Ischemic heart disease (IHD) is the leading cause of mortality worldwide, and finding cheap and accurate screening tests is crucial. This study aimed to evaluate the predictive value of C-reactive protein (CRP)/albumin ratio (CAR) in the diagnosis of IHD using myocardial perfusion imaging (MPI).
MethodsIn this cross-sectional study, a total of 112 patients were investigated to find any relationship between CAR and myocardial ischemia by using myocardial perfusion scintigraphy. Data were analyzed using SPSS, with a P-value below 0.05 considered statistically significant.
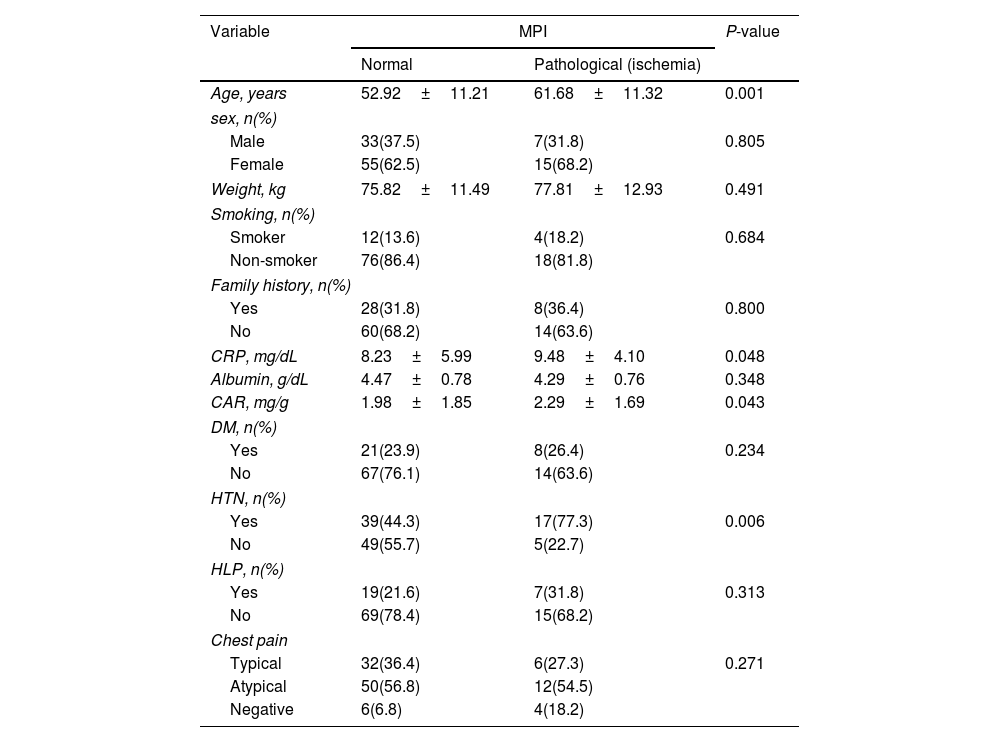
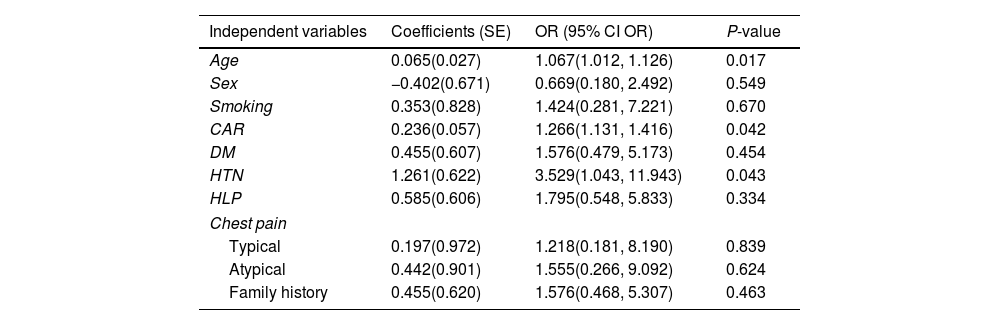
ResultsEighty-eight patients had normal MPI. Twenty-two patients had some degree of myocardial ischemia in MPI. The normal MPI and pathological MPI groups were similar in terms of sex, weight, smoking, family history of IHD, albumin levels, diabetes mellitus status, hyperlipidemia, and chest pain type. The CRP, and CAR means in the patients with myocardial ischemia were significantly higher than those with normal MPI.
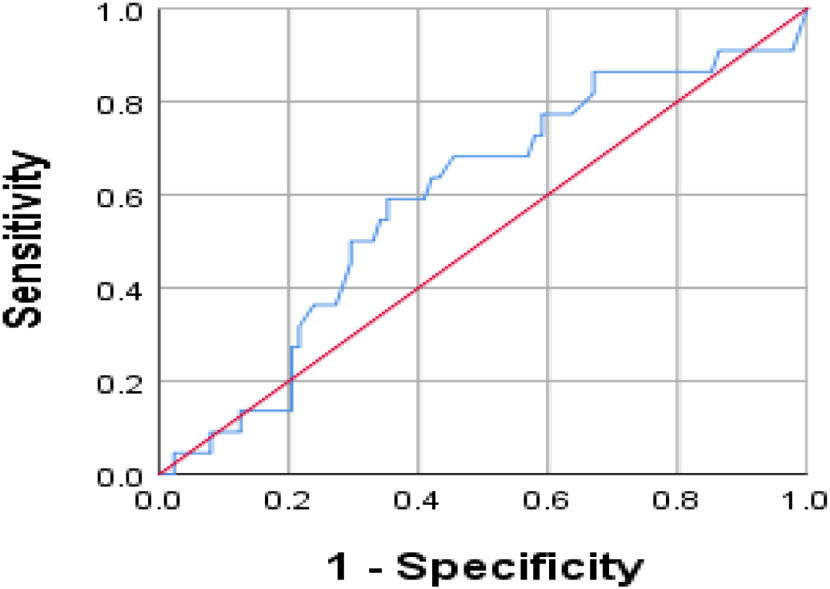
ConclusionAlthough the value of CAR was significantly higher in patients with myocardial ischemia compared to subjects with normal MPI and it was an independent predictor of IHD, the capability of CAR in diagnosing myocardial ischemia was not very strong with a sensitivity and specificity of about 60%.
La cardiopatía isquémica (CI) es la principal causa de mortalidad en todo el mundo, y encontrar pruebas de detección económicas y precisas es de gran valor. Este estudio tuvo como objetivo evaluar el valor predictivo de la relación proteína C reactiva (CRP)/albúmina (CAR) en el diagnóstico de la CI mediante imágenes de perfusión miocárdica.
MétodosEn este estudio transversal, se investigó a un total de 112 pacientes para encontrar alguna relación entre el CAR y la isquemia miocárdica mediante el uso de gammagrafía de perfusión miocárdica. Los datos se analizaron mediante SPSS® y un valor de p inferior a 0,05 se consideró estadísticamente significativo.
ResultadosOchenta y ocho pacientes tenían imágenes de perfusión miocárdica normales. Veintidós pacientes tenían algún grado de isquemia miocárdica en las imágenes de perfusión miocárdica. Mientras que los grupos con imágenes de perfusión miocárdica normal y anormal fueron similares en términos de sexo, peso, tabaquismo, antecedentes familiares de cardiopatía isquémica, niveles de albúmina, estado de diabetes mellitus, hiperlipidemia y tipo de dolor torácico. Las medias de CRP y CAR en los pacientes con isquemia miocárdica fueron significativamente más altas que en aquellos con imágenes de perfusión miocárdica normal.
ConclusiónAunque el valor de CAR fue significativamente mayor en los pacientes con isquemia miocárdica en comparación con los sujetos normales en las imágenes de perfusión miocárdica y fue un predictor independiente de CI, la capacidad de CAR en el diagnóstico de isquemia miocárdica no fue muy fuerte con una sensibilidad y especificidad de aproximadamente solo el 60%.