The applications of the Internet-based technologies and the concepts of fuzzy expert systems (FES) have created new methods for sharing and distributing knowledge. However, there has been a general lack of investigation in the area of web-based fuzzy expert systems. In this paper, the issues associated with the design, development, and use of web-based applications from a standpoint of the benefits and challenges of development and utilization are investigated. The original theory and concepts in conventional FES are reviewed and a knowledge engineering framework for developing such systems is revised. For a human advisor to have a satisfying performance, expertise is a must. In addition, some of advisory rules are subject to change because of domain knowledge update. The human requests may have linguistic or crisp forms and a conventional expert system (ES) is not able to overcome the fuzziness in the problem nature. In this research, a Web-based fuzzy expert system for Common Human Advisor (FES-CHA) is developed and implemented to be used as a student advisor at the department‘s web portal. The system is implemented by using Microsoft Visual Studio .NET 2010, MVC and Microsoft SQL Server 2012.
Knowledge-based and decision making systems are the branches of artificial intelligence which are based on imitating the human demeanor in finding the pattern of solutions to problems. In the real world, if definite and straightforward solution cannot be found, human expertise is needed. Experts often follow a trial-and-error approach for problem solving. Since there is no specific solution for this kind of problems, defining a certain computer method for achieving the solution is difficult. Therefore, expert systems are used to reach this goal. In these systems, the program consists of a set of rules. The knowledge in an expert human brain is also a set of if-then rules. M. H. Goodarzi [1,2,3] proposed the fuzzy application in student evaluating system, portfolio advisor system and educational advisor system. Fuzzy concepts can convert multiple crisp inputs to specific linguistic variables and use fuzzy rules to infer. In [4] the fuzzy-based advisor for elections and the creation of political communities was proposed. In [5], a web-based fuzzy expert system is used to help inexperienced Indian farmers in the use of pesticide for their farms. The initial version of this software was introduced in 1995 in a single-user form. In forums, usually a user starts a discussion and expresses his/her opinions and approaches to a particular problem. [6] Proposes a model for creating a fuzzy-based expert forum that intelligently responds to questions asked by users. Finding the right broker at the right time is another issue that requires expertise. This may be the reason for which inexperienced investors loose in stock markets. In [7] a stock expert system model is proposed. The goal of this system is to make a good suggestion based on information about goods and market in order to reduce the loss and increase the benefit. Educational consulting system tries to mimic the behavior of the staff addressing the educational consulting issues. In [8] a fuzzy expert system for intelligent tutoring systems with a cognitive mapping is proposed. Human cognition has become one of the most attractive areas of research and application in artificial intelligence in which human susceptibility is emulated. In [9] a new fuzzy method for hotel selection is introduced as a hotel advisory system. In [10] the student achievements and education system performance in a developing country is proposed. The current paper, includes five major sections: in the next section some of related works are reviewed. The third section describes the fuzzy rule-based and decision making systems and introduces the proposed model. In section 4 the proposed system is discussed in details. Section 5 includes a sample of the advisor system implemented in a university. Finally, a conclusion is provided.
2Literature reviewIn a real voting the total of both, positive and negative votes for the candidates are collected. A major problem for the voters is when they have to select their deputies from a large list of candidate. The problem is more serious in cases where the candidates are unknown to the voters. However, the creation of political societies interested in addressing political issues is a hurdle to overcome. In [4] an advisor system for elections and creation of political communities based on fuzzy logic is proposed. In this approach the recommendation engine works with a modified fuzzy C-means algorithm and the Sammon mapping technique used for visualization of recommendations.
Each year in India, many farms are destroyed due to pests attack and insufficient experience of the farmers. In 2001, the loss was about 6.3 billion dollars. Soybean pest expert system (SOYPEST) [5] is a fuzzy expert system that asks fuzzy questions in order to generate a web-based response for the user. SOYPEST is created by using JESS and gradually became more accurate by receiving feedback from the users and the experts. Mutual information interchange and the creation ng of forums on the web are important issues which captivate many researchers. One of the best known content management systems (CMS) tools for this purpose is Vbulletin. There are reasons that support the possibility of receiving irrelevant answers, no answers at all, different confusing answers from several other users and unclear answers. These drawbacks may be considered as the Achilles heel of such systems. In [6], linguistic expressions are categorized and then n-gram algorithm is used to edit and convert the sentences to a proper format. This system supports 15 languages and by default the questions are multiple choice questions. The strong point of this system is its gradual improving knowledge base, the extended number and the expanded fields of topics; however, no considerable effort is done to find the best answer and the problem is solved through partial simulation of the human brain.
3Fuzzy decision making systemMost humans face difficulties related to life rules and regulations during their problem solving process. These rules and regulations are changing every now and then therefore, an expert is needed to memorize these rules in order to be able to help humans in their issues. The state of each person regarding the rules and regulations may differ from that of other people. Human state (HS) is a member of a fuzzy set with a degree of membership equal to μHS.
The First Step: determining and fuzzificating the inputs to the system by using fuzzy rules. Following are some examples of the fuzzy sets of the system on hand:
Fuzzy set for Law in judgment system.
Fuzzy set for passed courses in university.
Fuzzy set for marks of selected courses in university.
Fuzzy set for the rank and grade of student in the entrance exam
And so on…
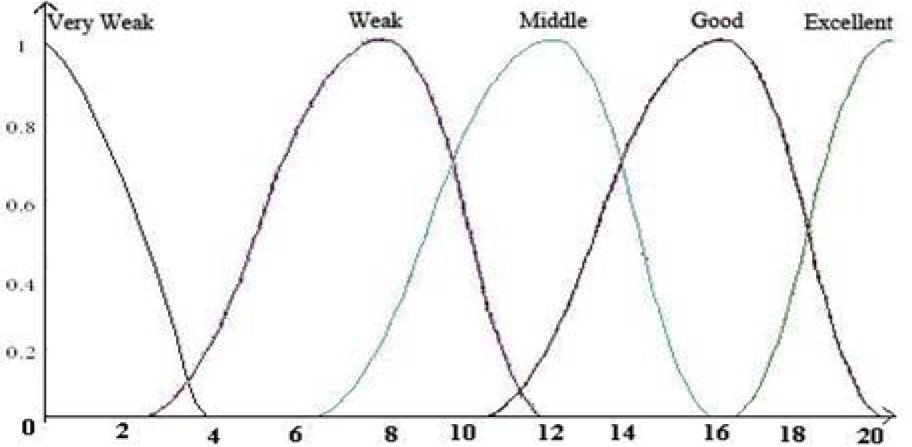
3.1One sample for fuzzification of the crisp variable of TA in university systemTotal grade point average (GPA) of students can be categorized into these groups: A, B, C, D and E. This categorization can be expressed through linguistic terms as Excellent, Good, Middle, Weak, Very Weak.
The Second Step: determining the degree of membership of linguistic terms including 3 following phases:
Phase 1. For each term, the value nearest to the numeric equivalent of the linguistic term which has the maximum degree of membership is selected. Here, the highest value for the linguistic term “Excellent” is 20 and 0 has the highest value in “Very Weak” fuzzy set.
Phase 2.For each term, the value (or values) which has (have) the membership degree of 0 is (are) determined.
Phase 3. point with μ=1 are connected to points with μ=0 by lines to form a gaussian (exponential) membership function. In cases in which there is more than one point with μ=1, a gaussian membership function is obtained. In this model, membership functions can be gaussian, Z-shaped and S-shaped. The membership function of GPA variable is shown in Figure 1.
For example: to fuzzify TA=3 into a linguistic variable, first of all, we write the formula for Z-shaped and gaussian membership function.
Then the result of equations for TA=3 are calculated giving the following equations:
TA=3 with μx(TA)=0.125 exists in "very weak" fuzzy collection and with μx(TA)=0.1353 is a member of "weak fuzzy" collection.
With competitive method the TA is changed to weak linguistic variable.
3.2Rule extractionThe core of the system is very flexible and can be applied in many advisory environments by substituting the knowledge-base of the system with an appropriate medical, judicial or sport, etc. advisory knowledge-base. For example, after an interactive negotiation with an advisor lecturer at a university, fuzzy rules can be elicited and used in the ES. The previous section illustrates how GPA can be fuzzified. The following rules are the result of the negotiations:
IfThe GPA is ModerateAnd
The number of semesters for which the student is registered is smallAnd
The courses that are not passed can be taken.Andpassed in one semesterAnd
The student has not given any pledgesAnd
The student has not received any disciplinary noticesAndThe student has not reached the maximum time period for his/her studiesAnd
The student has 5 marks between 10-12And
Some other student has had conditions similar to this Student
Then
To a large degree, it is possible thatthe student is allowed to continue his/her studies in the university by giving an official pledge of achieving a GPA over 14 in the next semester.
Else
According to the status of the student, the fuzzy system is not able to provide an answer. A human expert‘s opinion is needed.
3.3Publishing the system on the webThe rapid increase of information on the Internet is currently a key issue when one is looking for relevant information. The development of the World Wide Web and applying multimedia tools along accessibility of web sites from any place in the world makes feasible the design ofuser interface compatible with the web. Many expert systems in different fields of expertise are developed (EXSYS CORVID, SOYPEST, etc.) however, few are applied. Since linguistic terms and fuzzy sets are used, the process for inference should be done on the client rather than the server to reduce the server’s busy time. This procedure can be executed in browser by script languages like JavaScript, Java, VB Script, XML, AJAX and Applet.
3.4One application of the proposed system in a university portalBy implementing the proposed fuzzy advisor system in the university portal, before enrollment of the next semester, the students are checked and those who should be excluded are determined and prevented from registration for the next semester. This advisor system addresses his/her issue according to rules and regulations. In section 6 some questions and answers, which were provided by the advisor and the student, are shown.
4A look inside the systemThe proposed system is analyzed and designed by UML methodology and documents are generated with rational rose case tool.
The software is built on 5-tier layers such that when one of the layers is reconfigured or rebuild, other layers don‘t change. The framework of system is shown in Figure 2.
- a)
Initially, the user selects the type of advisory service and enters crisp data in web application layer via a web browser.
- b)
The input data related to the system is controlled for GPA, number of official notices received, educational level in university, criminal records (if any), type of illness in medical system (if any), etc. These are executed in Business Facade and business rules layer.
- c)
A request for fuzzification the Crisp variables and rules generation is submitted to knowledge-base of the system by data access layer with ADO.NET. Then the linguistic variables are generated just by view select, stored procedure & user define function execution. This section makes a database abstraction and prevents SQL-injection.
- d)
Linguistic variables are sent to inference engine and processed with mamdani model [11]. This section is accomplished by one stored procedure in database, named UstpInference.
- e)
Fuzzy answers are defuzzified and crisp output values are generated. This step is accomplished by one-user defined function in database, named UdfDefuzzifier.
Finally, the advisor system extracts answers to be shown to the user. Data object model of system is shown in Appendix 1.
4.1Implementation EnvironmentThe system is implemented in the 3 following layers:
Web Application layerThis layer includes Web Forms, Web User Controls, Web Component (Infragestics Grid Control) and Model View Control (MVC).
Business facade, business rules layerIncludes controls and business methods and attributes in C# classes:
- •
Fuzzy_decision.cs,
- •
Fuzzy_ruleInference.cs,
- •
Fuzzy_set.cs,
- •
Fuzzy_linguisticVariables.cs.
