Los objetivos del estudio fueron analizar la calidad de vida de pacientes asmáticos, evaluada mediante un instrumento genérico y otro específico, así como comprobar la correlación entre ambos.
Material y métodoEstudio trasversal, descriptivo y observacional en el que participaron 51 asmáticos adultos (26 varones y 25 mujeres) con edad media de 54,46 años (SD 19,17 años), todos reclutados a partir de las consultas externas del Hospital Universitario de Salamanca, entre octubre de 2008 y marzo de 2009. Se realizó una evaluación clínica inicial que incluía una espirometría, formulario sociodemográfico y la aplicación de las versiones españolas del World Health Quality of Life-Bref (WHOQOL-BREF) y del Saint George Respiratory Questionnaire (SGRQ).
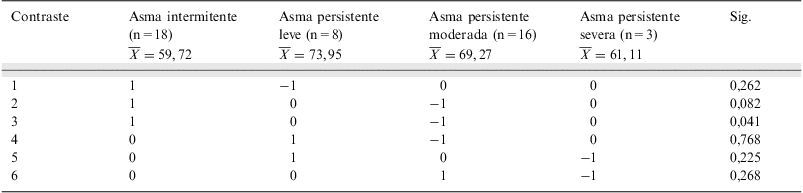
ResultadosLa edad correlacionó de forma inversa y significativa con todos los dominios del WHOQOL-BREF y solo con el dominio actividad del SGRQ. La clasificación de la gravedad y el volumen espiratorio forzado (FEV1%pred) no presentaron relación con ninguno de los dominios de ambos instrumentos. Los dominios físico y psíquico del WHOQOL-BREF correlacionaron de forma inversa y significativa con todos los dominios del SGRQ.
ConclusionesPese a la falta de relación entre la gravedad del asma y los distintos dominios del WHOQOL-BREF, el instrumento ha resultado ser sensible a la variable edad, y 2 de sus 4 dominios han correlacionado con todos los dominios del SGRQ.
This study has aimed to analyze the quality of life of asthmatic patients, evaluated by one generic and another specific instrument as well as to verify the correlations between them.
Material and methodsA cross-sectional, descriptive and observational study with 51 adult asthmatic subjects (26 men and 25 women) with a mean age of 54.46 years (SD 19.17 years), all recruited from the out-patient clinic of the University Hospital of Salamanca, Spain, from October 2008 to March 2009. A clinical evaluation was performed, this including the spirometry, a socio-demographical form and the application of the Spanish version of the World Health Organization Quality of Life (WHOQOL-BREF) and the Saint George Respiratory Questionnaire (SGRQ).
ResultsAge correlated inversely and significantly with all the WHOQOL-BREF domains and only with the activity domain of the SGRQ. The severity classification and forced expiratory volume (FEV1%pred) did not show any relationship with any of the domains of both instruments. The physical and psychic domains of the WHOQOL-BREF correlated inversely and significantly with all the SGRQ domains.
ConclusionsIn spite of the lack of relation between asthma severity and the different domains of the WHOQOL-BREF, the instrument is sensitive to the age variable and two of its four domains have correlated with all of the SGRQ domains.
Artículo
Si ya tiene sus datos de acceso, clique aquí.
Si olvidó su clave de acceso puede recuperarla clicando aquí y seleccionando la opción "He olvidado mi contraseña".Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora