Editado por: Andre R Brunoni, Marie-Anne Vanderhasselt, Leigh Chavert
Más datosRepetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) has emerged as a therapeutic solution in patients with treatment-resistant auditory verbal hallucinations. However, the optimal stimulation parameters remain unclear, especially for patients with clozapine-resistant symptoms.
MethodIn an open label retrospective study, we investigated whether parameters of stimulation that were useful in patients with major depressive disorder would help schizophrenia patients with treatment-resistant auditory verbal hallucinations. Fourteen participants, including 9 under clozapine, received 30 sessions of 1 Hz rTMS over 3 weeks (360 pulses per sessions delivered with 60 s ‘on’ and 30 s ‘off’ at 110% of the resting motor threshold, 2 sessions per day). Stimulations were applied over the left temporoparietal junction (T3-P3 according to 10/20 system).
ResultsAfter rTMS, a significant decrease of auditory verbal hallucinations was observed (−38.7% ± 31.8, p = 0.003) on the Auditory Hallucination Rating Scale. The beneficial effects were also significant in the 9 patients who were also receiving clozapine (−34.9% ± 28.4, p = 0.01).
ConclusionsLow frequency rTMS, 30 sessions over 3 weeks, appears to be a suitable approach to decrease treatment-resistant auditory verbal hallucinations, including in patients with clozapine-resistant symptoms. Results from the current retrospective study in the clinical settings need to be confirmed by large-scale randomized sham-controlled trials.
Auditory verbal hallucinations are a very common symptom in patients with schizophrenia. Although first-line antipsychotic treatments can help reduce these disabling symptoms, in 20–40% of the cases, the response to antipsychotics is insufficient and other therapeutic solutions are warranted (Kane et al., 2019; Samara et al., 2019). In such cases, repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) has been proposed as a complementary therapeutic strategy (Hoffman et al., 2003). rTMS is a noninvasive brain stimulation technique that consists of applying a coil of stimulation over the scalp of the participant with respect to a specific targeted brain region. Depending on the stimulation parameters and the location of the coil, rTMS has proven efficacy in reducing treatment-resistant symptoms in patients with various psychiatric conditions (Hyde et al., 2022). In the case of auditory verbal hallucinations, repeated sessions of low-frequency (1 Hz) rTMS are generally applied over the left temporoparietal junction (Hoffman et al., 2003). However, some discrepancies are observed in the literature. While some studies have observed beneficial effects of rTMS (e.g., Hoffman et al., 2003; Poulet et al., 2005), others have failed to observe superiority of active rTMS over sham stimulation (e.g., Slotema et al., 2011). Even within the positive studies, it was observed that although some patients could be qualified as responders to rTMS with a decrease of more than 50% of symptoms after rTMS, some others did not perceive any beneficial effect. A recent meta-analysis including 11 randomized sham-controlled trials reported that active rTMS was superior to sham to reduce auditory hallucinations with a moderate effect size (SMD = −0.27, 95%CI = −0.51 to −0.03) (Li et al., 2020). Despite the decrease in effect size and increase in placebo effect reported in published meta-analyses over time (e.g., d = −0.76, 95% CI = 0.36 to 1.17 in 2007 (see Aleman et al., 2007)), the superiority of active rTMS over sham remains significant in this 2020 meta-analysis. Furthermore, in a recent pooled analysis of randomized controlled trials, it was suggested that rTMS was inefficient in reducing auditory hallucinations in patients treated with clozapine (Wagner et al., 2021). Latest evidence-based guidelines on the therapeutic use of rTMS suggest a possible effect (Level C of evidence) of 1 Hz rTMS for hallucinations (Lefaucheur et al., 2020), a level of proof that was decreased from a Level A of evidence in previous guidelines (Lefaucheur et al., 2011). Overall, the current literature highlights the need for larger studies before clear conclusions can be drawn about the clinical value of rTMS in the treatment of hallucinations in the clinical setting (Brunelin, et al., 2022) and little is known regarding optimal combination between rTMS and antipsychotic medication. The fact that not all patients are responders to rTMS leaves much room for optimization strategies to increase clinical efficacy.
In most studies of 1Hz rTMS for hallucinations, only 10 sessions of rTMS were performed over 5 or 10 consecutive days, with a stimulation intensity set at 90% or 100% of the resting motor threshold. However, in the case of rTMS for major depressive disorder, it was clearly established that performing more than 10 sessions and at higher intensity resulted in better clinical effects (Gershon et al., 2003). Here, we therefore proposed to investigate whether delivering a larger number of 1 Hz rTMS sessions at higher intensity would lead to beneficial outcomes in patients with treatment-resistant schizophrenia, including those under clozapine medication. In this regard, we proposed to use the same parameters of stimulation over the left temporoparietal junction than those we successfully used in patients with treatment-resistant major depressive disorder when targeting the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (Brunelin et al., 2014).
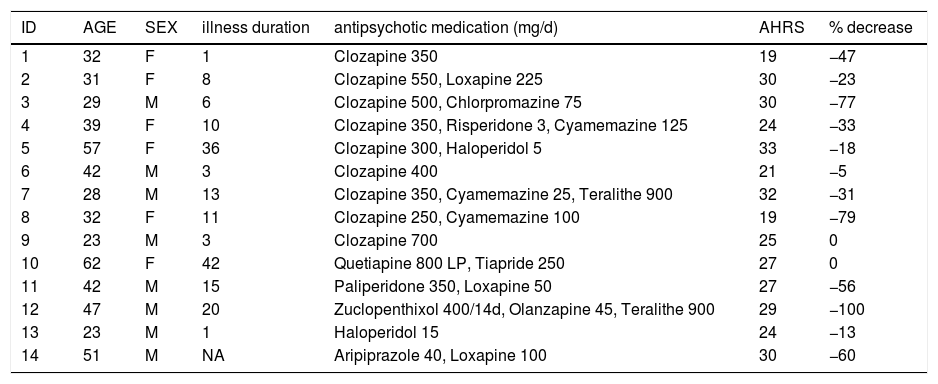
MethodsWe retrospectively assessed medical records from 22 patients with schizophrenia who presented difficult to treat symptoms and who were addressed to our Brain Stimulation unit for treatment-resistant symptoms at Le Vinatier Hospital (Ugo Cerletti Unit, Bron, France) between 2017 and 2022. All patients met the diagnosis of schizophrenia according to the DSM-5 criteria. They presented severe daily treatment-resistant auditory verbal hallucinations despite treated with antipsychotic medication at efficient dose and duration and despite the failure at least 2 previous medications with molecules from different pharmacological classes for the current episode. All patients provided their informed consent prior to receiving rTMS. The database was approved and registered (record number MR-003-2017-002) by the French national commission for information technology, data processing, and civil liberties (CNIL). Among the includible patients, psychometric data pre and post rTMS sessions were available only for 14 patients. Demographic and clinical details of the included patients were reported in Table 1.
Sociodemographic and clinical characteristics of patients at inclusion.
Age is expressed in years; AHRS: Auditory hallucination rating scale; F: Female; M: Male; NA: Not available.
Patients received 30 sessions of low-frequency rTMS with the following parameters: 6 trains of 1-min duration at 1 Hz frequency separated by 30-s inter-train "off" periods, as done in our previous study registered on clinicatrials.gov NCT00714090 (Brunelin et al., 2014). The duration of a single session was 8 min 30 s, and the 30 sessions were delivered over 3 weeks. We delivered 10 sessions per week, 2 sessions per day separated by at least 2 h (Poulet et al., 2005). The intensity of stimulation was set at 110% of the individual resting motor threshold (RMT) of the left hemisphere. The RMT was determined during the baseline visit by a trained psychiatrist using a visual method. The coil was placed on a point situated midway between T3 and P3 (according to the international 10–20 electrode placement system). Stimulations were performed using a MagPro X100 (Mag2Health, France) with a figure-of-eight 65 mm coil.
The severity of auditory hallucinations was evaluated twice with the Auditory Hallucination Rating Scale (AHRS) (Dondé et al., 2020; Hoffman et al., 2003) by a trained psychiatrist, once at the baseline visit and again 3 weeks later, within 3 days of the last session of rTMS.
AHRS scores at baseline and after rTMS were compared using Wilcoxon signed-rank tests for intragroup comparisons in JASP (version 0.16.3). Intergroup comparisons (clozapine versus non clozapine groups) were carried out with U Mann Whitney tests. Additionally, the effect sizes r were calculated as Z statistics divided by the square root of the sample size. The interpretation values for r according to Cohen's classification are: 0.1 to 0.3 (small effect), 0.3 to 0.5 (moderate effect) and superior to 0.5 (large effect).
ResultsAll patients received the 30 sessions of rTMS, except one who received only 20 sessions (Patient #2). Stimulation sessions were well tolerated by all patients and no adverse effects were observed. However, due to the pain experienced at each stimulation by two participants with a relatively high RMT (80% and 87% of the maximum output of the device), the stimulation intensity was decreased from 110% RMT to 100% RMT in these 2 patients (patients #11 and #14). The mean age of the patients was 38.4 years (± standard deviation 12.3, range 23–62). All patients were right-handed except one (Patient #3). The concurrent medication was kept unchanged throughout the study period. Nine patients received clozapine during the stimulation protocol, with a mean dose of 416.7 mg/day (± 141.4, range 250–700) (Table 1).
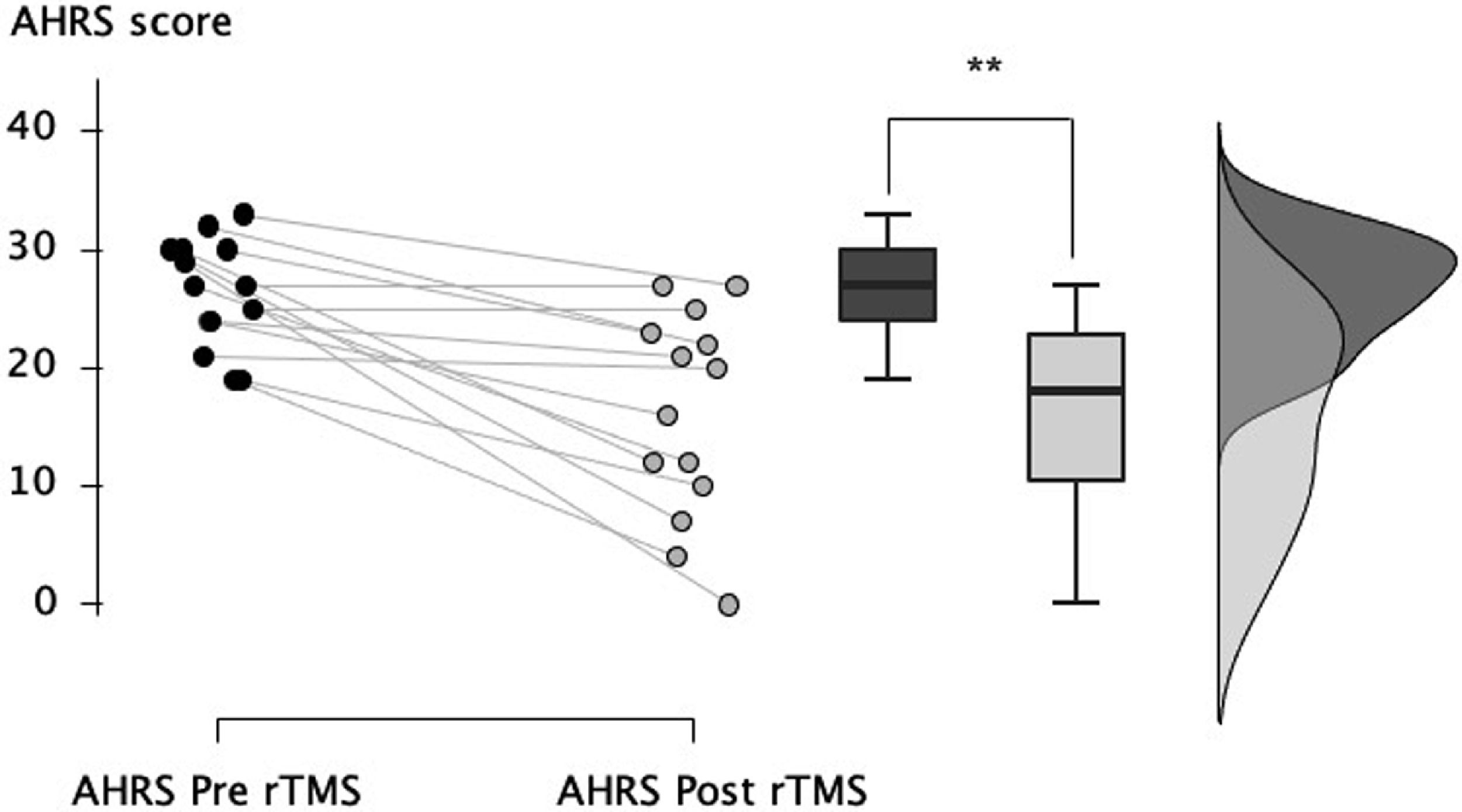
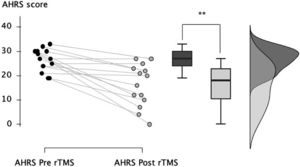
After completion of the rTMS sessions, the patients showed a significant reduction in auditory hallucinations from 26.4 ± 4.6 to 16.1 ± 8.7 (mean reduction of −38.7% ± 31.8, W = 78.0, p = 0.003, Fig. 1), with a large effect size (r = 0.82). At the end of the stimulation sessions, 5 patients (36%) were considered as responders and showed an at least 50% diminution of auditory hallucinations; 9 (64%) displayed a partial response defined as an at least a 20% diminution of hallucinations.
In the 9 patients with clozapine-resistant auditory hallucinations, we also observed a significant reduction in auditory hallucinations from 25.9 ± 5.5 to 17.1 ± 8.4 (mean reduction of −34.9% ± 28.4, W = 36.0, p = 0.01), with a large effect size (r = 0.84). Two clozapine-resistant patients (22%) were considered as responders and showed an at least 50% diminution of auditory hallucinations at the end of the stimulation sessions; 6 (67%) displayed a partial response defined as an at least a 20% diminution of hallucinations.
There was no significant difference in the decrease observed between the clozapine group (−8.8 ± 7.0) and the non-clozapine group (−13.0 ± 11.8; U = 18.0; p = 0.59) after the rTMS sessions.
DiscussionIn this open-label study conducted in 14 patients with schizophrenia who experienced treatment-resistant auditory hallucinations, we found a significant effect of 30 sessions of 1 Hz rTMS applied to the left temporoparietal junction (2 per day for 3 weeks) at 110% RMT on auditory hallucinations.
This study provides insights into the tolerability and feasibility of delivering more than 20 sessions of 1 Hz rTMS over the temporoparietal junction in patients with schizophrenia and auditory hallucinations. Indeed, although the total number of pulses delivered in our study (10,800) is quite similar to that of previous studies, only a few studies have proposed 1 Hz rTMS protocols with more than the standard 10 repeated sessions: 2 studies delivered 12 sessions (Bais et al., 2014; Vercammen et al., 2009), 2 delivered 15 sessions (Hoffman et al., 2013; Slotema et al., 2011) and 2 delivered 20 sessions (Blumberger et al., 2012; de Jesus et al., 2011). The idea of increasing the number of sessions to improve efficacy is supported by studies showing that repeated application of rTMS can induce longer lasting neuroplastic changes than a single continuous application (Goldsworthy et al., 2012; Nyffeler et al., 2006). Increasing the number of sessions could therefore be an alternative to increasing the rTMS dose, i.e., the total number of pulses delivered during an rTMS protocol, as this strategy has not been shown to substantially improve clinical outcomes in depression (Fitzgerald et al., 2020). This also ensures that the risk of side effects is not increased, as evidenced by the lack of adverse events in the current study.
In addition, although most of the TMS clinical studies have used once-daily sessions of rTMS, we proposed to deliver sessions twice-daily in line with our previous studies in schizophrenia (Brunelin et al., 2022; Poulet et al., 2005). Some studies in depression have directly compared once- to twice-daily protocols while matching the same total number of pulses and showed nonsignificant differences in final response or remission rates between conditions (Blumberger et al., 2021; Schulze et al., 2018), however, clinical improvement was faster (Schulze et al., 2018) and tends to be stronger (Modirrousta et al., 2018) with twice-daily sessions. Repeating sessions twice daily, which can be considered an 'accelerated' protocol of rTMS (Caulfield et al., 2022), is relevant to clinical practice because it reduces the number of days patients need to visit the clinical unit and thus can potentially increase adherence to treatment in certain clinical populations such as patients with schizophrenia (Brunelin et al., 2022).
One interesting aspect that emerged from our findings is that patients treated with clozapine seems to respond to 1 Hz rTMS with a similar rate as patients under other antipsychotic treatments. These results are not in line with those of Wagner et al., who found no differences between active and sham rTMS in reducing auditory hallucinations in patients treated with clozapine (Wagner et al., 2021). However, the stimulation parameters were not the same as in the present study. Future studies are needed to investigate the efficacy of 1 Hz rTMS in a larger sample of patients treated with clozapine and to conclude on the specificity of this protocol to induce beneficial clinical effects in clozapine patients.
ConclusionsIn conclusion, the current open-label study has presented a novel approach to reduce treatment-resistant auditory hallucinations in patient with schizophrenia using 30 twice-daily sessions of low-frequency 1 Hz rTMS. The lack of a sham group and of a longer follow up period are major limitation to drawn any clear conclusion on the usefulness of such intervention in clinical routine. Our results are encouraging, including for patients treated with clozapine, and the clinical value of such a protocol should be validated by a larger sample size in randomized placebo-controlled trials.
The authors thank the nurses of the Cerletti Unit, Le Vinatier Hospital for providing stimulation sessions and the CRA-study nurses Delphine Janin and Imelda Hegron for their help.
Role of the funding source: No role
Funding sources: This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.