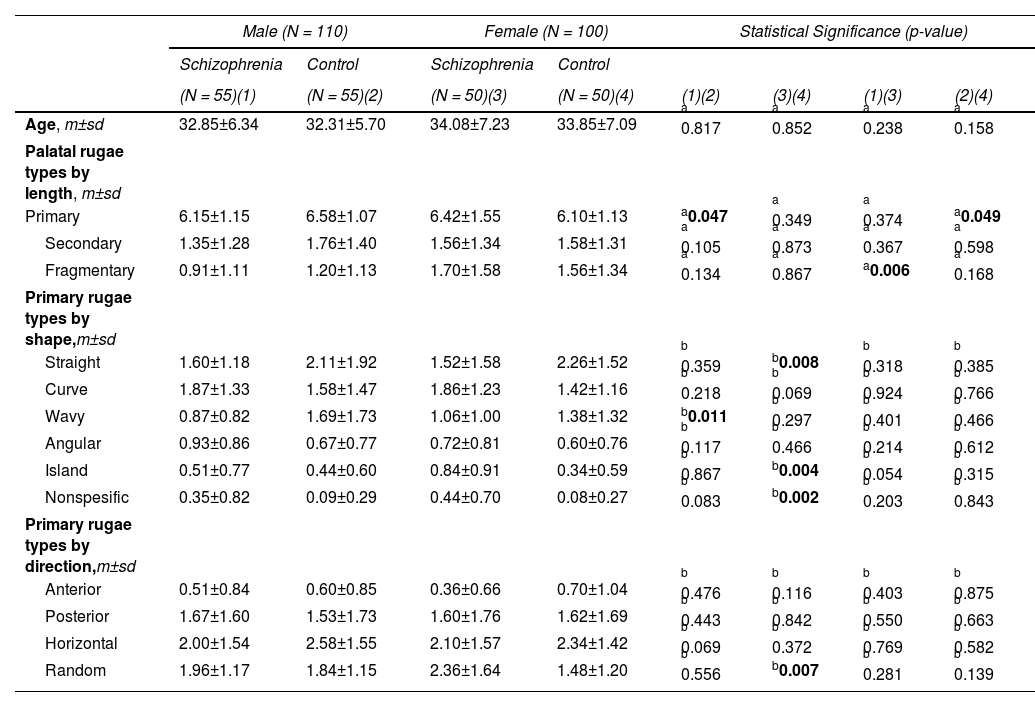
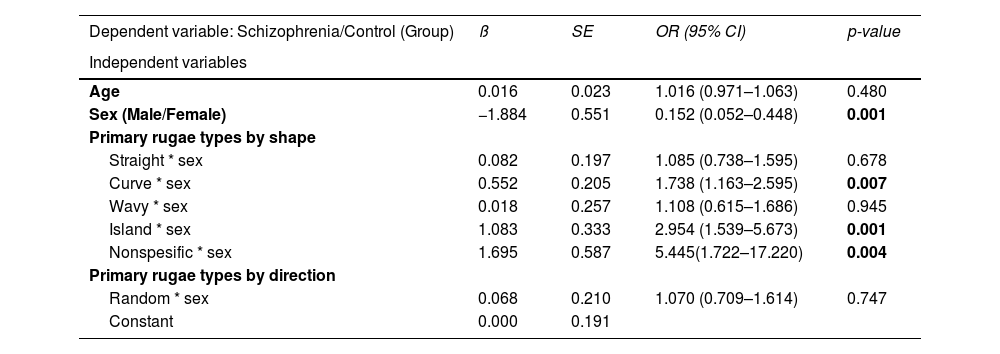
ResultsThe most detected palatal rugae were the primary ones in both groups. The primary, secondary, and fragmentary rugae numbers in both groups were no different. There were significant differences in the shape and orientation of the primary rugae between the two groups. Curved (OR:1.76, p = 0.006), island (OR:2.97, p = 0.001) and nonspecific (OR:5.44, p = 0.004) primary rugae shape were found to be significant predictive variables for schizophrenia. Randomly oriented rugae numbers were higher in schizophrenics than controls (p = 0.018). The two sexes had different preferences in primary rugae shapes and directions compared to same-sex controls in patients with schizophrenia.
ConclusionIdentifying subtle changes in the primary rugae pattern, which appear to be sex-specific, is consistent with impaired neurodevelopment in schizophrenia.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora