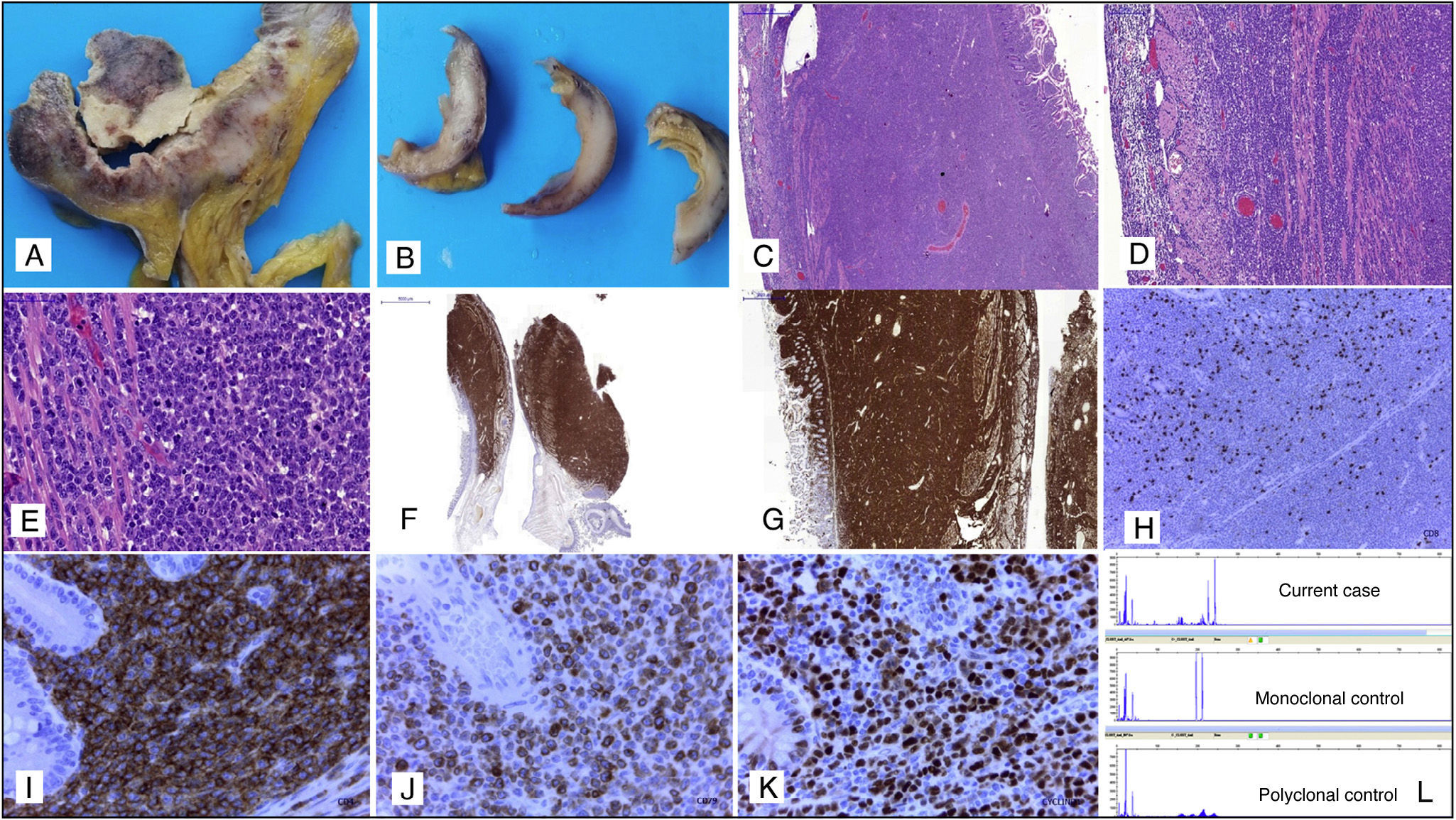
The presence of intestinal involvement in tumour-stage mycosis fungoides (MF) is exceptional, with only isolated cases having been reported.1–4 Considering the rarity of this complication and the clinical, radiological and pathological difficulties that it entails, we present a recent case of intestinal infiltration by high-grade large T-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) in a patient with a history of tumour-stage MF. The patient was a 78-year-old man with a history of MF cutaneous T-cell NHL, which in recent months had evolved to tumour stage with histological and immunohistochemical (IHC) confirmation. The patient underwent an emergency laparotomy for symptoms of acute abdomen secondary to intestinal perforation, in which a segment of small intestine was removed that presented signs of fibropurulent peritonitis and multiple tumour nodules, with full-thickness necrosis and invasion (Fig. 1A and B). Histological study showed infiltration of all layers of the intestine by a high-grade large-cell lymphoproliferative process (Fig. 1C–E). Differential diagnosis with the blastoid variant form of mantle cell lymphoma, diffuse large B-cell lymphoma or primary or secondary intestinal T-cell lymphoma related with the tumour-stage MF was initially considered. The IHC study showed strong, diffuse staining in tumour cells for CD2, CD3, CD5, CD43, CD4, CD7, CD79a and cyclin D1 (Fig. 1F–K). CD20, CD8 and PAX-5 were negative. CD30 showed focal positivity, and a Ki-67 index of 95%. The molecular biology study showed a monoclonal T-cell population (Fig. 1L). The IHC profile of the tumour cells in the intestinal infiltration was similar to that described in previous skin biopsies, where the tumour-stage MF was diagnosed, and where we also observed aberrant expression of cyclin D1 and CD79a. Similarly, the monoclonal T-cell receptor peak coincided in skin and intestine, thereby confirming that they were both lesions from the same tumour.
(A, B) Macroscopic appearance of the transmural intestinal infiltration by high-grade T-cell lymphoma. (C–E) Histopathology study with haematoxylin and eosin, in which transmural infiltration by high-grade non-Hodgkin lymphoma in the small intestine can be seen, 10×, 20× and 40×, respectively. (F) Immunohistochemical staining: the tumour lymphoid infiltrate is strongly and diffusely positive for CD2, 4×. (G) Tumour lymphoid infiltrate positive for CD7 with transmural intestinal involvement, 10×. (H) CD8-negative tumour cells with presence of accompanying isolated non-neoplastic CD8-positive T-lymphocytes, 10×. (I) Strongly positive CD4 staining in the tumour cells with negativity in the intestinal glands, 40×. (J) Aberrant expression of CD79a in tumour cells of a T-cell lymphoma, 40×. (K) Nuclear overexpression of cyclin D1 in tumour cells, 40×. (L) Molecular biology study in which a monoclonal T-cell population can be observed.
In view of the histopathology, IHC and molecular findings, the diagnosis was extensive intestinal infiltration by high-grade large T-cell NHL, tumour-stage MF, with overexpression of cyclin D1 and aberrant expression of CD79a.
Intestinal involvement in tumour-stage MF is extremely rare, with only isolated cases having been reported in the English language medical literature.1–4 Moreover, T-cell lymphomas in any location can have overexpression of cyclin D15 and aberrant expression of B-cell markers, such as CD79a,6 making differential diagnosis difficult, especially with mantle cell lymphoma, which is one of the most common histological sub-types of intestinal lymphomas. In the case reported, the history of MF, predominantly T-cell IHC profile and T-cell monoclonality confirmed the diagnosis of intestinal infiltration by high-grade T-cell lymphoma.
Conflict of interestsThe authors have no conflict of interests.
Please cite this article as: Machado I, Sanmartin O, Diez-Ares JA, Traves V, Avaria A, Salazar C, et al. Infiltración intestinal por linfoma no Hodgkin-T de células grandes de alto grado con sobreexpresión de ciclina-D1 y expresión aberrante de CD79a en paciente con diagnóstico de micosis fungoide en estadio tumoral. Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016;39:362–364.