Ensuring participation and adherence to exercises in the clinic poses a challenge for physiotherapists. This study was designed to identify the type and factors that influence participation and adherence to exercises by patients with knee osteoarthritis (KOA).
Material and methodThis quasi-experimental study randomized 105 patients referred for physiotherapy for KOA into three groups. Patients were required to exercise either aerobically using a cycle ergometer, strengthening exercises using weights and a quadriceps bench or stretching exercises on a gymnasium mat. The exercises were over 5 weeks, 3 times per week and of 30min duration per session. The Self-Report Scale of Adherence to Physiotherapy was used to determine adherence to exercises and modified 12-item questionnaire for factors influencing adherence. Data were depicted using descriptive and inferential statistics with p<0.05 statistical significance.
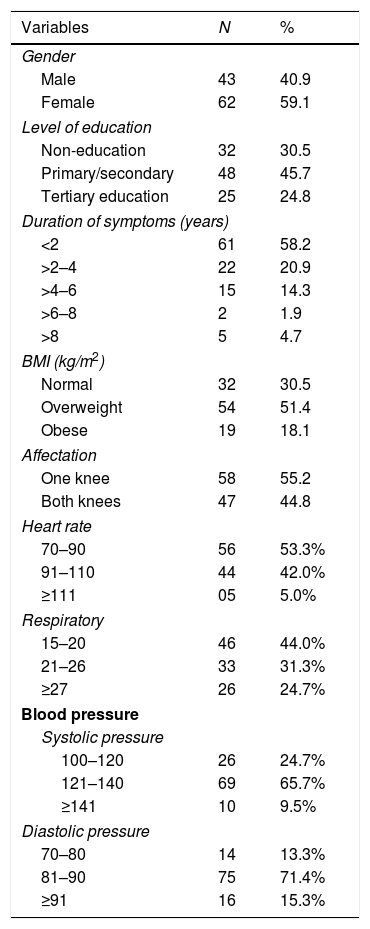
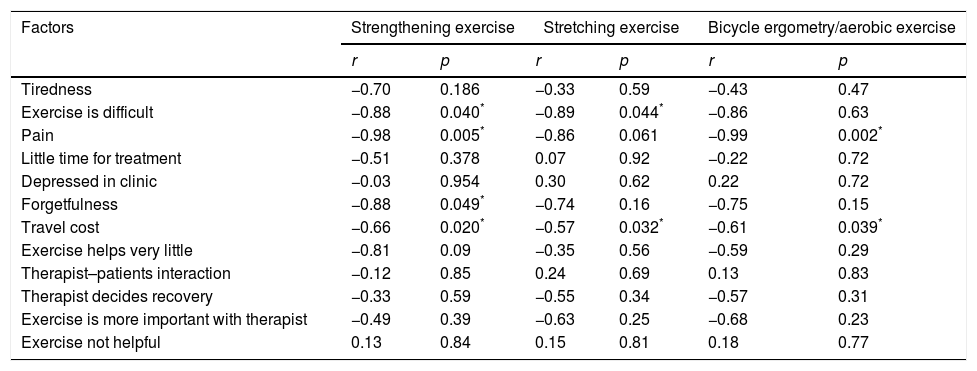
ResultA total of 70 (66.7%) patients completed the study with a mean age of 62.4±10.8 years. Adherence to aerobic exercises was 28 (80%); strengthening 25 (71%) and stretching 17 (49%). The education level of the individuals and the decreased level of pain when engaging in the exercises had a statistically significant (p<0.05) positive influence on participation and adherence. Travel costs to the hospital, forgetting the exercises and increasing pain while engaging in the exercises had a negative impact on participation and adherence to exercises in the clinic.
ConclusionPhysiotherapists must consider the type, level of pain, complexity of exercises and travel costs when prescribing exercises in the clinic for patients with KOA. These are relevant factors for participation and adherence to exercises in the clinic.
La participación y adherencia al ejercicio en clínica constituyen un reto para los fisioterapeutas. Este estudio fue diseñado para identificar el tipo y los factores que influyen en la participación y adherencia al ejercicio en pacientes con artrosis de rodilla (AR).
Material y MétodoEn este estudio casi-experimental participaron 105 pacientes remitidos a fisioterapia para AR, que fueron aleatorizados en tres grupos. Realizaron ejercicio aeróbico con cicloergómetro, fortalecimiento usando mancuernas y banco de cuádriceps o estiramientos durante más de 5 semanas, 3 veces por semana, 30 minutos por sesión. Se utilizó la Escala autoadministrada de Adherencia a la Fisioterapia y el cuestionario modificado para los factores que influyen en la adherencia. Se realizó estadística descriptiva e inferencial con una significación estadística p<0,05.
ResultadosParticiparon 70 (66,7%) pacientes, con edad media de 62,4±10,8 años. La adherencia al ejercicio aeróbico fue de 28 (80%), de 25 (71%) en el fortalecimiento y de 17 (49%) en los estiramientos. El nivel educativo y el nivel de dolor reducido al realizar los ejercicios mostraron una influencia estadísticamente significativa (p<0,05) en la participación y adherencia. Los gastos de desplazamiento al hospital, el olvido de los ejercicios y el aumento del dolor con los ejercicios influyeron negativamente en la participación y adherencia.
ConclusiónLos fisioterapeutas deben considerar el tipo y nivel de dolor, la complejidad del ejercicio y los gastos de desplazamiento al prescribir ejercicios en pacientes con AR. Estos son factores relevantes para la participación y adherencia al ejercicio en clínica.
Artículo
Si ya tiene sus datos de acceso, clique aquí.
Si olvidó su clave de acceso puede recuperarla clicando aquí y seleccionando la opción "He olvidado mi contraseña".Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora