We report a case of a cirrhotic patient who developed a spontaneous bacterial empyema due to Clostridium perfringens. To our knowledge, only two cases of spontaneous bacterial empyema due to C. perfringens in cirrhotic patients were previously reported in literature. It should be suspected in a Child C cirrhotic patient, with a previous history of pleural effusion, fever and dyspnea. It has a fatal outcome as far as it has been described.
Se presenta el caso de un paciente con cirrosis que desarrolló un empiema bacteriano espontáneo causado por Clostridium perfringens. Según nuestros conocimientos, en la literatura sólo se han reportado dos casos de empiema bacteriano espontáneo debido a Clostridium perfringens en pacientes cirróticos. Se debe sospechar en un paciente cirrótico con una clasificacion C de Child, además de una historia previa de derrame pleural, fiebre y disnea. En todos los casos descritos el desenlace ha sido mortal.
A 69-year-old man was admitted due to abrupt onset of dyspnea and right pleuritic pain. He had been followed for one year in our department due to Child C cryptogenic cirrhosis, MELD-Na score 21, with refractory ascites and large esophageal varices. He had two previous admissions in a year due to hepatic encephalopathy. One year prior to this admission, thoracic computed tomography scan revealed a right pleural effusion. Echocardiography was normal. Refractory ascites and pleural effusion were treated with low salt diet, fluid restriction and regular paracentesis. No therapeutic thoracocentesis was ever performed.
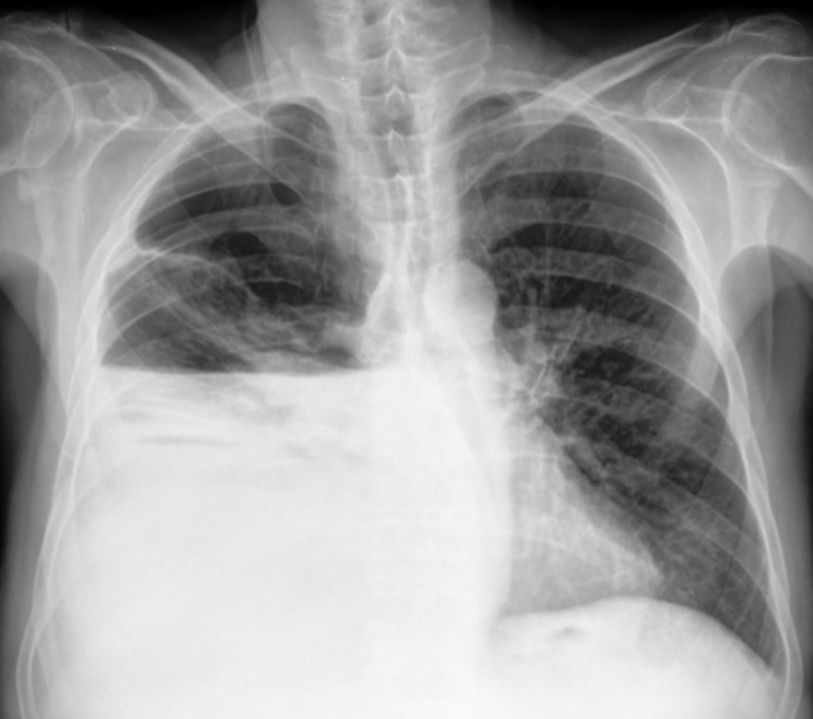
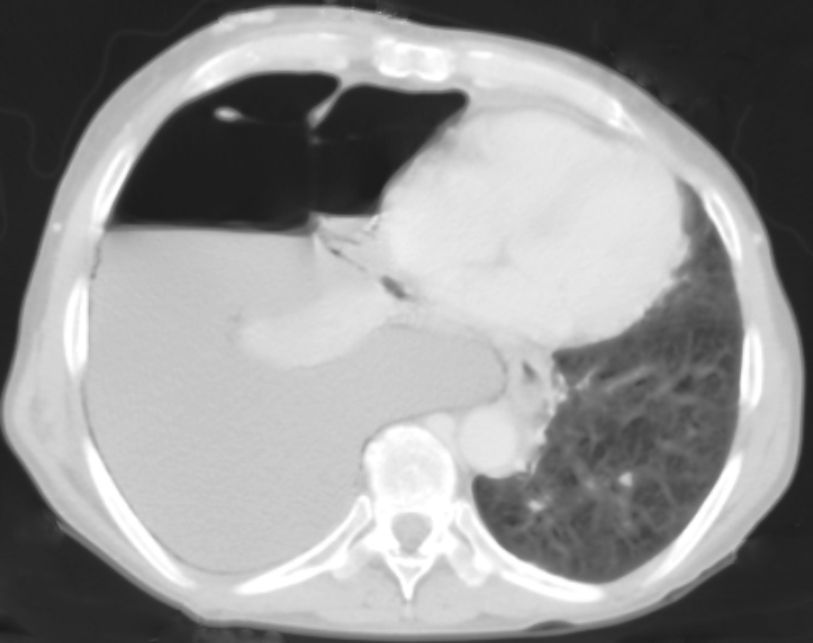
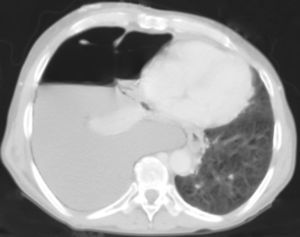
On examination patient was conscious, afebrile, with a respiratory rate of 39min−1, pulse 90beats/min, oral temperature 37°C and blood pressure 90/50mmHg. Lung percussion showed dullness of the inferior right lung and abolition of vesicular murmur. He had ascites. A blood sample was collected and revealed anemia (hemoglobin 11.7g/dL), hypoalbuminemia (albumin 2.0g/dL), low protein level (4.2g/dL), hyponatremia (sodium 126mequiv./L), normal leukocytes count (9.03×109L−1), platelets (171×109L−1), lactic dehydrogenase 195U/L and potassium (5.0mEq/L); an elevated creatinine (1.8mg/dL), total bilirubin (5.03mg/dL) and CRP level (50mg/L). MELD-Na score at admission was 29. Blood gases analysis revealed a lactic acidosis; blood pH 7.25, PO2 100mmHg with 97% saturation, PCO2 36mmHg, bicarbonate 15mEq/L and lactates 8mEq/L. Electrocardiogram was normal. The chest X-ray (Fig. 1) and thoracic CT scan (Fig. 2) confirmed an enlarged right pleural effusion. There was no evidence of patient aspiration and CT scan did not reveal any lung consolidation or unilateral or bilateral opacities suggestive of pneumonia. Abdominal CT scan revealed ascites, but there was no evidence of any abdominal lesion, namely intestinal perforation.
Patient clinical condition rapidly deteriorated, and he was intubated and admitted to intensive care unit (UCI). A chest tube was inserted and a total of 2000mL of dark and fetid fluid was drained. Pleural fluid analysis revealed characteristics of an exudate, lactic dehydrogenase 733U/L and protein 3.2g/dL, with low pH (7.2) and glucose levels. Leukocyte count was 10,995μL−1 (92% neutrophils). A diagnostic paracentesis was performed and the peritoneal fluid leukocyte count was 8363μL−1 (87% neutrophils), glucose level 83mg/dL, lactic dehydrogenase 575U/L and protein 3.9g/dL (exudate).
Vancomycin and imipenem were started.
Cultures of the pleural and peritoneal fluid yielded an anaerobic gram-positive bacillus, Clostridium perfringens. Blood, urine and sputum cultures were negative.
Patient condition deteriorated and finally died from respiratory failure and sepsis.
DiscussionHepatic hydrothorax is defined as the pleural effusion associated with cirrhosis and portal hypertension without a primary cardiac, pulmonary or pleural disease. It is an uncommon manifestation of portal hypertension and occurs in 5–6% of patients with cirrhosis. The ascitic fluid moves transdiaphragmatically through diaphragmatic defects into pleural space along a pressure gradient.1 This patient had a previous diagnosed hepatic hydrothorax, refractory to medical therapy.
Spontaneous bacterial empyema (SBE) is the infection of a preexisting hydrothorax in which pneumonia has been excluded.1 It can occur due to bacteremia or by spread of an infected ascitic fluid to the pleural cavity via defects in the diaphragm.1–3 Diagnosis is established when the pleural fluid analysis shows a positive culture and more than 250neutrophils/mm3 or a negative culture and more than 500neutrophils/mm3, in the absence of lung infection.4
In a study from Taiwan3 the incidence of SBE in cirrhotic patients with hydrothorax was 16%. In a study from Spain,5 the percentage was 13% and in 43% of cases, SBE was not associated with spontaneous bacterial peritonitis (SBP).
The most common bacteria involved are Enterobacteriaceae (Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumonia) and some gram-positive bacteria such as Streptococcus species and Enterococcus species.1 Clostridium are uncommon causes of pleuropulmonary infection.6
C. perfringens is an anaerobic gram-positive found in large amounts in the colonic flora but rarely in the oral cavity.7 Primary pleural infections occur mainly with chest trauma or thoracotomy.6,7 In this case, no trauma or iatrogenic causes were found.
Our patient had SBP and SBE, with both cultures (pleural and peritoneal fluid) positive for C. perfringens. Blood cultures were negative, so spread of infected ascitic fluid to the pleural cavity through the diaphragm was the most likely explanation.
SBE has a high mortality rate and independent factors related with poor outcome are high MELD-Na score, initial ICU admission and initial antibiotic failure.3 This patient had all three poor prognosis factors.
There were only two previous reported cases of SBE in cirrhotic patients due to C. perfringens, to our knowledge. In 1984, Streifler et al.7 reported a case of an empyema of the left pleural cavity in a nonalcoholic cirrhotic patient, developing in a previously known pleural effusion. In 1989, Xiol et al.2 reported eleven cases of SBE in cirrhotic patients, with one case of SBE due to C. perfringens, this also occurring in a previous known pleural effusion. To our knowledge, there are six previously reported cases of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis due to these bacteria in cirrhotic patients.2,8–12
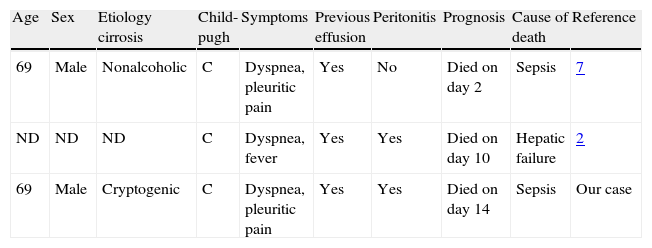
Revision of all three cases of SBE (including our case) revealed that all patients had Child C cirrhosis (Table 1); dyspnea was a common symptom, empyema developed in a previous effusion and had a fatal outcome (all patients died).
Previous reported cases of SBE in cirrhotic patients due to Clostridium perfringens.
| Age | Sex | Etiology cirrosis | Child-pugh | Symptoms | Previous effusion | Peritonitis | Prognosis | Cause of death | Reference |
| 69 | Male | Nonalcoholic | C | Dyspnea, pleuritic pain | Yes | No | Died on day 2 | Sepsis | 7 |
| ND | ND | ND | C | Dyspnea, fever | Yes | Yes | Died on day 10 | Hepatic failure | 2 |
| 69 | Male | Cryptogenic | C | Dyspnea, pleuritic pain | Yes | Yes | Died on day 14 | Sepsis | Our case |
ND: not described.