The class Cls_DataAccess.cs supports ADO.NET 3 and connectionless performance. First of all, users login to the portal site and select the advisor system link and select their problems category. System asks the questions related to the problems. Collecting the answers provided by the user, the CHA translates the user inputs to linguistic variables, makes the fuzzy rules and generate the fuzzy answer. Then with Segono model the fuzzy answer are defuzzified to crisp output and is reported to user. The implementation architecture of the system is shown in Figure 3. In implementation architecture diagram 3 sources can submit requests to the web server user, knowledge engineer and web service). Then the web server controls the requests and sends the appropriate interface for this request. After entering user information, the fuzzy question generator creates the fuzzy questions for the user. User enters the inputs and submits the data to server. When the user inputs are received by the web server, with rule generator, the fuzzifier and knowledge base, the If-part for the rules is generated. Then the inference engine refers to the system Knowledge base and if a match is found for the pattern within a fuzzy statement by using the Mamdani model, the fuzzy answers for theThen-part of the rules are generated. In case that the input data does not match any patterns in the rule base, an appropriate message stating that the system cannot find the answer is displayed. If the fuzzy answer is found, the system transfers that to the deffuzzifier and finally the crisp answer is reported to the user in the desired format including MS Excel, HTML, XML, histogram and report file. This system can connect to another database for refining the output and generates the additional information.
4.2Advantages of Fuzzy Expert systemsThe major advantage of these systems is that knowledge gradually turns into wisdom and can be used as a decision making tool in critical situations which replaces the conventional FAQ. Some other features are:
- •
More accessibility: Many experiments can be done. Simply an expert system is a mass production of experiments.
- •
Cost reduction: The cost of gaining experience by the user is decreased considerably.
- •
Risk reduction: The expert system can work in environments dangerous, harmful or unpleasant for human.
- •
Eternity: Obviously, these systems don’t die.
- •
Multiple experts: An expert system can be the result of knowledge elicitation from several experts.
- •
More reliability: These systems don’t get tired or sick, they do not go on a strike and they do not conspire against their managers. On the contrary, these are often done by human experts.
- •
Explanation capability: An expert system can explain the way in which the results are obtained. On the contrary, due to many reasons (fatigue, unwillingness, etc.) human experts are not able to provide such explanations all the time.
- •
Quick response: Expert systems respond quickly.
- •
Responsibility in any condition: In critical conditions and/or emergencies an expert may be unable to make the right decision due to stress or other factors while an expert system’s decision making is not affected by these events.
- •
Experience base: An expert system can provide access to a massive amount of experience.
- •
User training: An expert system can act like an intelligent tutor, i.e., problems are presented to the system and the way of reasoning can be obtained.
- •
Ease of knowledge transmission: one of the most important advantages of expert systems is its convenience to move the knowledge from the system to somewhere else on the globe.
A student is going to be dismissed from the university and is going to lose a bachelor degree. The advisor asks a few questions to provide an answer.
Advisor: How many semesters have gotten a GPA under 12?
Student: 2
Advisor: How many undertakings have you been given?
Student : 0
Advisor: How many disciplinary notices have you received from the university?
Student : 1
Advisor: How many semesters have you passed successfully?
Student : 11
Advisor: How many grades under 10 have you gotten?
Student : 23
Advisor: How many course units have you passed out of 144?
Student : 95
Advisor: What is your GPA?
Student : 11.16
The crisp student‘s answers, fuzzy values and the linguistic values of each question are shown in Table 1.
Inference phase:
IF fv1 is high And
fv2 is very low And
fv3 is low And
fv4 is high And
fv5 is very high And
fv6 is middle And
fv7 is low
THEN
You are dismissed with a probability of 33 percent.
ELSE
Not in knowledge base.
6ConclusionThis paper glanced at the definitions and introductory concepts of fuzzy logic and fuzzy decision making and some implemented examples of such systems were presented. Finally, a web-based student consulting expert system was proposed and its capability in enhancing the consulting process has been shown.