A 62-year-old woman presented with left upper quadrant pain and anorexia for 1 month. She had a past medical history of nephrolithiasis, extramembranous glomerulonephritis and a relevant atopic background.
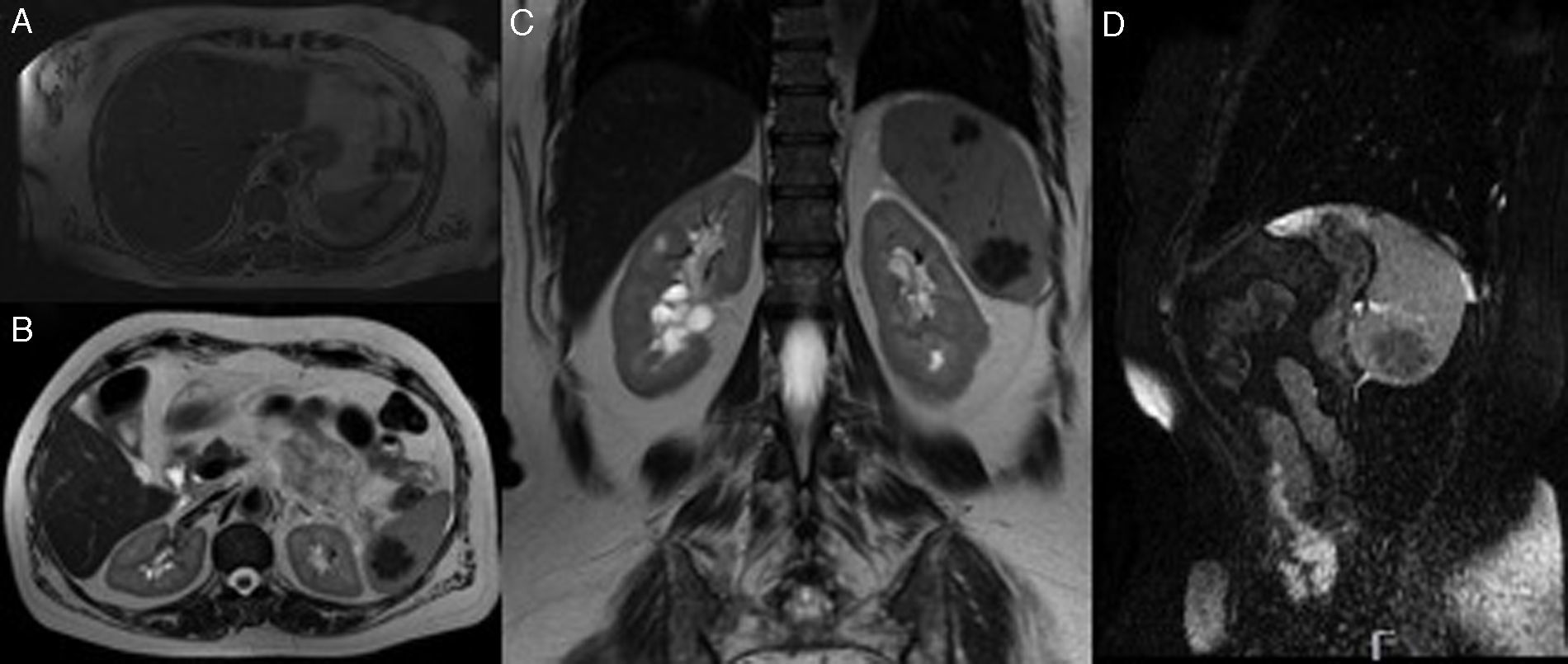
Physical examination as well as laboratory tests were unremarkable. Abdominal computed tomography, performed without endovenous contrast due to patient's atopic history, highlighted a nodular density between the pancreatic tale and splenic hilum. On unenhanced magnetic resonance imaging this corresponded to a vascular structure, next to the spleen, with a “serpentine” shape and apparently in continuity with this organ. Additionally, within the spleen there were three, well circumscribed, macronodular lesions, with lobular borders, the biggest measuring 2.5cm in greater diameter. These lesions were isointense on T1-weighted sequences and hypointense with mildly hyperintense septa on T2 and FATSAT Fiesta sequences (Fig. 1). No other relevant lesions were identified.
Magnetic resonance imaging. (A) T2-weighted sequences (axial plane) showing a vascular structure in the splenic hilum with a nodular configuration. A macronodular lesion is also seen in this image, within the spleen, exhibiting low signal. (B and C) T2-weighted sequences (axial and coronal plane, respectively) showing nodular lesions, in the upper spleen and the lower spleen, with lobular borders, hypointense, sketching internal micronodular formations. (D) Fiesta FATSAT (sagittal plane) sequence showing a hypointense lesion in the lower spleen, with discrete hyperintense septa.
Considering the limitations of unenhanced radiological examinations, concerns about malignancy and the potential for splenic vein thrombosis, splenectomy was indicated. Intraoperatively, the splenic vein presented with a tortuous and nodular configuration, which corresponded to the structure previously described in the splenic hilum. Splenectomy was performed without complications.
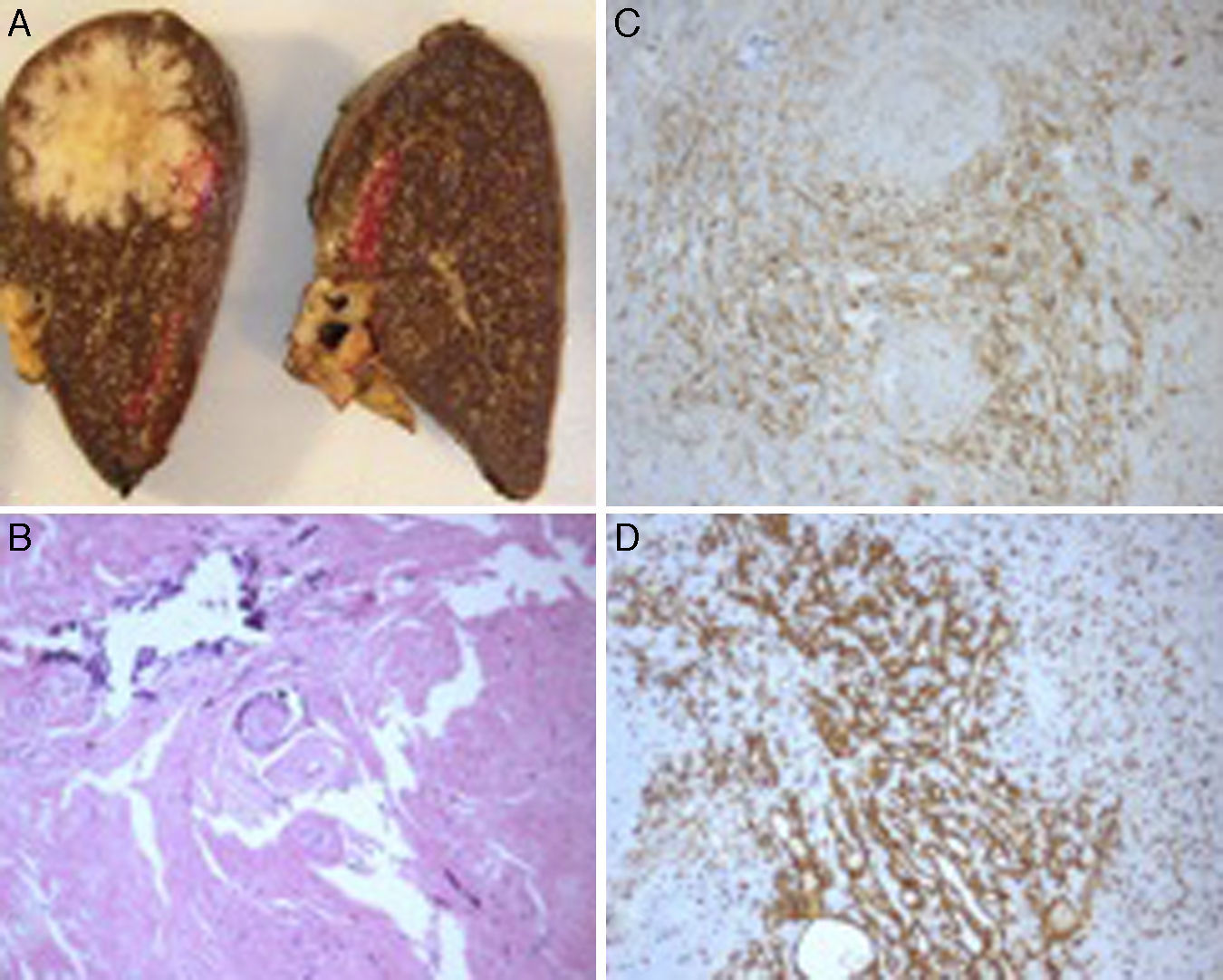
The ressected spleen weighed 154g and had a round-shaped prominent lesion. On sectioning, the lesion was solid, white in color, with a yellowish center, well-circumscribed, lobulated and measured 2.5cm in diameter. There were two other similar lesions within the splenic parenchyma (1.2 and 1.8cm in diameter). Microscopically, each lesion was composed of multiple angiomatoid nodules surrounded by sclerotic tissue. These angiomatoid nodules consisted of capillaries, sinusoids and small veins as evidenced by immunohistochemical staining (CD8, CD34 and CD31 positivity) (Fig. 2). Nuclear atypia, mitotic figures and necrosis were absent. The diagnosis of sclerosing angiomatoid nodular transformation of the spleen (SANT) was established. The patient remained asymptomatic with no recurrence after 10 months of follow-up.
(A) Sectioning images of the ressected spleen showing the bigger lesion within splenic parenchyma. On macroscopy, it is a well-circumscribed, round-shaped, lobulated lesion. (B) Microscopy image showing angiomatoid nodules surrounded by a stroma with intense fibrosis, hialinization and calcifications (hematoxylin and eosin staining, 100×). (C) Immunohistochemical staining for CD31 showing the abundant vascular structures (capillaries, sinusoids and veins) (100×). (D) The sinusoids showing strong immunoreactivity for CD8 (100×).
SANT of the spleen is a rare benign vascular lesion, first described by Martel et al.,1 in 2004, with few more than a 100 cases published in the literature.2 It is most commonly encountered in middle-aged adults as an incidental finding on imaging.1,3,4 When symptomatic, abdominal pain predominates.1,3,4
According to former studies, there is a slight female preponderance.1,3 The pathogenesis of this recently described entity is still unclear.1,3 Some authors hypothesize that SANT may represent a peculiar transformation of the red pulp of the spleen in response to an exaggerated stromal proliferation.1,3
The differential diagnosis of SANT includes both benign and malignant vascular lesions such as hemangiomas, hamartomas, lymphangiomas, hemangioendotheliomas, littoral cell angiomas, inflammatory myofibroblastic lesions, angiosarcomas (the commonest nonlymphoid malignant primary tumor of the spleen)5 or nodular transformation of the splenic red pulp in response to metastatic carcinoma.6
Typical pattern on computed-tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a well-circumscribed splenic mass with smooth or lobular borders.2,5,7 Although more frequently solitary, multiple nodules (as in our case) have been described.8,9 It has iso to mild hypodensity compared to surrounding parenchyma on non-enhanced CT.2,5,9 For this reason, in our case, it went unnoticed on the first imaging study. On MRI, SANTs most commonly show low to intermediate signal intensity on T1-weighted sequences. On T2-weighted sequences, lesions have typically low signal, in contrast to most differential diagnosis.2,5,7 Several authors describe a “spoke-wheel” appearance after contrast administration on CT, MRI and on contrast-enhanced ultrasound that may suggest the diagnosis. This pattern refers to peripheral and septal enhancement with a hypoenhancing central stellate scar, which correlates to the pathological findings.2,5,7,10 However, there are no completely reliable radiological features for the diagnosis of SANT and concerns for malignancy and the potential for splenic rupture often lead to splenectomy.3
In our case, patient's relevant history of atopy made it prudent to perform the investigation with non-enhanced radiological examinations. The findings on MRI namely on T2-weighted and Fiesta FATSAT sequences suggested the diagnosis though not completely reliable. In fact, histopathological characterization appears to remain the diagnostic “gold standard”.3 Furthermore, the patient presented with abdominal pain and had a concurrent vascular anomaly in the splenic hilum, which made us to consider the potential for splenic vein thrombosis. At the end, this anomaly corresponded to the splenic vein with a peculiar configuration, not previously described in association with SANT.
Microscopic findings include multiple angiomatoid nodules with a distinctive immunohistochemical profile, in a fibrosclerotic background. These angiomatoid nodules are composed of three types of vessels which resemble the normal vascular structure of splenic red pulp: the cord capillary-type (CD31+/CD34+/CD8−), the sinusoid-type (CD31+/CD34−/CD8+) and the small vein-type (CD31+/CD34–/CD8–).1,3 Other splenic vascular lesions such as hemangioma, hamartoma and littoral cell angioma lack the nodular pattern of SANT and these mixture of vessels that gives rise to its characteristic immunophenotype.1,6 Our case is in accordance with the pathological findings previously described.
Splenectomy is useful and effective without described recurrence after surgery.4
The authors report a new case of symptomatic SANT. As more cases are reported a complete characterization of this disease becomes possible. We highlight the imaging and pathological features that may suggest this uncommon lesion and facilitate differential diagnosis and patient's management.
Source of fundingNone declared.
Conflicts of interestNone declared.