Several techniques for managing migrated and misplaced self-expanding esophageal metal stents have been described.1–5 However, most of these techniques apply only when there is distal stent dislodgment. When there is proximal stent migration or misplacement, and unless there is a lasso at the distal flange, trying to reposition the stent distally through the stenotic tumor can be challenging. Although it may be tried by grasping distal tines with forceps or inflating a dilating balloon within the stent and applying gentle pressure, it seldom results. We herein report an endoscopic approach for an easy and safe reposition of proximal dislodged esophageal metal stents that, as far as we are aware, was never described before.
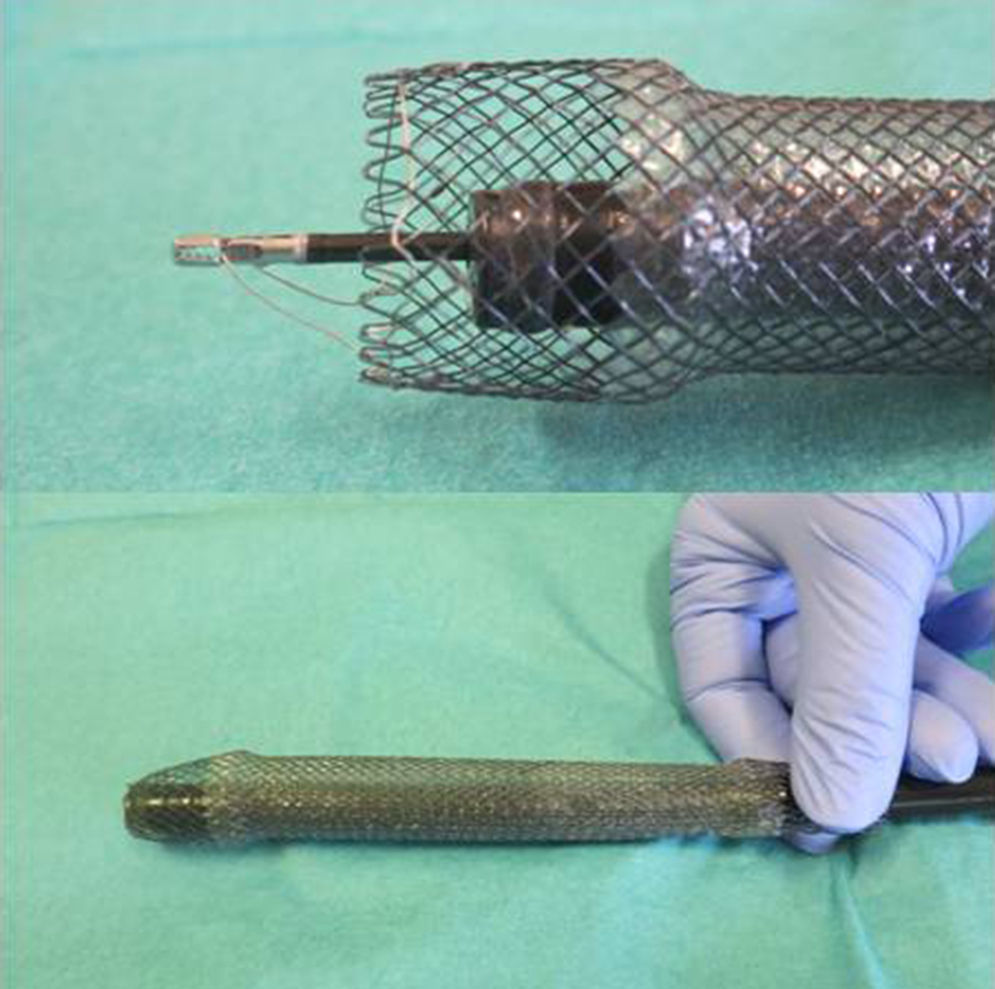
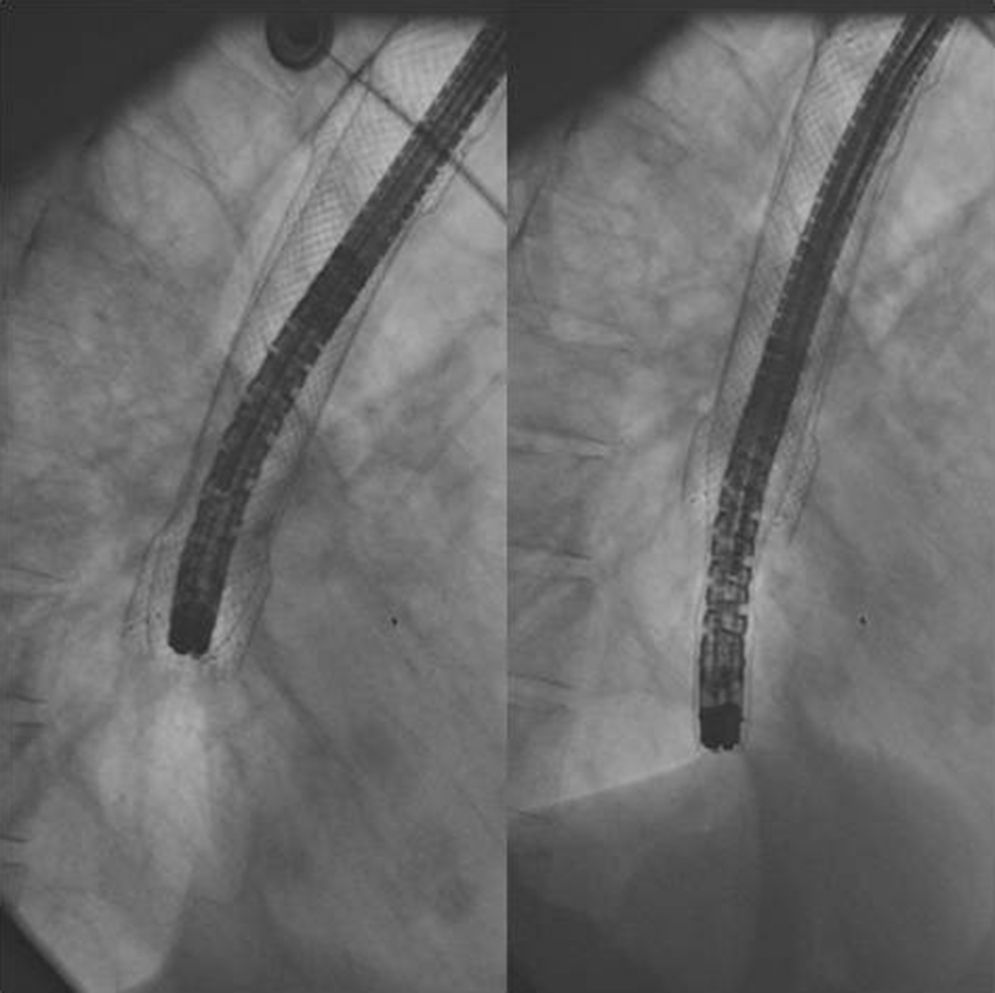
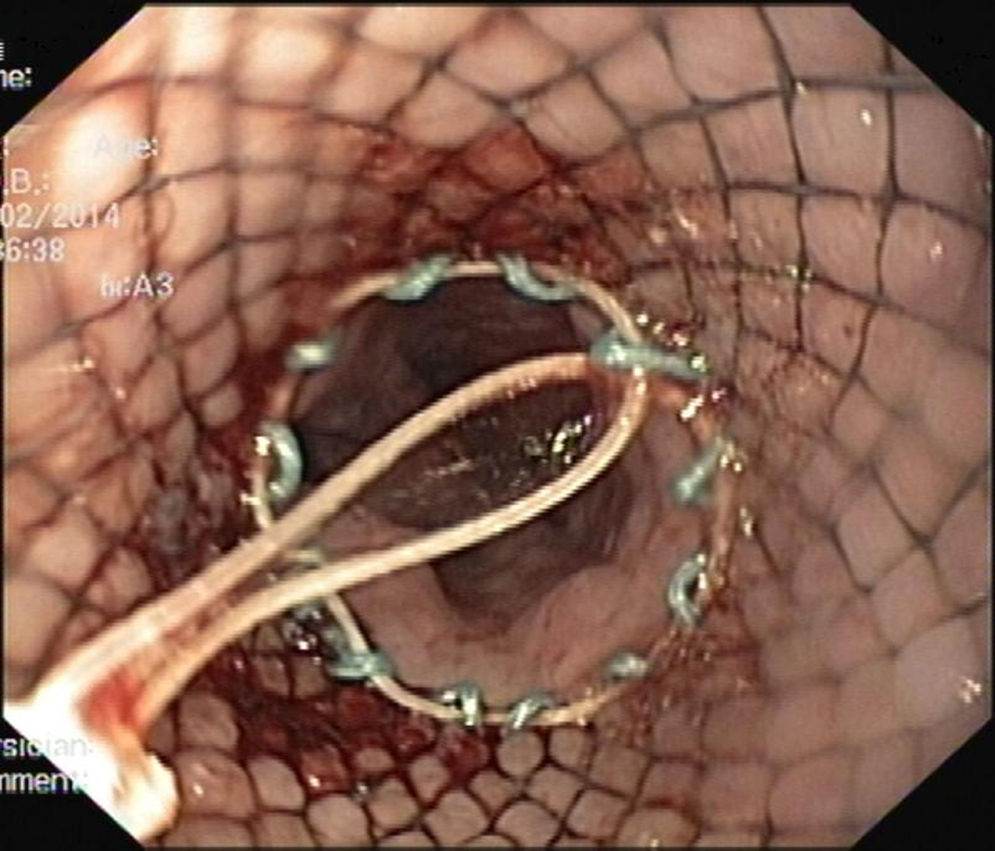
The stent is removed by grasping the lasso on the proximal end of the stent with an alligator jaw grasping forceps. Outside the patient, the lasso is released and the stent is turned upside down. The endoscope is then introduced through the distal end of the stent until the proximal end, where the lasso is re-grasped by the forceps and pulled back, allowing the upper flange of the stent to collapse over the tip of the endoscope (Fig. 1). The body of the stent is generously lubricated with aqueous jelly and stretched along the endoscope. The patient is reintubated with gently passage of the endoscope and the stent through the pharynx and cricopharyngeus into the upper esophagus. Under fluoroscopic guidance and direct visualization, the endoscope is than advanced through the tumor (Figs. 2 and 3). If significant narrowing prevents the safe passage of the endoscope along with the stent, gentle esophageal dilation to 11–13mm is performed. The lasso is then released and the stent deployed according with the marks previously placed.
We have performed this technique in 3 patients during the last four years, with successful stent repositioning and no complications.
Ethical disclosuresProtection of human and animal subjectsThe authors declare that no experiments were performed on humans or animals for this study.
Confidentiality of dataThe authors declare that no patient data appear in this article.
Right to privacy and informed consentThe authors declare that no patient data appear in this article.
Conflicts of interestConsultant for Cook Medical and Boston Scientific Corporation.