Gastrointestinal endoscopy and the acquisition of tissue samples are essential for the diagnosis and treatment of various diseases of the digestive system. However, given the differences between the recommendations and the clinical practice, the inexorable increase of requests for endoscopic examinations and the financial burden associated with it, it is crucial that we concentrate on the challenge that endoscopic biopsies represent. In this review we describe the available evidence in the literature, including the more recent published guidelines, on when or not to perform endoscopic biopsies in upper and lower endoscopy, focusing on the precise diagnosis of the most common gastrointestinal diseases that motivate endoscopic examinations and on the rational use of available resources without compromising proper management of patients.
A endoscopia digestiva e a aquisição de amostras tecidulares são essenciais para o diagnóstico e tratamento de diversas patologias do tubo digestivo. No entanto, tendo em conta a diferença entre as recomendações e a prática clínica, o inexorável aumento de pedidos de exames endoscópicos e os encargos financeiros associados, é fundamental que nos debrucemos sobre o desafio que as biópsias endoscópicas representam. Nesta revisão, pretendemos descrever a evidência disponível na literatura, incluindo as mais recentes guidelines publicadas, sobre quando ou não realizar biópsias em endoscopia digestiva alta e baixa, com foco no diagnóstico das mais comuns doenças gastrointestinais que motivam exames endoscópicos, e no uso racional dos recursos disponíveis, sem comprometer o bom acompanhamento dos doentes.
Gastrointestinal endoscopy and the acquisition of tissue samples are essential for the diagnosis and treatment of various diseases of the digestive system. Given the differences between the recommendations and the clinical practice, the inexorable increase of requests for endoscopic examinations and the financial burden associated with it, it is essential that we concentrate on the challenge that endoscopic biopsies represent. In order to rationalize the use of histopathological examinations, it is crucial to understand why some gastroenterologists perform biopsies more often than others. One possible explanation relates to the evidence that clinicians with less experience are more likely to perform unnecessary biopsies.1
Another crucial point is the communication with the anatomopathologists. The histological opinion is, as the radiological opinion, entirely dependent on the clinical information provided and the questions that are being asked. As such, it is essential that each endoscopy unit develop, in conjunction with the pathology departments, simple guidance on what information provide on requisitions.
In this review we describe the available evidence in the literature, including the more recent guidelines published, on when or not to perform endoscopic biopsies in upper and lower endoscopy.2,3 These are pragmatic approaches that are based on the principle that the biopsies should be performed only when have potential to change the future approach to the patient. However, it is necessary to admit that in certain conditions the available evidence does not allow to establish strong recommendations and, in such cases, it is upon the gastroenterologist decision-making about the cost-benefit of biopsies.4
Tables 1 and 2 summarize the proposals to perform biopsies in upper and lower endoscopy, respectively.
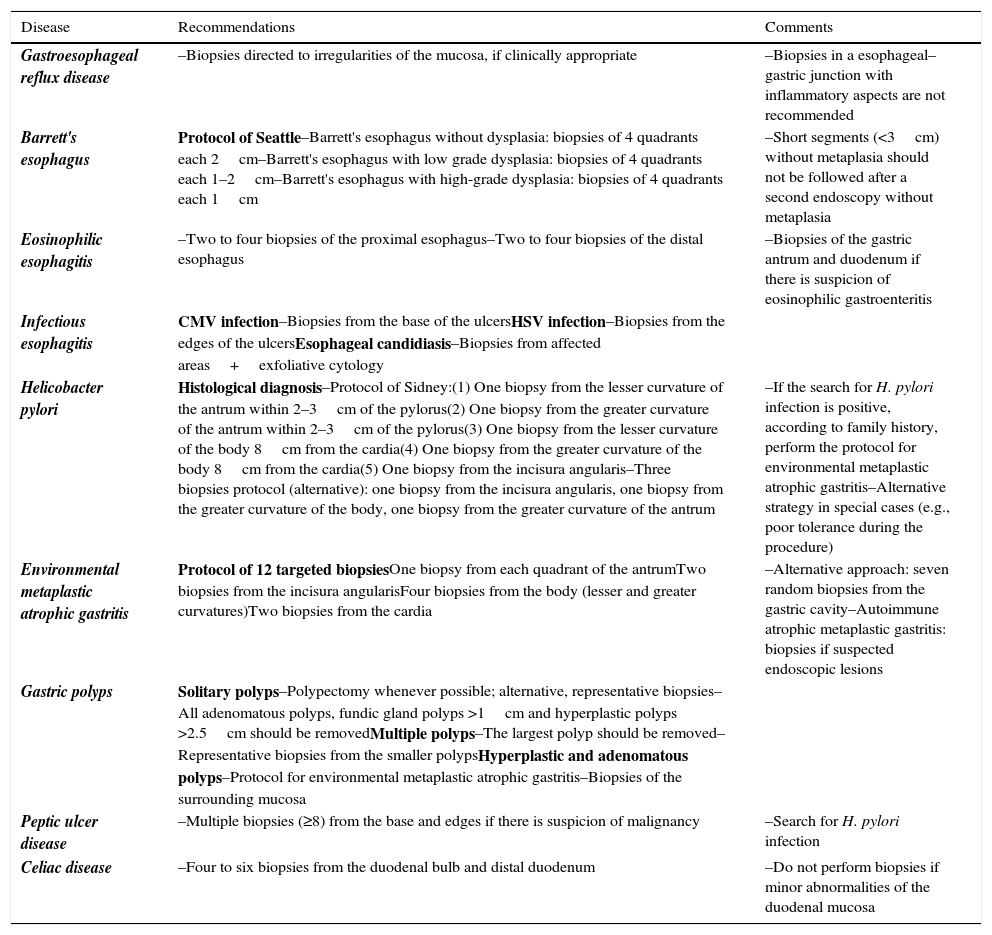
Summary of recommendations for biopsies in upper endoscopy.
| Disease | Recommendations | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| Gastroesophageal reflux disease | –Biopsies directed to irregularities of the mucosa, if clinically appropriate | –Biopsies in a esophageal–gastric junction with inflammatory aspects are not recommended |
| Barrett's esophagus | Protocol of Seattle–Barrett's esophagus without dysplasia: biopsies of 4 quadrants each 2cm–Barrett's esophagus with low grade dysplasia: biopsies of 4 quadrants each 1–2cm–Barrett's esophagus with high-grade dysplasia: biopsies of 4 quadrants each 1cm | –Short segments (<3cm) without metaplasia should not be followed after a second endoscopy without metaplasia |
| Eosinophilic esophagitis | –Two to four biopsies of the proximal esophagus–Two to four biopsies of the distal esophagus | –Biopsies of the gastric antrum and duodenum if there is suspicion of eosinophilic gastroenteritis |
| Infectious esophagitis | CMV infection–Biopsies from the base of the ulcersHSV infection–Biopsies from the edges of the ulcersEsophageal candidiasis–Biopsies from affected areas+exfoliative cytology | |
| Helicobacter pylori | Histological diagnosis–Protocol of Sidney:(1) One biopsy from the lesser curvature of the antrum within 2–3cm of the pylorus(2) One biopsy from the greater curvature of the antrum within 2–3cm of the pylorus(3) One biopsy from the lesser curvature of the body 8cm from the cardia(4) One biopsy from the greater curvature of the body 8cm from the cardia(5) One biopsy from the incisura angularis–Three biopsies protocol (alternative): one biopsy from the incisura angularis, one biopsy from the greater curvature of the body, one biopsy from the greater curvature of the antrum | –If the search for H. pylori infection is positive, according to family history, perform the protocol for environmental metaplastic atrophic gastritis–Alternative strategy in special cases (e.g., poor tolerance during the procedure) |
| Environmental metaplastic atrophic gastritis | Protocol of 12 targeted biopsiesOne biopsy from each quadrant of the antrumTwo biopsies from the incisura angularisFour biopsies from the body (lesser and greater curvatures)Two biopsies from the cardia | –Alternative approach: seven random biopsies from the gastric cavity–Autoimmune atrophic metaplastic gastritis: biopsies if suspected endoscopic lesions |
| Gastric polyps | Solitary polyps–Polypectomy whenever possible; alternative, representative biopsies–All adenomatous polyps, fundic gland polyps >1cm and hyperplastic polyps >2.5cm should be removedMultiple polyps–The largest polyp should be removed–Representative biopsies from the smaller polypsHyperplastic and adenomatous polyps–Protocol for environmental metaplastic atrophic gastritis–Biopsies of the surrounding mucosa | |
| Peptic ulcer disease | –Multiple biopsies (≥8) from the base and edges if there is suspicion of malignancy | –Search for H. pylori infection |
| Celiac disease | –Four to six biopsies from the duodenal bulb and distal duodenum | –Do not perform biopsies if minor abnormalities of the duodenal mucosa |
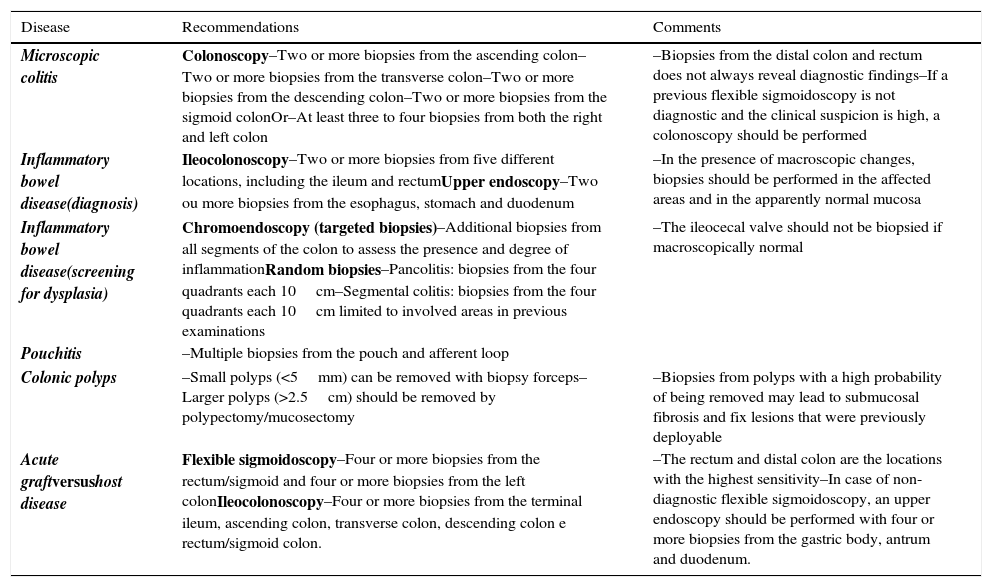
Summary of recommendations for biopsies in lower endoscopy.
| Disease | Recommendations | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| Microscopic colitis | Colonoscopy–Two or more biopsies from the ascending colon–Two or more biopsies from the transverse colon–Two or more biopsies from the descending colon–Two or more biopsies from the sigmoid colonOr–At least three to four biopsies from both the right and left colon | –Biopsies from the distal colon and rectum does not always reveal diagnostic findings–If a previous flexible sigmoidoscopy is not diagnostic and the clinical suspicion is high, a colonoscopy should be performed |
| Inflammatory bowel disease(diagnosis) | Ileocolonoscopy–Two or more biopsies from five different locations, including the ileum and rectumUpper endoscopy–Two ou more biopsies from the esophagus, stomach and duodenum | –In the presence of macroscopic changes, biopsies should be performed in the affected areas and in the apparently normal mucosa |
| Inflammatory bowel disease(screening for dysplasia) | Chromoendoscopy (targeted biopsies)–Additional biopsies from all segments of the colon to assess the presence and degree of inflammationRandom biopsies–Pancolitis: biopsies from the four quadrants each 10cm–Segmental colitis: biopsies from the four quadrants each 10cm limited to involved areas in previous examinations | –The ileocecal valve should not be biopsied if macroscopically normal |
| Pouchitis | –Multiple biopsies from the pouch and afferent loop | |
| Colonic polyps | –Small polyps (<5mm) can be removed with biopsy forceps–Larger polyps (>2.5cm) should be removed by polypectomy/mucosectomy | –Biopsies from polyps with a high probability of being removed may lead to submucosal fibrosis and fix lesions that were previously deployable |
| Acute graftversushost disease | Flexible sigmoidoscopy–Four or more biopsies from the rectum/sigmoid and four or more biopsies from the left colonIleocolonoscopy–Four or more biopsies from the terminal ileum, ascending colon, transverse colon, descending colon e rectum/sigmoid colon. | –The rectum and distal colon are the locations with the highest sensitivity–In case of non-diagnostic flexible sigmoidoscopy, an upper endoscopy should be performed with four or more biopsies from the gastric body, antrum and duodenum. |
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is an extremely common pathology. It is estimated that approximately 15% of the population of the United States presents symptoms of chronic reflux.5 The most common complication of GERD is esophagitis, observed in 20% of the individuals submitted to endoscopy in western countries. However, the weak correlation between endoscopic and histologic findings prevents the definition of a biopsies protocol in this situation. The clinical implication of histological abnormalities in patients without macroscopic changes is unknown, and the biopsies should be directed only to irregularities of the mucosa, if clinically appropriate.6 Also, performing endoscopic biopsies in an esophageal–gastric junction with inflammatory signs without other changes reflects a situation often associated with unnecessary use of resources. If the histological examination reveals intestinal metaplasia in this context (ultra-short segment Barrett's esophagus), the clinical significance and the follow-up to be done are unknown, by which, in this situation, the biopsy is not recommended.7
2.2Barrett's esophagusThe most worrying histological complication in GERD is the development of Barrett's esophagus, in particular by its association with esophageal adenocarcinoma (20 times increased risk), whose incidence has increased.8 Barrett's esophagus is identified endoscopically and histologically confirmed by the replacement of the normal mucosa of the distal esophagus by metaplasic columnar epithelium,9 and is currently the main cause for esophageal biopsies. Prague classification is recommended to describe the extension of the Barrett's esophagus, taking as a point of reference the proximal limit of the gastric folds.10 The presence of intestinal metaplasia and the extent of the changes determine the subsequent follow-up. Seattle protocol has been broadly used in the characterization of lesions compatible with Barrett's esophagus, and there is evidence that its adoption increases the success rate of the endoscopic diagnosis, in particular the detection of dysplastic changes.11 The protocol consists in performing biopsies in the four quadrants at each 2cm. In agreement with the histological findings, the follow-up should be the following:
- o
In Barrett's esophagus without dysplasia it is recommended to perform biopsies of the four quadrants at each 2cm every 3–5 years;
- o
In Barrett's esophagus with low grade dysplasia it is recommend to perform biopsies of the four quadrants at each 1–2cm every 6–12 months;
- o
In Barrett's esophagus with high-grade dysplasia it is recommended to perform biopsies of the four quadrants each 1cm every three months, in the absence of treatment for its eradication.
Short segments (<3cm) without intestinal metaplasia should not be followed after a second endoscopy confirming the absence of metaplasia.4
2.3Eosinophilic esophagitisThe incidence of eosinophilic esophagitis has been increasing in recent decades. Population-based studies suggest prevalence greater than 1:1000 individuals, with higher incidence in males, and there is a clear association with other atopic pathologies.12 The main symptoms include dysphagia and food impaction, and its diagnosis requires the integration of clinical, endoscopic and histological features.4 The histological findings may be discontinuous in its distribution and a variable number of eosinophils per high power field have been reported. The studies revealed that the completion of 3–6 biopsies presents sensitivity between 97 and 100% when using a cut-off of 15 eosinophils per high power field.13 It is important to mention that other conditions may present eosinophilia of the esophageal mucosa, in particular GERD, although in this case it is expected to be limited, or more exuberant, in distal esophagus. As such, the scheme of biopsies most universally accepted consists in performing two to four biopsies of the proximal esophagus, two to four biopsies of the distal esophagus and biopsies of the gastric antrum and duodenum in suspected cases of eosinophilic gastroenteritis.14 In the presence of eosinophilia compatible with the diagnosis, endoscopy should be repeated after a trial of eight weeks with a pump inhibitor proton.
2.4Infectious esophagitisWith the increasing use of immunosuppressants in the context of organ transplantation and chronic inflammatory diseases, in oncological situations with need of chemotherapy and with the epidemic infection by the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), infections caused by pathogens such as cytomegalovirus (CMV), human herpesvirus (HSV) and Candida spp. have become relatively common. Viral esophagitis presents macroscopically as ulcerated lesions. CMV infects predominantly columnar cells, and biopsies directed to the base of the ulcers increases the diagnostic accuracy. Although there are not a stipulated minimum number of biopsies, the obtaining of three samples has a sensitivity of at least 80%. The qualitative research of CMV by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) has a higher sensitivity than the histopathological evaluation, although it does not distinguish a latent infection from a clinically significant one.15 In contrast to CMV, HSV infects mainly the squamous epithelial cells, and, in suspected cases, the biopsies should be oriented toward the edges of the ulcers. The analyses by PCR or viral culture may help in establishing the diagnosis.16Candida colonization is frequency in the oropharynx, but it may become pathogenic and cause esophagitis in immunocompromised individuals. Candida albicans is the most common species. In suspected esophageal candidiasis, it is recommended to perform multiple biopsies of the affected area. The complementation of biopsies with an exfoliative cytology may increase the diagnostic sensitivity.17
2.5Helicobacter pylori infectionGastric infection by Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) is the main cause of peptic ulcer disease, and has an important role in the pathogenesis of MALT lymphoma and gastric adenocarcinoma.18 The choice of the diagnostic approach depends heavily on the clinical situation, costs and local expertise. The endoscopy based tests include tissue activity of urease (faster and cheaper, sensitivity and specificity greater than 90–95%), histological evaluation (sensitivity 80–90% and specificity >95%) and cultural test (expensive, time-consuming, allows antimicrobial sensitivity testing). Whenever possible, we should opt for the urease test.2,4 In this situation, it is recommended that one or two biopsies are taken 5cm proximal to the pylorus, in the lesser curvature near the incisura angularis or in the great curvature opposite to the incisura angularis.19 However it is important to take into account that in the presence of therapy with a proton pump inhibitor (PPI), bismuth or antibiotics, and in the context of upper gastrointestinal bleeding, the sensitivity of this rapid test decreases considerably. As such, in these situations, it should be considered the histological evaluation if the urease test is negative.2 PPIs should be stop at least one week before the endoscopy. The histopathological diagnosis does not yet have a generally accepted biopsies protocol. The most recent literature describes basically two optional approaches, both with similar sensitivity:
- o
Three biopsies approach, including the incisura angularis, the great curvature of the body and the great curvature of the antrum2;
- o
Protocol of Sydney, which includes five biopsies encompassing the lesser curvature of the antrum within 2–3cm of the pylorus, the great curvature of the antrum within 2–3cm of the pylorus, the lesser curvature of the body 8cm distal to the cardia, the great curvature of the body 8cm distal to the cardia, and the incisura angularis.20
Sidney protocol presents the theoretical advantage of identifying the micro-organism in individuals with chronic gastritis with more than 15–20 years of evolution with atrophic changes in the antrum and consequent reduction of H. pylori population in this location. If the search of H. pylori infection is positive, it is recommended to perform biopsies for screening of metaplasic atrophic gastritis.2 In the absence of another reason for a new endoscopy, the confirmation of eradication should be made through non-invasive methods.
2.6Environmental metaplastic atrophic gastritisBy the age of 70, virtually all individuals present with chronic gastritis. The environmental metaplastic atrophic gastritis (or chronic gastritis type B) is the most common form, and H. pylori infection is in the genesis of its development. Historically described as “predominantly antral”, it is estimated that the conversion into pangastritis is dependent on the time of evolution, and it occurs after 15–20 years.21 The biopsies in this context aim to establish the diagnosis, define the origin and distribution of the disease and to evaluate the presence and extent of dysplastic or neoplastic changes.2 In the absence of risk factors such as family history of dysplasia or gastric cancer, biopsies for histological evaluation of a stomach without changes or endoscopic aspects suggestive of gastritis are not necessary.4 But in the presence of family history, especially in the presence of H. pylori infection, it is currently necessary to rule out the presence of metaplastic atrophic gastritis. The best available evidence is described for two optional approaches:
- o
Seven random biopsies of the stomach fundus, body and antrum22;
- o
Twelve biopsies protocol: one in each quadrant of the antrum (2–3cm from the pylorus), two of the incisura angularis, four of the body (lesser and great curvature) and two of the cardia.3
The protocol for environmental metaplastic atrophic gastritis should be sufficient for the histological diagnosis of H. pylori infection.2
2.7Autoimmune atrophic metaplastic gastritisAutoimmune atrophic metaplastic gastritis (or chronic gastritis type A) affects mainly the gastric fundus and body, sparing the antrum. Traditionally, this form of gastritis is associated with pernicious anemia in the presence of circulating anti-parietal cells and/or anti-intrinsic factor antibodies (hence the term “autoimmune”), and presents an increased risk of adenocarcinoma and carcinoid tumors.21 As there is no described endoscopic approach defined for these cases, it should be individualized. The biopsies should be directed to the presence of ulcers, nodules, polyps or masses for exclusion of malignancy.2
2.8Gastric polypsGastric polyps are usually asymptomatic and discovered accidentally. The gastric epithelial polyps can be classified as fundic glands polyps (risk of malignancy in the context of familial adenomatous polyposis), hyperplastic polyps (foci of dysplasia in up to 20% of cases), adenomatous polyps (higher risk of malignancy) or neuroendocrine tumors (NETs).2 The incidence and significance of gastric polyps differ among themselves and between the different populations. The decreased incidence of H. pylori infection reduced the incidence of hyperplastic and adenomatous polyps.18 On the other hand, the increased chronic use of PPIs has been associated with an increasing incidence of fundic glands polyps.2
In the presence of solitary polyps, it is recommended that they should be submitted to biopsy or removed. The following approach will be determined by the histology. All the adenomatous polyps, the fundic glands polyps with more than 10mm, and all hyperplastic polyps with more than 5mm should be removed.23 In the case of multiple polyps, the greater ones should be removed by polypectomy, and representative samples of smaller polyps must be obtained. Again, the following approach will be determined by the histology.4
Once the hyperplastic polyps and adenomas are associated with atrophic gastritis and H. pylori infection, the apparently normal mucosa of the antrum and body must be submitted to biopsy (by adopting one of the strategies described in the environmental metaplastic atrophic gastritis) to evaluate the stage of gastritis and, consequently, the risk of cancer. Patients with evidence of H. pylori infection should be treated.2
Gastric NETs are classified into 3 types, according to their pathogenesis. The types I and II are associated with the presence of hypergastrinemia, which can be primary (type II) or secondary to chronic atrophic gastritis (type I). These two types of NETs can be treated conservatively because their course is usually benign. However, the type III gastric NETs is more aggressive, sporadic and develops in the context of normal levels of serum gastrin. These tumors should be resected, usually by surgery. Therefore, if there is suspicion of NETs, gastric biopsies in initial endoscopy, together with the determination of serum gastrin will make the differentiation between the various existing types and will influence the subsequent approach.24
2.9Peptic ulcer diseaseGastric and duodenal ulcers share many characteristics in particular in terms of pathogenesis, diagnosis and treatment.25 However, while a duodenal ulcer rarely presents with malignant features, gastric ulcers often represent malignant ulcerated neoplasms. Therefore, it is recommended to perform multiple biopsies (≥8) in the base and edges of gastric ulcers if there is suspicion of malignancy or if the endoscopy characteristics suggest such diagnosis.4 An exfoliative cytology may be complementary to biopsy.2 The gastric ulcers deserve endoscopic control until full healing, as it is proven that the failure to comply with this recommendation is associated with missed cancers.26 In the presence of peptic ulcer disease it is mandatory to search for H. pylori infection, as previously described.
The gastric adenocarcinoma of diffuse type is less common, but can occur without changes in the mucosa. In these cases, the presence of suspicious signs (low distensibility and suggestive clinical context) should lead to biopsies.4
2.10Celiac diseaseBiopsies in the small intestine are required for the establishment of a suspected diagnosis of celiac disease, being the main indication for biopsy in the duodenum. The biopsies should be performed in patients with symptoms and laboratory abnormalities suggestive of malabsorption and/or nutrient deficiency with positive anti-celiac antibodies.27 Since the clinical presentation of celiac disease is often subtle, it is important that the threshold for biopsy be relatively low.28
The implementation of multiple biopsies from various locations prevents inadequate sampling due to the discontinuous nature of the distribution of histological changes, and there is some evidence that the duodenal bulb is less affected by this non-uniform distribution.4 As such, it is recommended to perform four to six biopsies of the duodenal bulb and distal duodenum, which must be placed in separate containers, regardless of the macroscopic findings.2 Similarly, in the absence of a suspected diagnosis of celiac disease in the presence of minor abnormalities of the duodenal mucosa, biopsies are not indicated.
3Lower endoscopy3.1Microscopic colitisThe suspicion of microscopic colitis is the main reason for conducting biopsies in the colon in the presence of a normal mucosa.29,30 Two distinct forms of microscopic colitis are described: collagenous colitis and lymphocytic colitis. Histologically, the collagenous colitis presents two main findings: increased subepithelial deposition of collagen and intraepithelial lymphocytic infiltration (this finding alone defines lymphocytic colitis). Microscopic colitis is more common in women, and is usually diagnosed in the sixth or seventh decade of life in the context of watery chronic diarrhea (identified in up to 20% of these cases).31 Although the etiology of microscopic colitis is not fully defined, there is a clear association with the intake of NSAIDs and, more recently, and with celiac disease (that should always be excluded in this situation).30
Colonoscopy should be the preferred approach since biopsies of the distal colon and rectum does not always reveal diagnostic findings.32 In this case, it must include two or more biopsies of the ascending colon, two or more biopsies of the transverse colon, two or more biopsies of the descending colon and two or more biopsies of sigmoid colon.2 As an alternative strategy three to four biopsies of both the right colon and the left colon should be performed.30
3.2Inflammatory bowel disease – diagnosisIn patients with suspected inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) the endoscopic studies are usually reserved for patients with disease apparently slight to moderate.33 Obtaining biopsies during the colonoscopy is mandatory, regardless of the addition of time or potential risks. Biopsies are fundamental for diagnostic confirmation and for the determination of the extent of the disease, information that is fundamental to the definition of the therapeutic strategy. However, biopsies alone are not sufficient for definitive diagnosis, and their results should be integrated into clinical context.34
Ileocolonoscopy is the endoscopic examination recommended in all patients, and two or more biopsies in five different locations, including the ileum and rectum should be obtain.35 In the presence of macroscopic changes, it is recommended that the biopsies be performed in areas apparently involved by disease and in the mucosa of normal appearance around, and they should be separated and identified from proximal to distal.2 In the presence of ulcerated lesions, two or more tissue samples should be labeled separately for the identification of viral inclusions; moreover, biopsies from the edges of ulcers or aftoid erosions increase the detection rate of granulomas.30
If there is suspicion of upper digestive tract involvement, it should be considered an upper endoscopy with two or more biopsies of the esophagus, stomach and duodenum.36
3.3Inflammatory bowel disease – screening of dysplasiaThe endoscopic surveillance of colonic dysplasia is currently recommended in patients with long-term ulcerative colitis or Crohn's colitis, and should be initiated 8–10 years after the diagnosis of a pancolitis and 12–15 years after the diagnosis of a left colitis.37,38
Taking into account the present evidence, chromoendoscopy with targeted biopsies should be the global approach in the near future. If there is a gastroenterologist with experience in performing chromoendoscopy, this technique should be prioritized. It is recommended that the additional biopsies in all segments of the colon should be made to assess the presence and degree of inflammation. The observance of this technique is associated with a detection rate of dysplasia 3 times greater than that described for the protocol of random biopsies.30
However, in the majority of centers, the protocol of random biopsies remains as the endoscopic approach. In the case of pancolitis, it is recommended biopsies of the four quadrants each 10cm from the cecum to the rectum, with a minimum number of 33 biopsies.2 In the absence of pancolitis, it is recommended to perform biopsies of the four quadrants each 10cm limited to areas with endoscopic or histological involvement in previous examinations.39 Any lesion suspected of containing dysplasia should be submitted to biopsy or, ideally, removed, and the surrounding mucosa should also be sampled if involved by inflammatory disease.30 The ileocecal valve should not be subject to biopsies if macroscopically normal.
3.4PouchitisPouchitis is the main complication in patients with ulcerative colitis undergoing proctocolectomy with ileo-anal anastomosis, occurring in 30–50% of cases. Patients’ complaints involve abdominal cramps, urgency, night incontinence, and fever. Patients with symptoms of pouchitis after proctocolecomy should be submitted to endoscopy with multiple biopsies of the ileo-anal pouch and afferent loop. In the presence of macroscopic changes on the afferent loop, the possibility of a Crohn's disease should be considered, and the diagnosis can be confirmed by histology.40
3.5Polypoid lesions of colonMost colo-rectal cancers, regardless of its etiology, come from adenomatous polyps, of which only a minority become malignant (<1%). Adenomas are identified in approximately 30% of middle-aged individuals and in approximately 50% of the elderly population. Colonoscopy is considered the best approach for screening and prevention of colorectal cancer. Clinically, the likelihood of an adenomatous polyp evolve for cancer depends on its macroscopic appearance, its dimensions, and the histological characteristics.41
As a general rule, polypoid lesions are excised and not submitted to biopsy. Small lesions (<5mm) can be removed with a forceps biopsy or through polypectomy. Lesions of larger dimensions can be removed by polypectomy or mucosectomy, if technically possible.30 This approach allows a more definitive histopathological evaluation, and can be curative. Biopsies in lesions with a high probability of being subsequently submitted to endoscopic resection can promote the development of submucosal fibrosis and fix lesions previously deployable. In addition, it should always be considered the potential variability of biopsies that may not be able to identify foci of adenocarcinoma in lesions of large dimensions. In these cases it should be considered the primary excision of the lesions. Furthermore, this attitude decreases the risk of “contaminate” biopsies of other benign lesions with possible foci of adenocarcinoma of greater risk lesions.30
3.6Acute graft versus host diseaseThe ideal endoscopic approach is not defined. Rectum and distal colon are the sites with the highest sensitivity, even in patients with symptoms suggestive of involvement of the upper digestive tract.42,43 Two potential approaches are described in the literature.2 The first involves the implementation of a flexible sigmoidoscopy with four or more biopsies in the rectum/sigmoid and four or more biopsies in left colon. If the sigmoidoscopy is not diagnostic, it is suggested to perform an upper endoscopy with four or more biopsies in the gastric antrum and body and duodenum, and may also be considered the distal esophagus. The second approach is to conduct an ileocolonoscopy with four or more biopsies in the terminal ileum, four or more biopsies in the right colon, four or more biopsies in the transverse colon, four or more biopsies in the left colon and four or more biopsies in the rectum/sigmoid.
4ConclusionThis review seeks to condense the existing evidence concerning the performing of biopsies in gastrointestinal endoscopy, focusing on the precise diagnosis of the most common gastrointestinal diseases that motivate endoscopic examinations through the rational use of resources, without compromising the proper follow-up of patients. In addition, it also describes situations in which the histopathological evaluation may not be justifiable by its low sensitivity and specificity, in addition to possibly unnecessary costs. The development of policies together with the pathologic department it is fundamental to the effective establishment of these practices.
Ethical disclosuresProtection of human and animal subjectsThe authors declare that no experiments were performed on humans or animals for this study.
Confidentiality of dataThe authors declare that no patient data appear in this article.
Right to privacy and informed consentThe authors declare that no patient data appear in this article.
Conflict of interestThe authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.