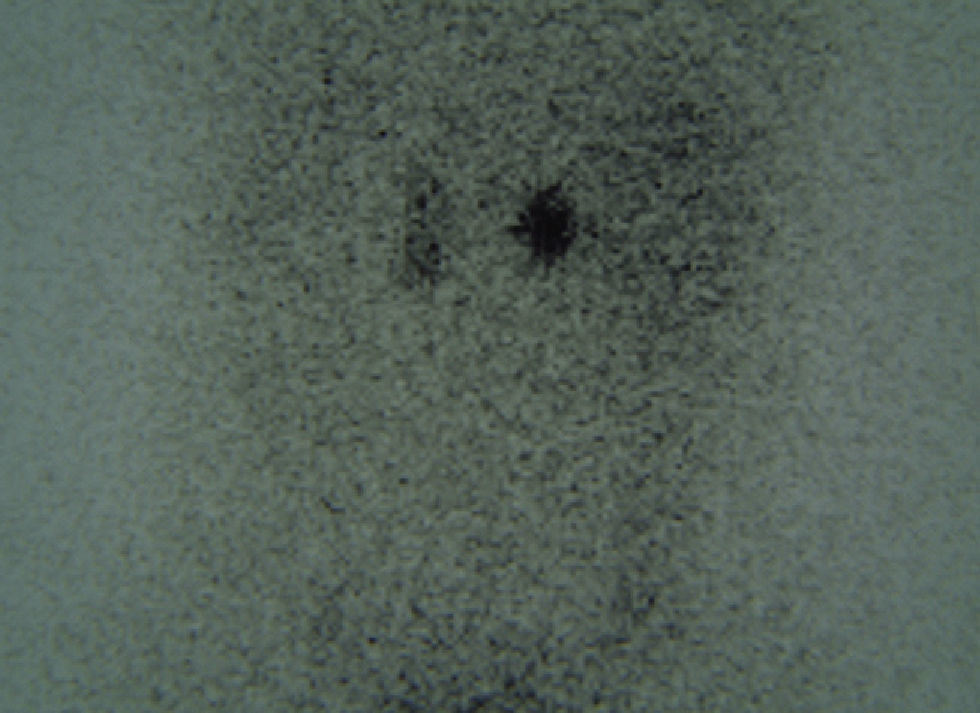
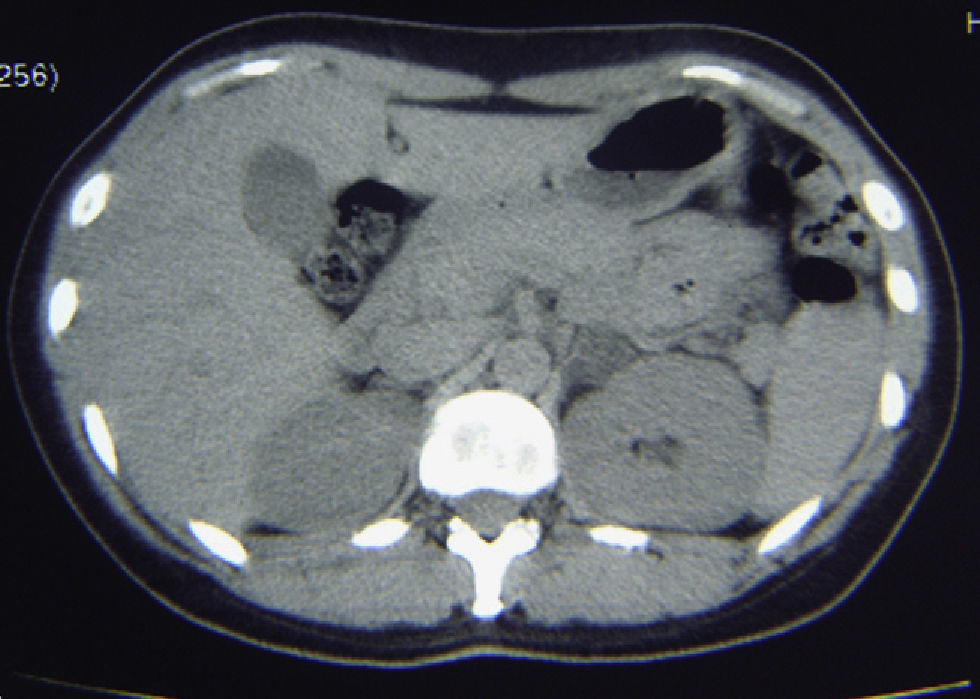
Presentamos el caso de una mujer de 33 años con HTA e hipopotasemia sintomática, que fue tratada con betabloqueantes y diuréticos, añadiéndose posteriormente telmisartán y potasio. En la consulta de nefrología se sustituyó toda la medicación por un bloqueante alfa, ingresandola para estudio de hipertensión secundaria. Durante el ingreso se comprobó la existencia de hipopotasemia, hiperpotasuria, renina plasmática disminuida basal y tras estimulación, aldosterona elevada basal y tras estimulación, cociente aldosterona/actividad de renina plasmática elevado. En un TAC abdominal se constató la existencia de una masa en la glándula suprarrenal izquierda, confirmando la hipersecreción de aldosterona mediante cateterización de venas adrenales y gammagrafia suprarrenal con 131 icolesterol.
We present the case of a 33-year old woman with arterial hypertension and symptomatic hypokalemia who was treated with beta blockers and diuretics, with subsequent addition of telmisartan and potassium. In Nephrology, all of her medication was replaced by an alpha blocker and she was admitted for study of secondary hypertension. During her hospitalization, the existence of hypokalemia, hyperkaliuria, low basal and post-stimulation plasma renin, elevated basal and post-stimulation aldosterone, elevated aldosterone/plasma renin ratio was verified. The abdominal CT scan demonstrated the existence of a left adrenal gland mass, confirming aldosterone hypersecretion by catheterization of the adrenal veins and adrenal scintigraphy with 131Icolesterol, laparoscopically excising the mass. The diagnosis was Conn's syndrome due to left adrenal adenoma. The interest of this case is due to the diagnostic difficulty based on imaging tests and the aid of the adrenal vein catheterization.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora