A 82-year-old man has been followed in our oncology hospital after prostatic cancer and prostatectomy. He was medicated with gonadotropin releasing hormone superagonist goserelin and olmesartan for arterial hypertension.
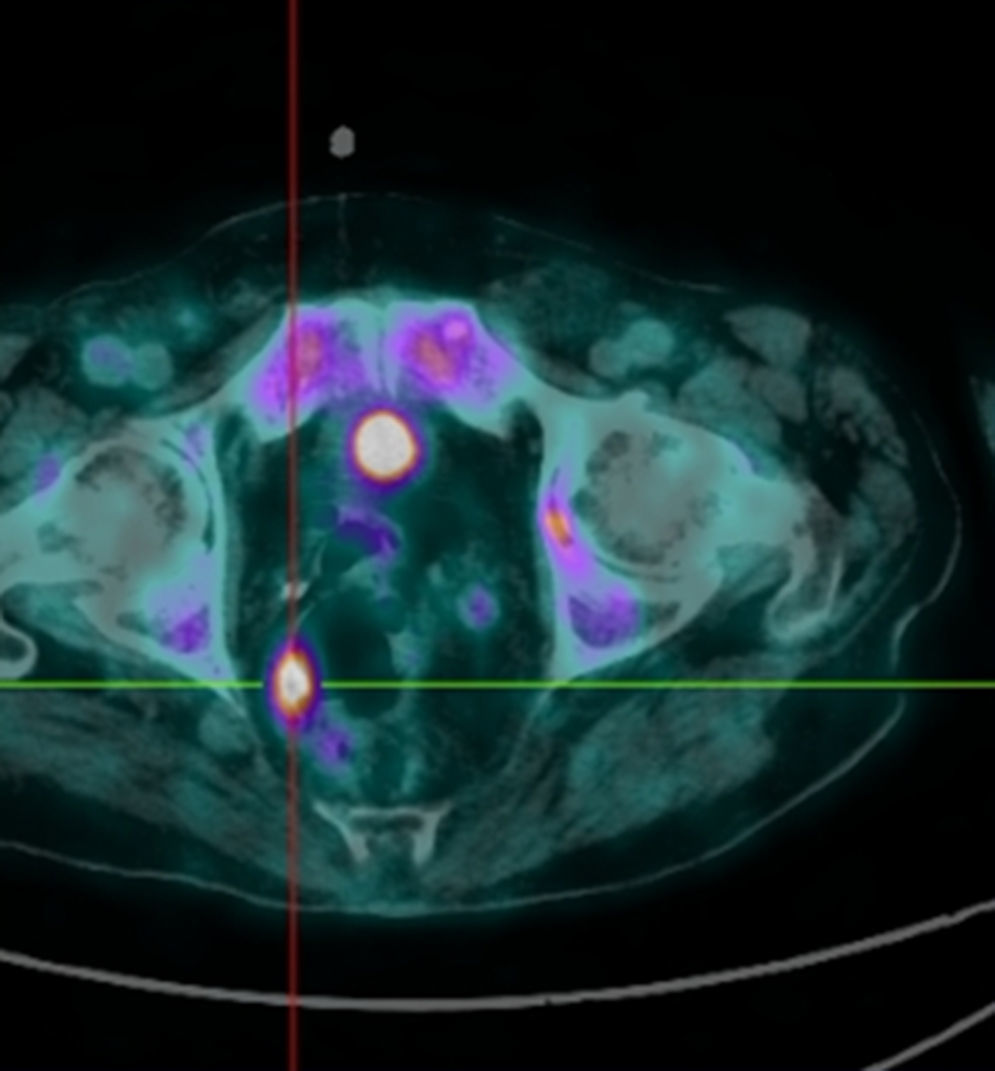
Due to the recent installation of orthopnea, a chest X-ray was carried out, revealing a mass in the right hilar region which was subsequently characterized as right hilar and mediastinal lymphadenopathy by chest CT. Bronchoscopy with bronchial biopsies, citology and microbiological studies revealed no signs of malignancy or infection. Taking into consideration the patient's medical history and the occasional back pain he referred, PET scan was thought to be the appropriate following exam. In addition to confirming hypermetabolism in the already known lymphadenopathies, PET-CT scan also showed a hypermetabolic focus at the rectosigmoid junction (Fig. 1).
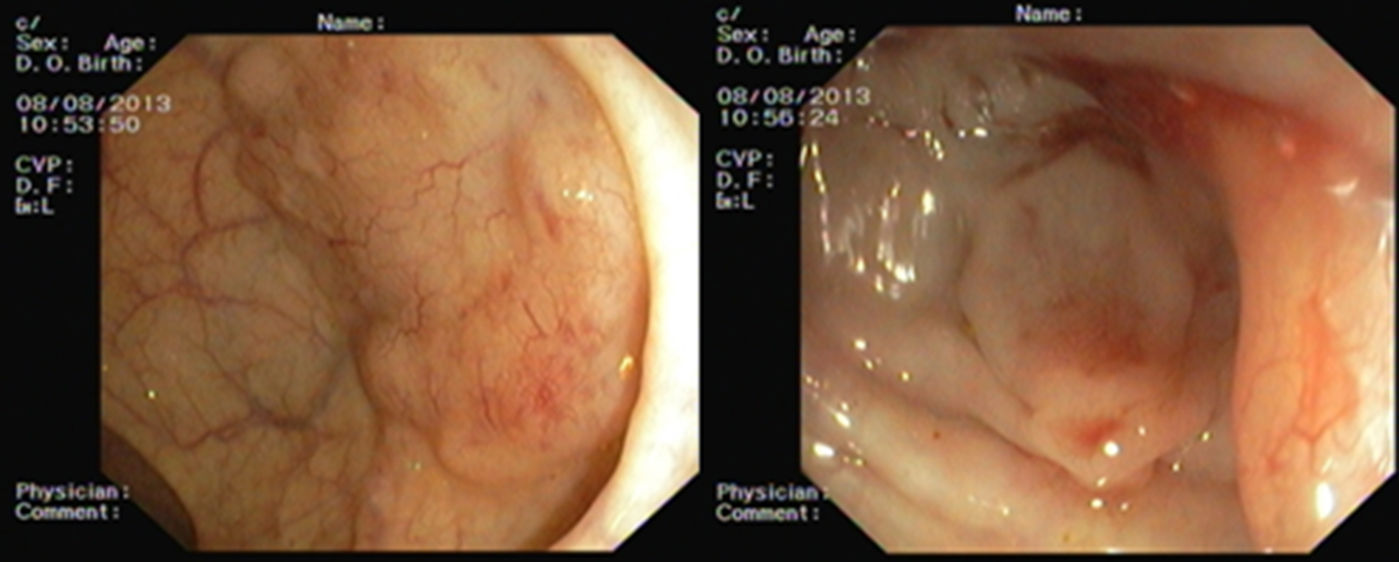
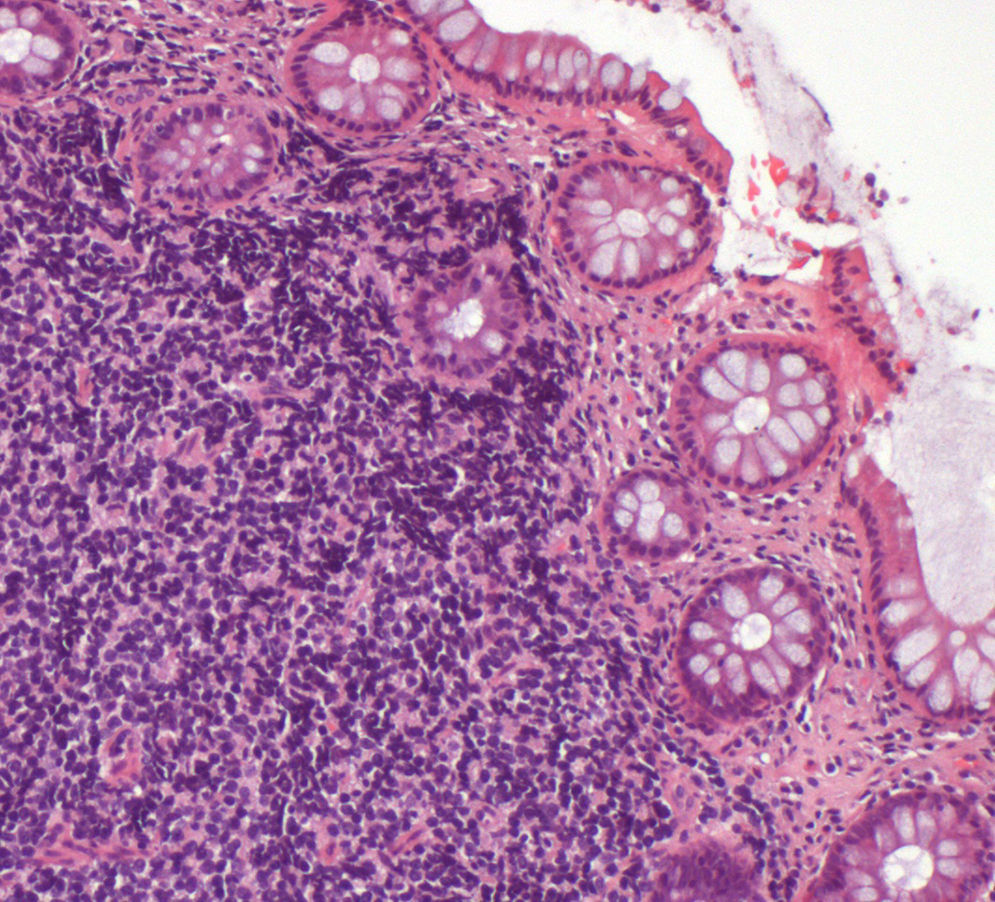
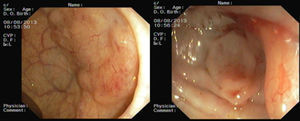
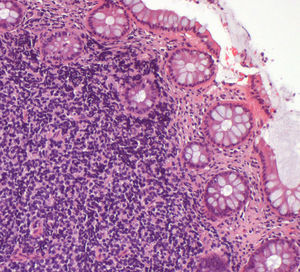
Sigmoidoscopy was performed and revealed two subepithelial lesions at 10 and 18cm from the anal verge (Fig. 2). Biopsy specimens were obtained by using a “biopsy-on-biopsy” technique. Histological examination showed the presence of a lymphoid neoplasia of small sized cells with irregular nuclei, fine chromatin, small inconspicuous nucleoli and pale indistinct scant cytoplasm, with the peculiarity that there was involvement of the epithelium (Fig. 3). Immunophenotype studies were consistent with the diagnosis of mantle cell lymphoma: expression of CD20 and other pan-B cell antigens and overexpression of cyclin D1. The patient was referred to the onco-hematology department to start treatment.
Approximately 40% of lymphomas have extranodal manifestations, and the most common site of extranodal involvement is the gastrointestinal tract.1 Nonetheless, colorectal lymphoma remains a rare clinical entity.2 Gastrointestinal involvement in mantle cell lymphoma, presenting with intestinal symptoms, was estimated at 30% but recent studies show an infiltration even in 92% of cases.3 The clinical case reported by the authors report a first diagnosis by colonic biopsy/approach, an interesting finding with iconography that supports the case.
Ethical disclosuresProtection of human and animal subjectsThe authors declare that no experiments were performed on humans or animals for this study.
Confidentiality of dataThe authors declare that they have followed the protocols of their work center on the publication of patient data.
Right to privacy and informed consentThe authors have obtained the written informed consent of the patients or subjects mentioned in the article. The corresponding author is in possession of this document.
Conflicts of interestThe authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.