Comprobar la eficacia de un tratamiento de fisioterapia perineal en mujeres con incontinencia urinaria (IU). Se buscó determinar la mejoría objetiva y la percepción de la calidad de vida, así como la relación entre dicha mejoría y el cumplimiento posterior del tratamiento en domicilio.
Pacientes y métodosEstudio observacional prospectivo: 46 mujeres con IU que reciben tratamiento de fisioterapia perineal durante el año 2010. Las pacientes fueron evaluadas antes del tratamiento y a los 3 meses. Se analizaron tanto variables objetivas (analizadas con el test de la t de Student) como subjetivas.
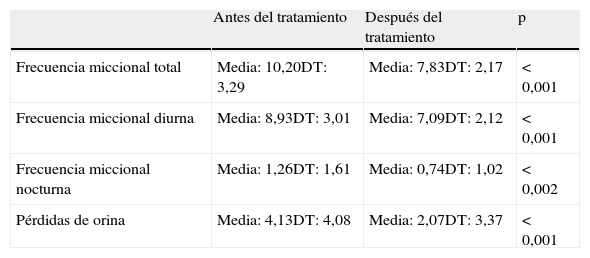
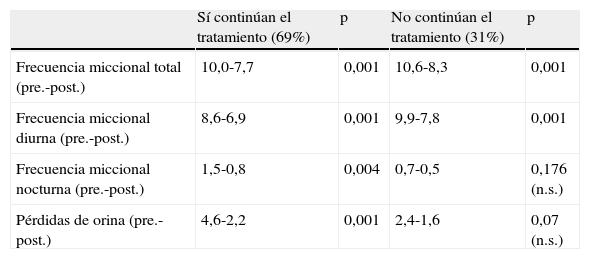
ResultadosSe observó que la realización de los ejercicios abdominoperineales en el domicilio disminuyó significativamente (p<0,001) las variables objetivas (frecuencias miccionales total, diurna y nocturna, y frecuencia de pérdidas de orina), especialmente el número de pérdidas de orina (reducción del 52%). Por el contrario, las pacientes que no realizaron los ejercicios mejoraron (p<0,001) solo en las variables relacionadas con la reeducación de hábitos miccionales (frecuencias miccionales total y diurna). Se demostró que dos tercios de las mujeres tenían percepción de mejoría tras la realización de los ejercicios abdominoperineales.
ConclusionesLas pacientes con IU que recibieron el tratamiento de fisioterapia perineal presentaron una mejoría objetiva y subjetiva. Su eficacia está relacionada con la continuidad en el tiempo en la realización de los ejercicios abdominoperineales.
This study aimed to verify the efficacy of perineal physiotherapy in women suffering from urinary incontinence (UI). It was aimed to determine objective improvement, perception of improvement in the quality of the patient's life, and the relation between said improvements and subsequent treatment compliance in the home.
Patients and methodsA prospective observational study was performed in a sample of 46 female patients suffering from UI who received perineal physiotherapy during 2010. Patients were assessed before receiving treatment and again three months after initiation of treatment. Objective (analyzed with the Student's T test) and subjective variables were analyzed.
ResultsOur study has shown that implementation of the abdominoperineal physical exercises in the home significantly decreased (P<.001) objective indicators of UI (total voiding frequency, daytime voiding frequency, nighttime voiding frequency, urine leakage frequency), especially the number of urine leakage which showed a 52% reduction. On the contrary, patients unwilling to implement the prescribed physical exercises at home only experienced improvement (P<.001) in the indicators related to the reeducation of their voiding habits (total voiding frequency, day-time voiding frequency). The study also showed that 2/3 of the sampled patients perceived some improvement after having completed their abdominoperineal physical exercises.
ConclusionsUI patients receiving perineal physiotherapy experienced both objective and subjective improvement in their condition. The efficacy of the treatment is apparently a function of the patients’ perseverance to carry out the prescribed abdominoperineal physical exercises over time.
Artículo
Si ya tiene sus datos de acceso, clique aquí.
Si olvidó su clave de acceso puede recuperarla clicando aquí y seleccionando la opción "He olvidado mi contraseña".Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora