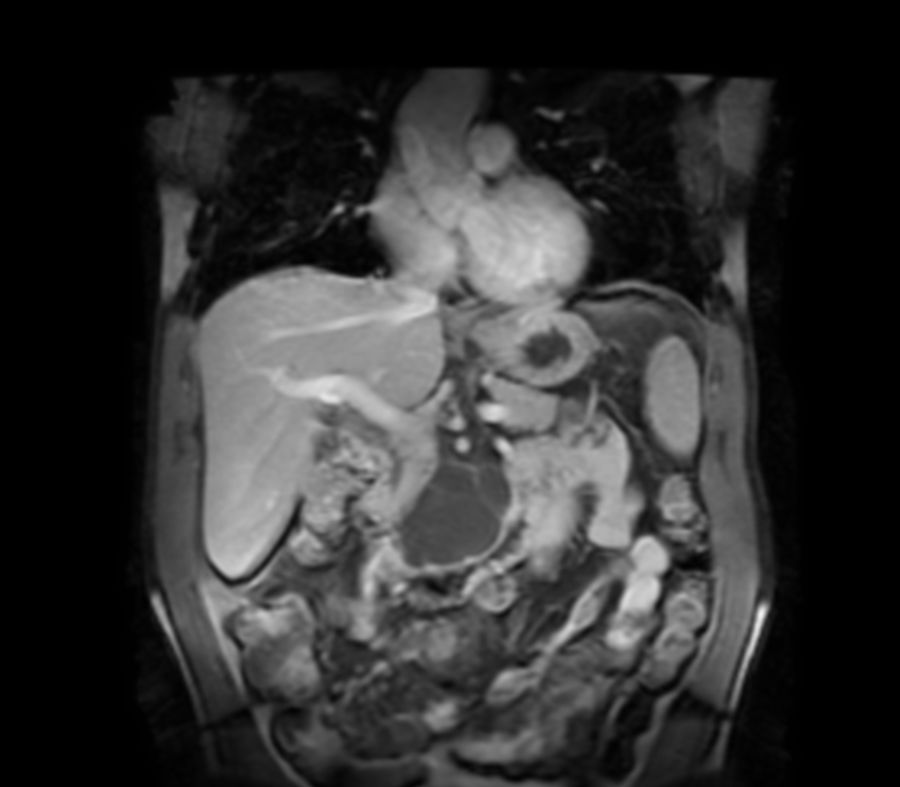
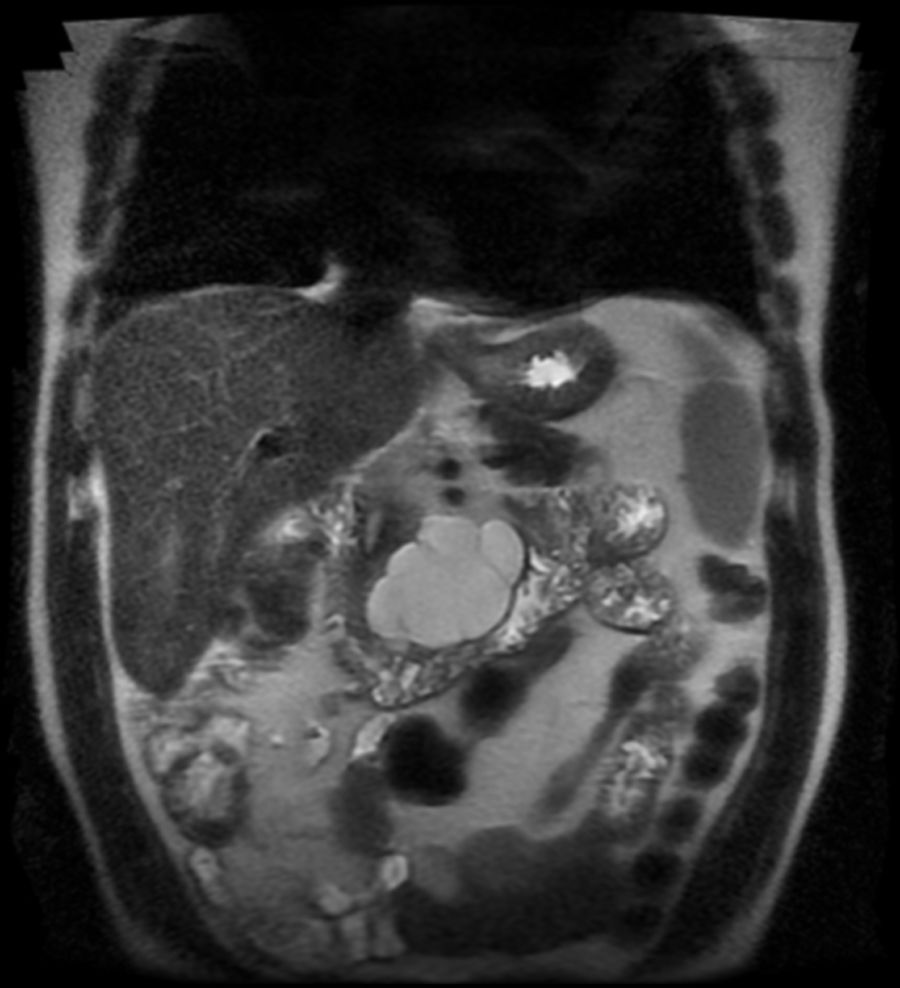
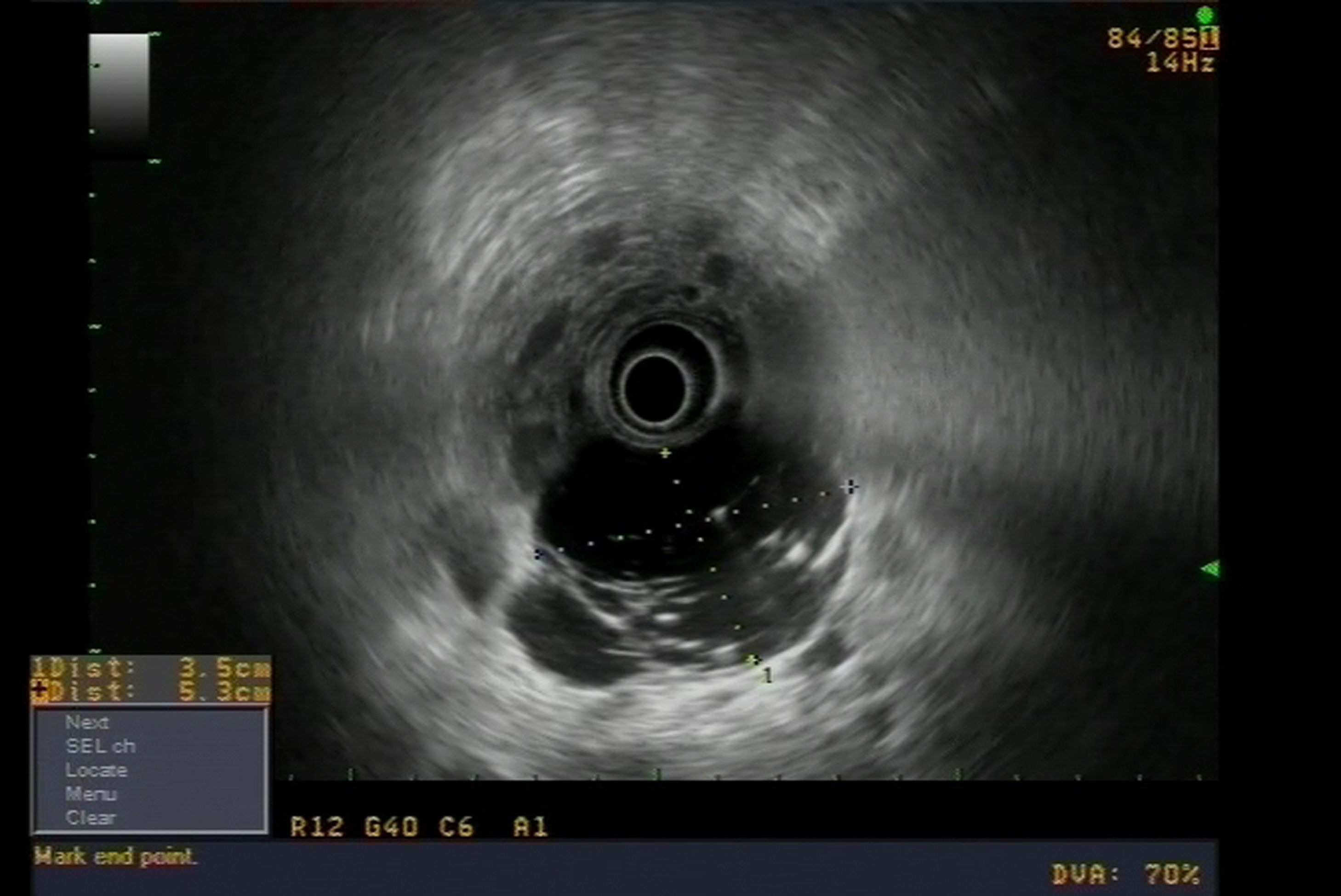
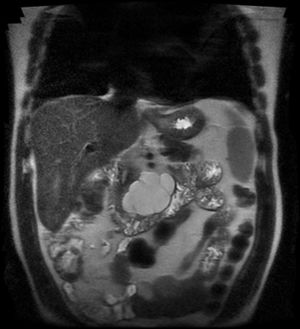
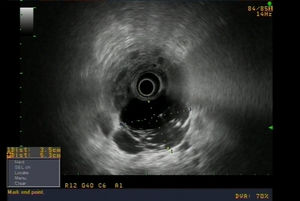
An asymptomatic 62-year-old male patient had an incidental finding on abdominal computed tomography (CT) of a hypodense mass on the uncinate process of the pancreas, with linear calcifications measuring 5.5 × 4.2 cm (Fig. 1). Abdominal magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) showed a multiloculated macrocystic lesion on the uncinate process with exophytic growth and internal septa that neither restricted diffusion nor enhanced with contrast (Fig. 2). Endoscopic ultrasound showed a cystic lesion measuring 5.5 × 5 cm with thin septa delimiting large cystic cavities with hyperechoic points in the fluid (Fig. 3). EUS-FNA was performed to extract 10 cc of a thick, milky, non-mucinous fluid. Testing revealed glucose 96 mg/dl, proteins 4.86 g/dl, amylase 113 U/l, CEA 3.94 ng/ml and TGs 4308 mg/dl. Cytology testing was acellular.
Pancreatic lymphangiomas are extremely uncommon, accounting for less than 1% of abdominal lymphangiomas. Fewer than 100 have been reported in the literature. They primarily affect young women and tend to be located on the body or tail of the pancreas. They are generally asymptomatic. CT and MRI are unable to distinguish lymphangiomas from other cystic lesions of the pancreas. The diagnosis is based on extraction of milky fluid and high TG levels (although they cannot always be detected).1 They are benign lesions. Surgical treatment is pursued when symptoms develop due to growth or infection.2,3
Please cite this article as: del Olmo Martínez L, Velayos Jiménez B. Quiste pancreático infrecuente: linfangioma. Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021;44:726–727.